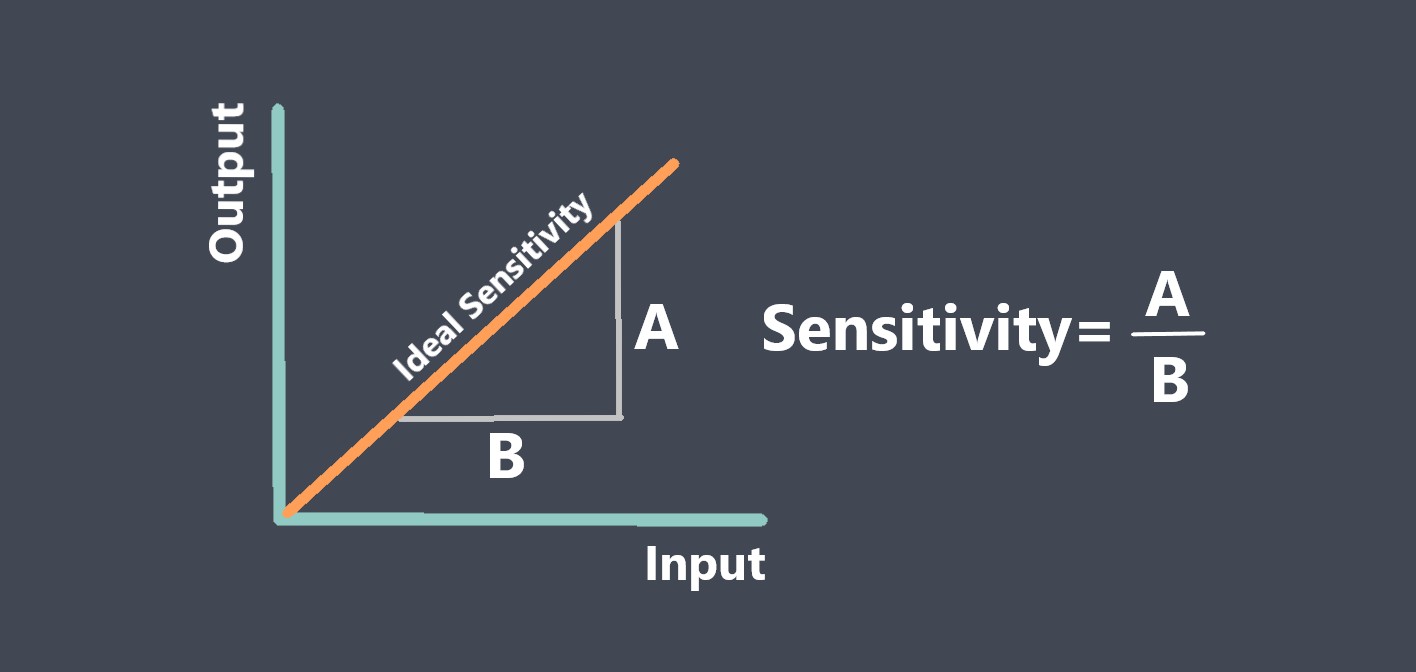
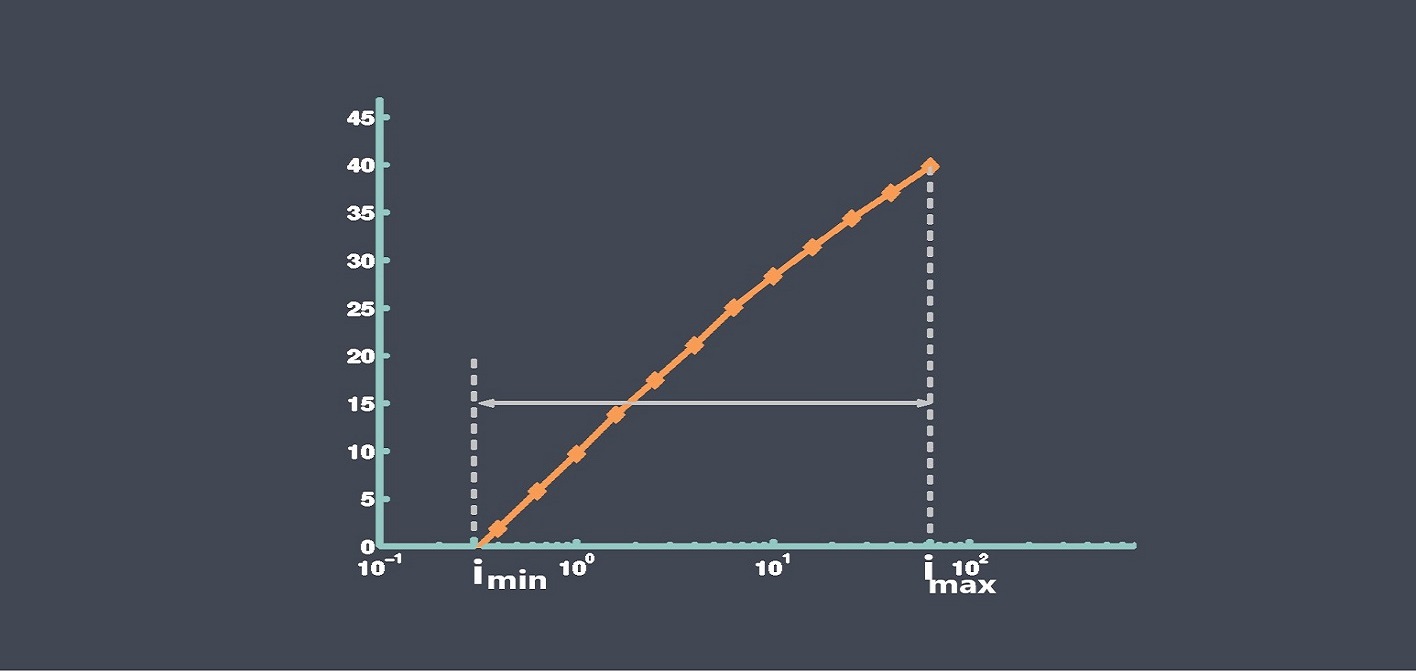
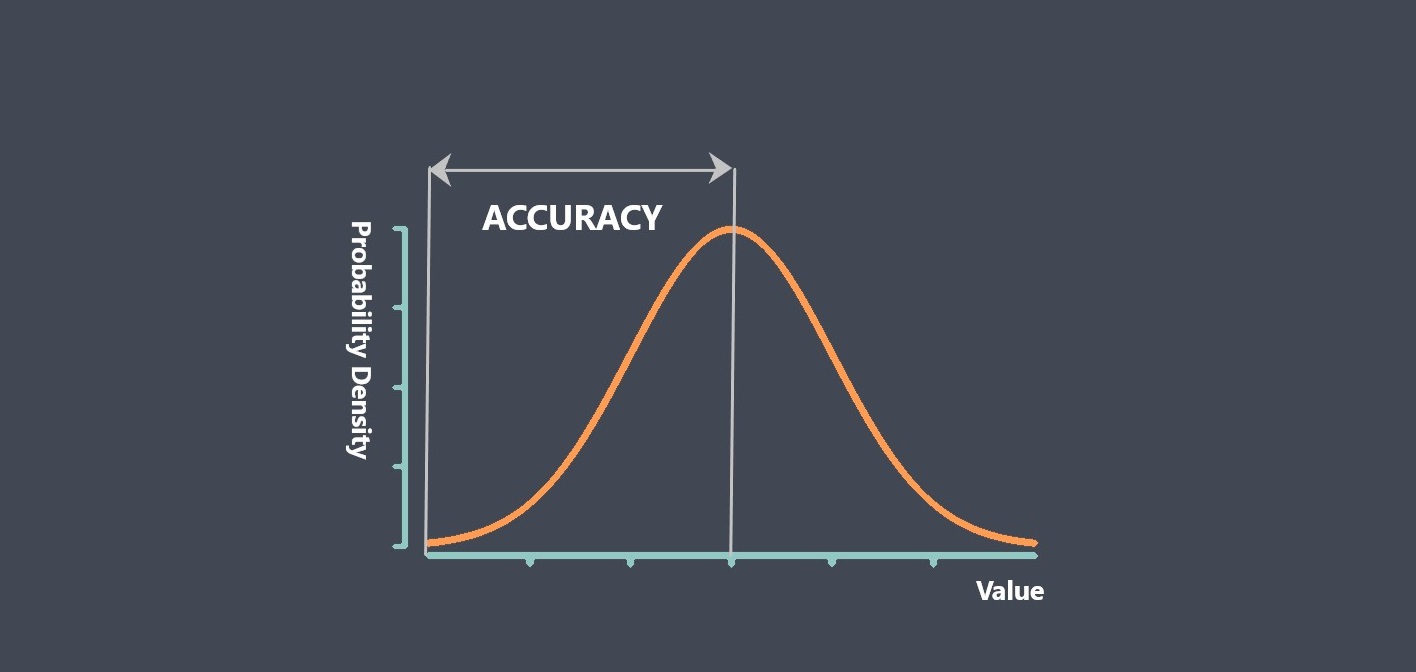
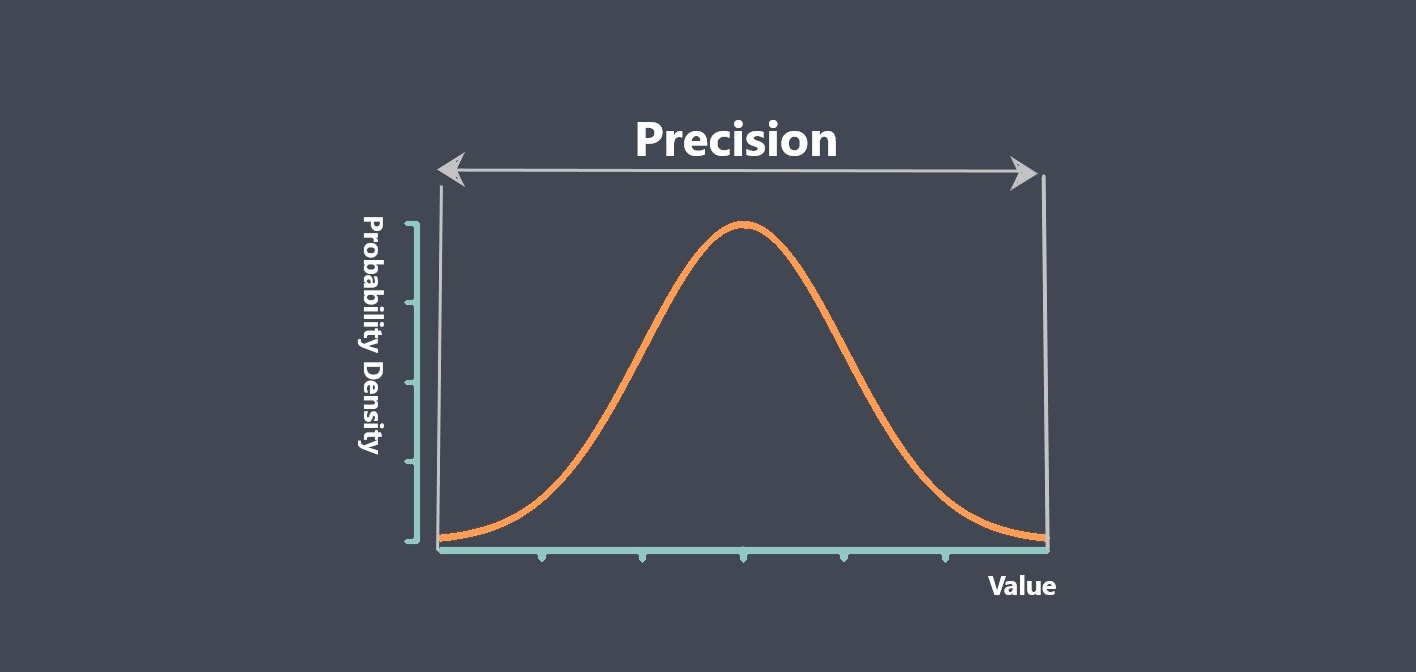
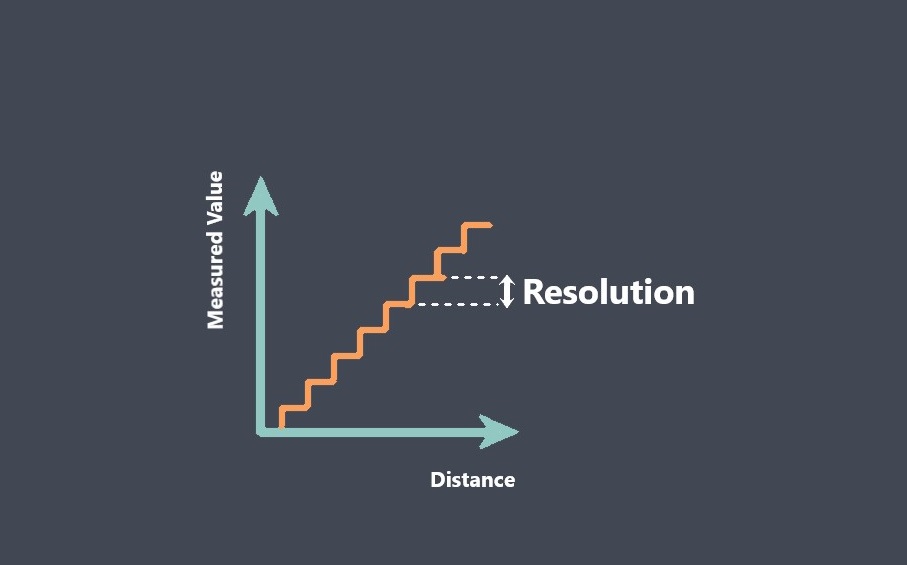
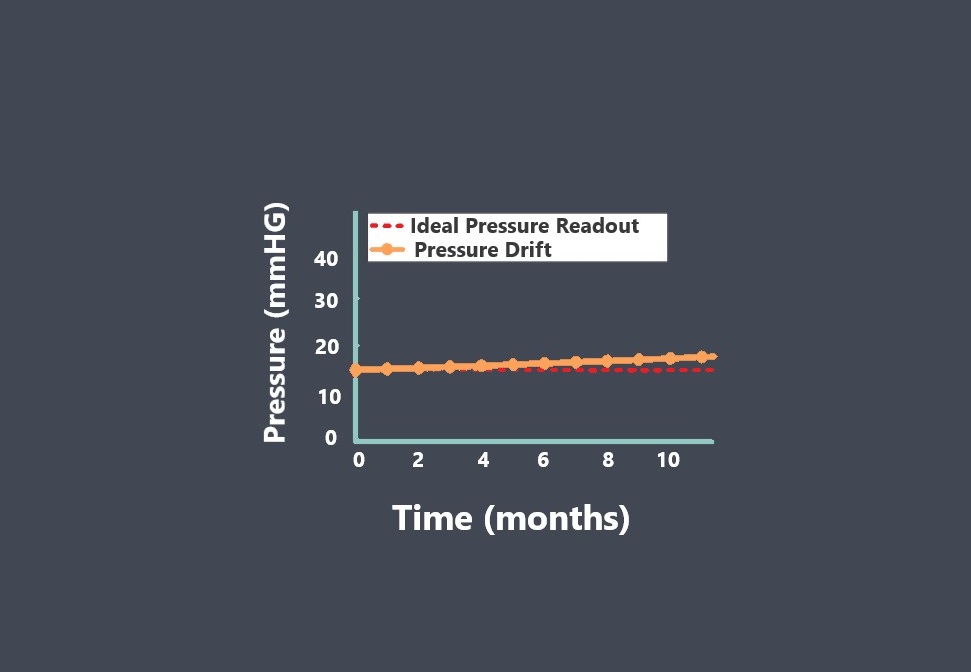
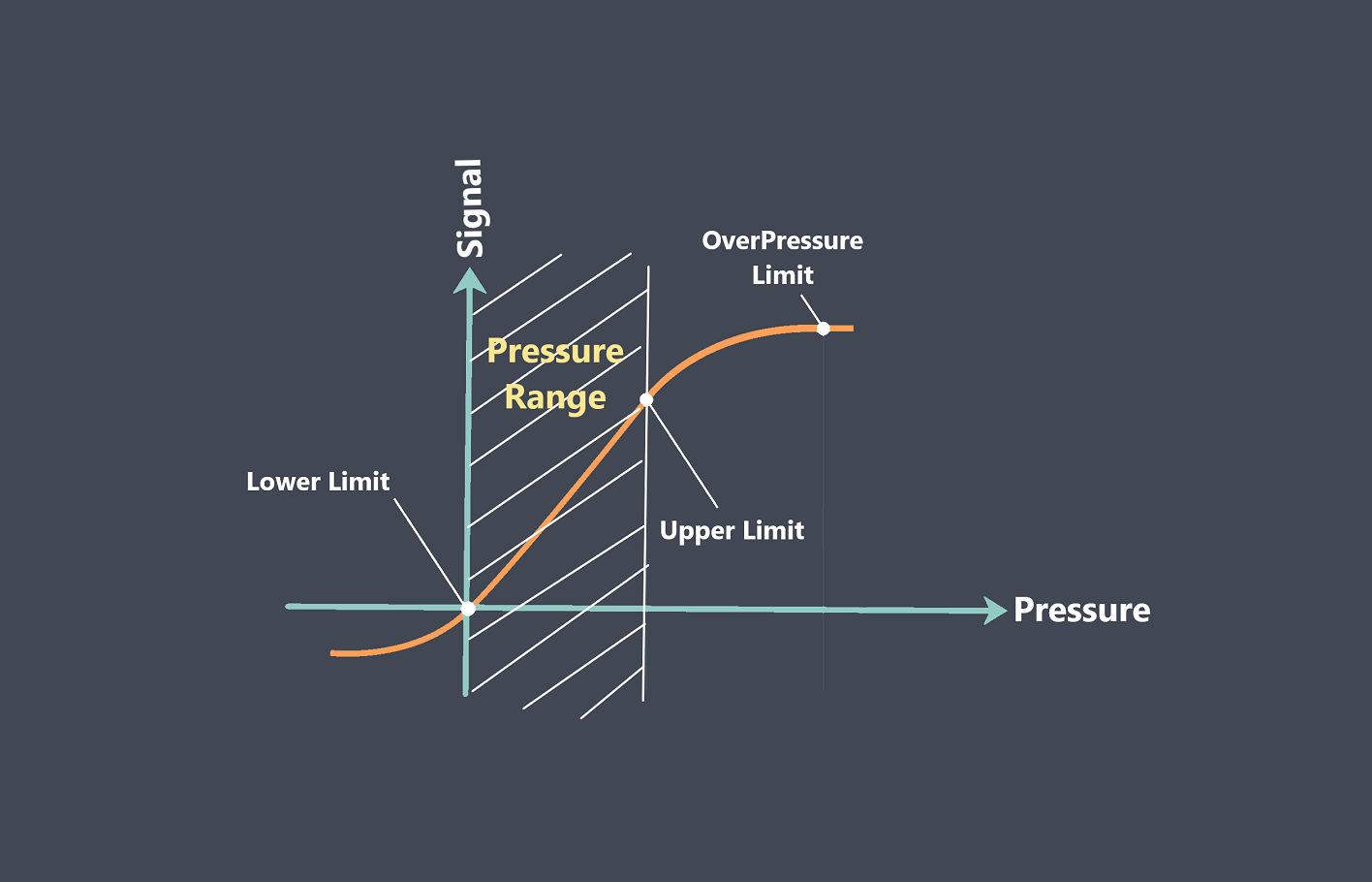
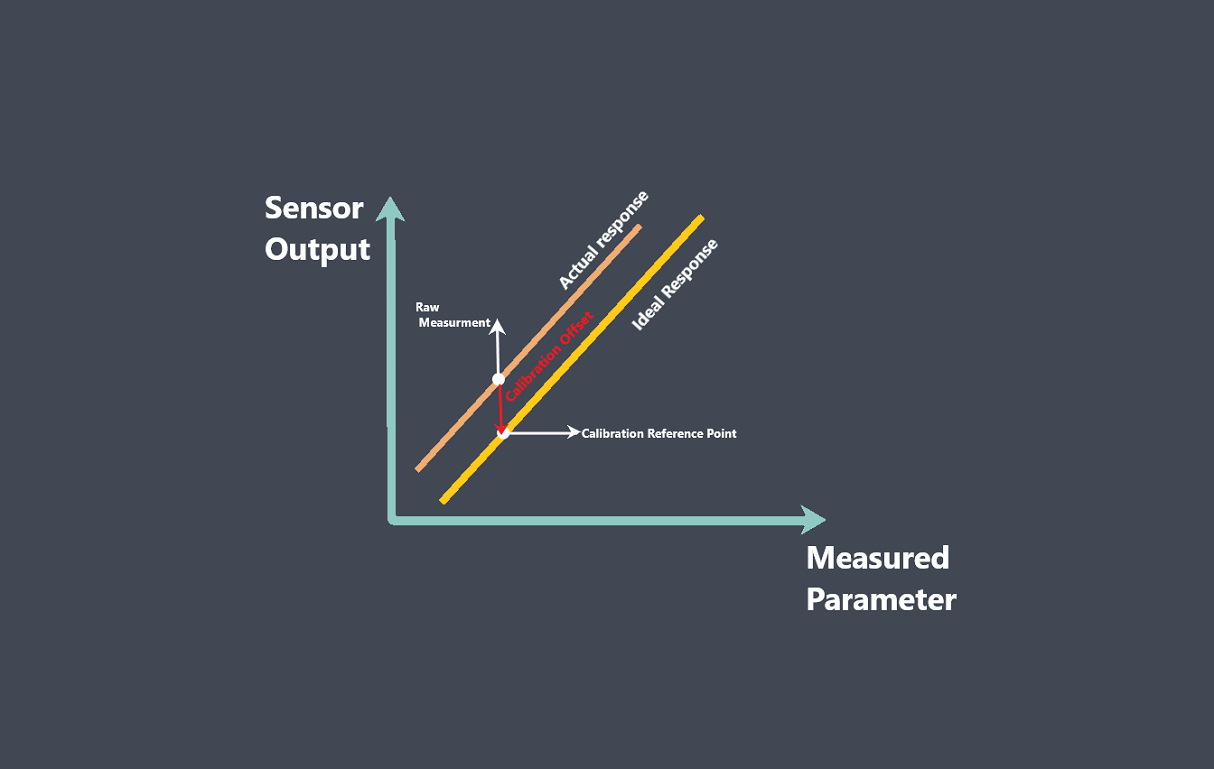
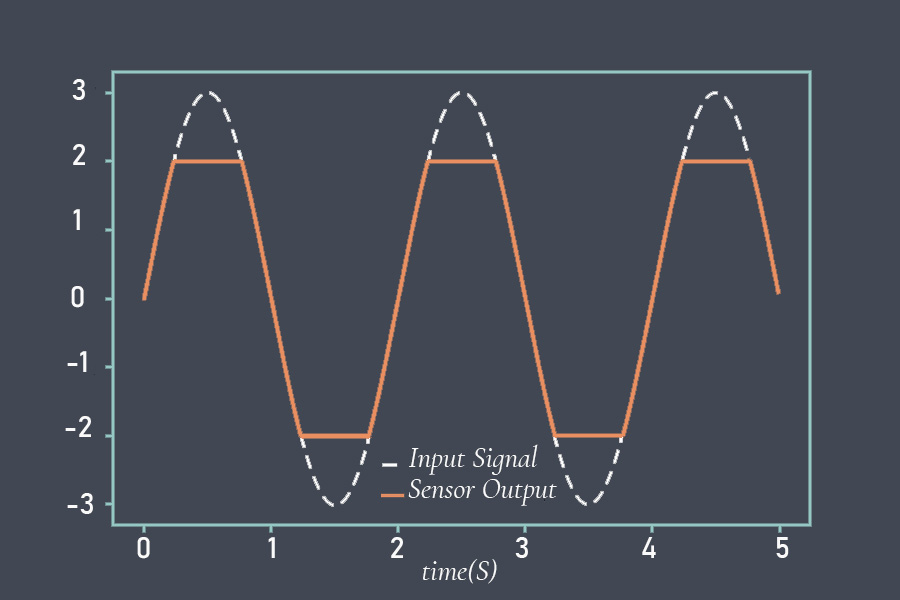
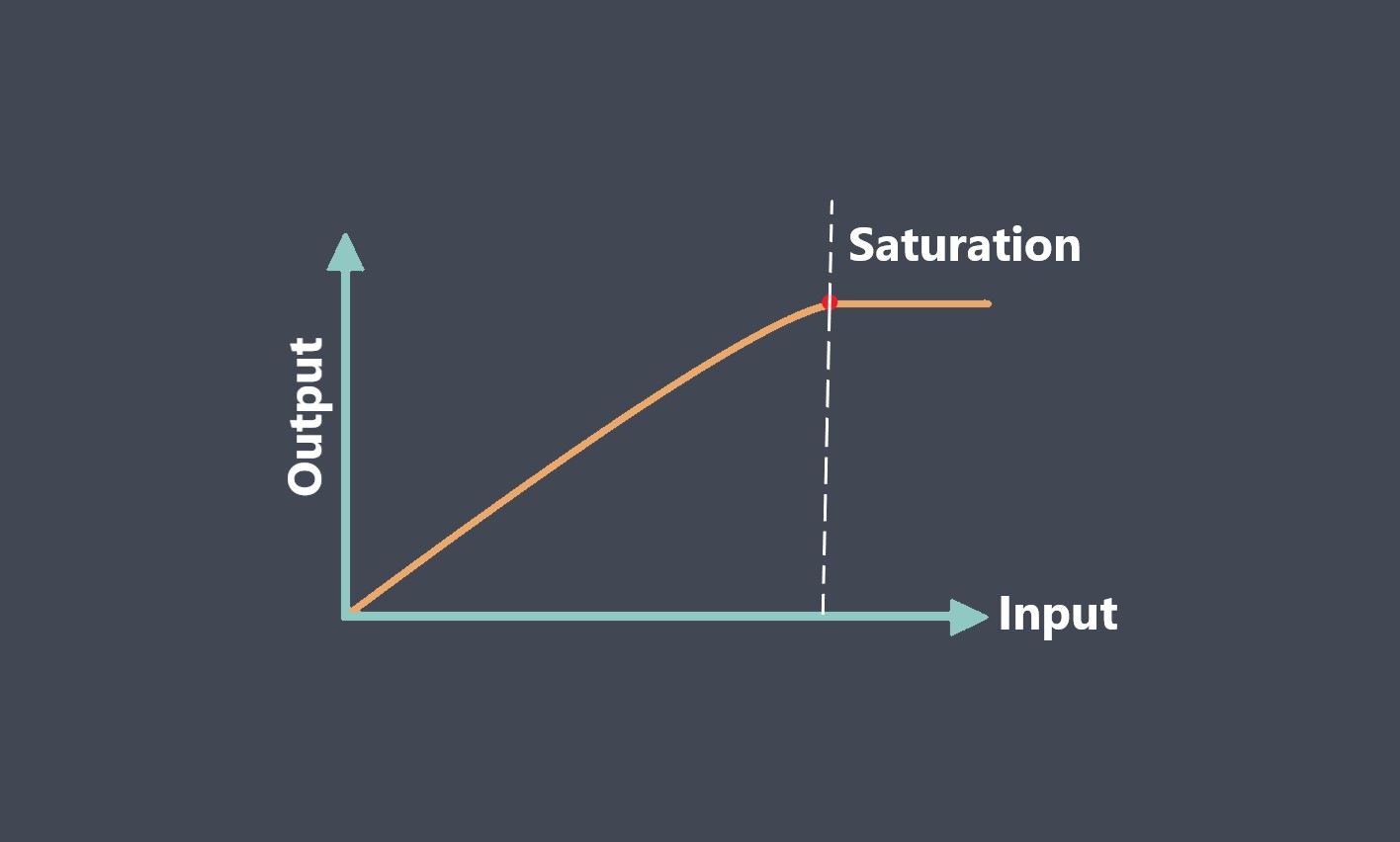
Sensor calibration is the process of adjusting a sensor to ensure that its output signal accurately represents the measured quantity. During calibration, the output signal of the sensor is compared to a known reference standard, and adjustments are made to the sensor to minimize any discrepancies between the output signal and the reference standard.
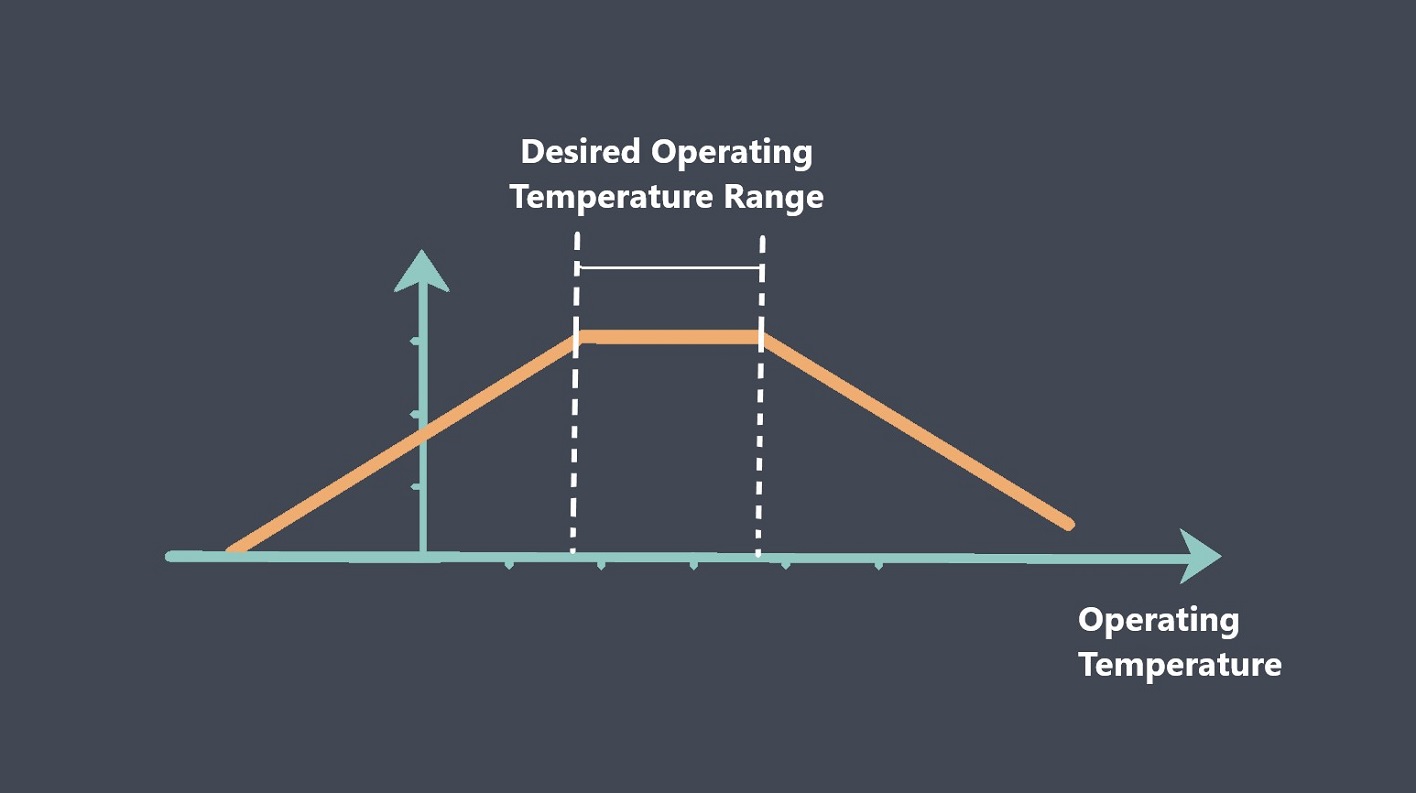
Calibration is important because sensors can drift or become less accurate over time due to environmental factors, wear and tear, or other factors. Calibration helps ensure that the sensor provides accurate and reliable measurements over its working range.
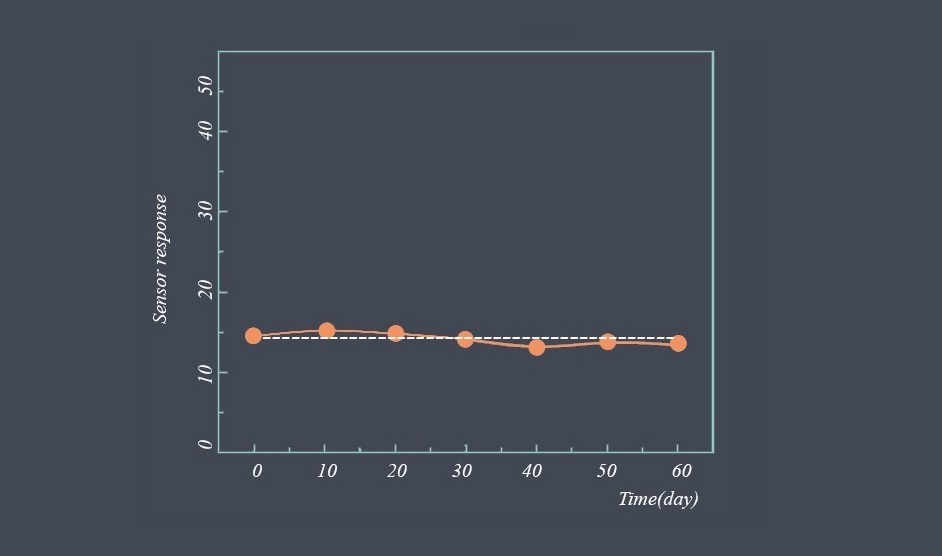
Sensor calibration should be performed periodically, depending on the application and the sensor’s operating conditions. Calibration intervals may range from daily to several years, depending on the sensor’s accuracy requirements and environmental factors.
Calibration equipment
Calibration equipment may include reference standards, calibration software, signal generators, and other measurement instruments. The calibration equipment should be traceable to national or international standards to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Calibration process steps
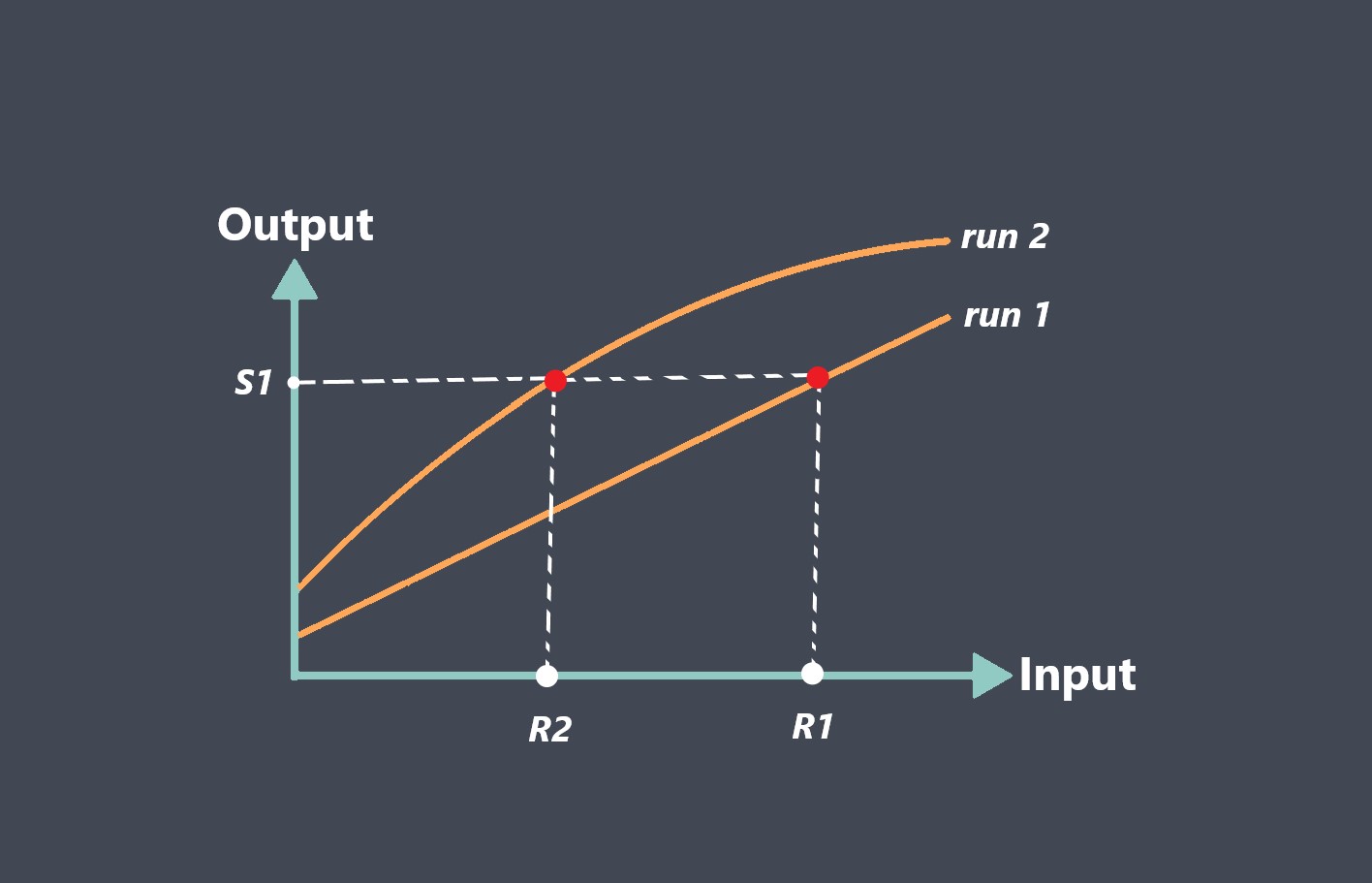
There are different methods for calibrating sensors, depending on the type of sensor and the application. One common method is to use a reference standard, which is a device or method that is used to provide a known value for the measured quantity. The output signal of the sensor is compared to the reference standard, and adjustments are made to the sensor to improve its accuracy.
This type of calibration process typically involves the following steps:
Determine the reference standard
A reference standard is a device or method that is used to provide a known value for the measured quantity. The reference standard should be accurate and have a traceable calibration history.
Compare the sensor output to the reference standard
The output signal of the sensor is measured and compared to the value provided by the reference standard.
Make adjustments to the sensor
If the sensor output is not within an acceptable range of the reference standard value, adjustments are made to the sensor to improve its accuracy.
Verify the calibration
Once the adjustments have been made, the sensor is tested again to ensure that the output signal matches the reference standard value within an acceptable margin of error.
Other calibration methods include self-calibration, where the sensor has built-in calibration functions, and dynamic calibration, where the calibration is performed while the sensor is in operation.
After a sensor has been calibrated, a calibration certificate is often issued to document the calibration process and the results. The certificate typically includes information about the sensor, the calibration equipment used, the reference standards, and the results of the calibration.
Overall, sensor calibration is an important process that helps ensure the accuracy and reliability of sensors over their working range.
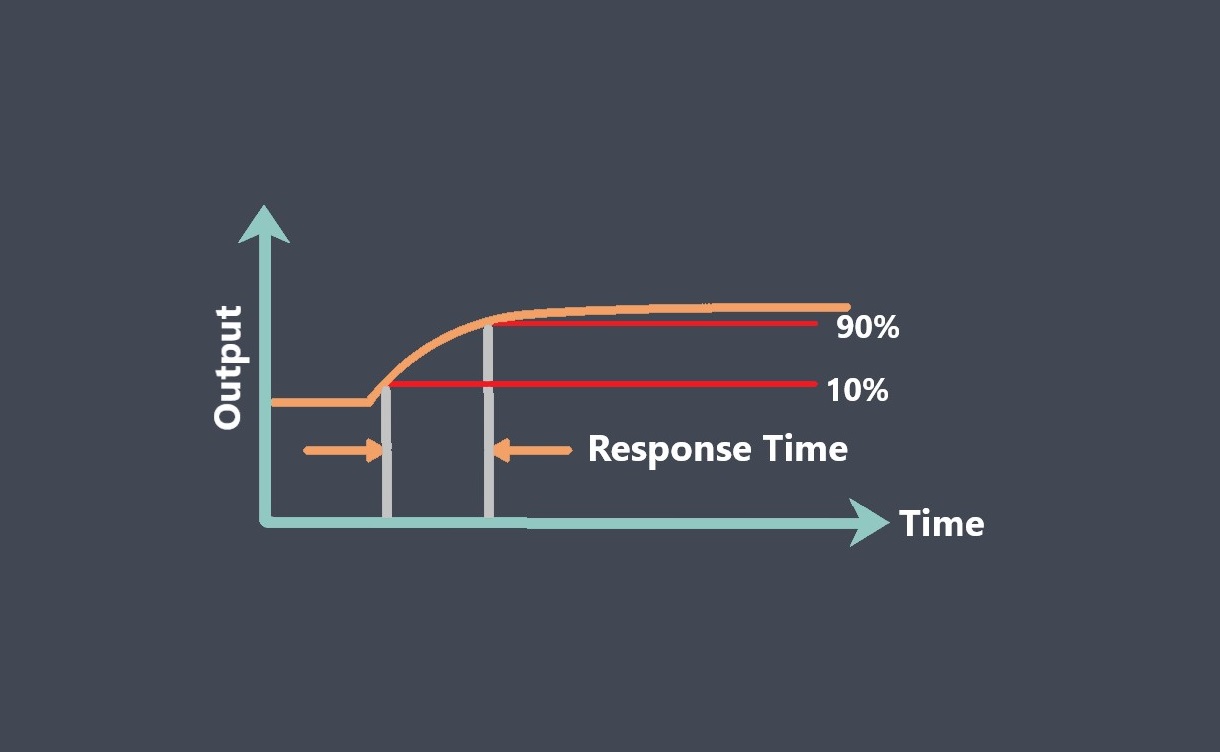
What is sensor calibration error?
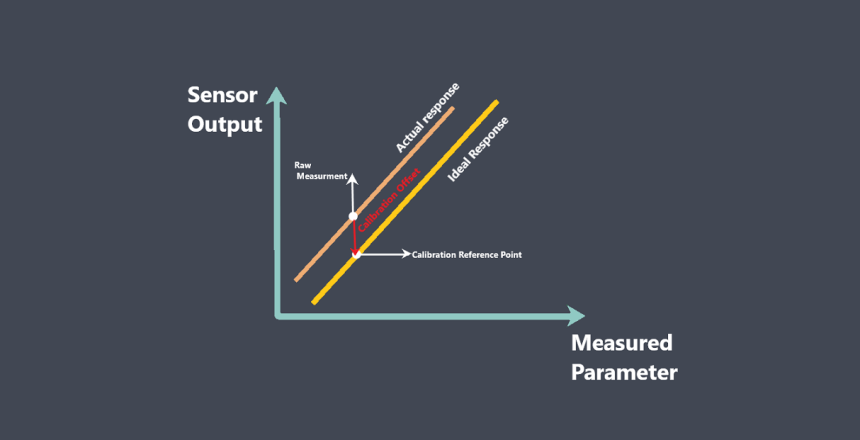
Sensor calibration error refers to the difference between the measured output signal of a sensor and the true value of the
quantity being measured, as determined by a reference standard during the calibration process.
In other words, it represents the amount of error or discrepancy between the sensor’s output signal and the expected or correct measurement.
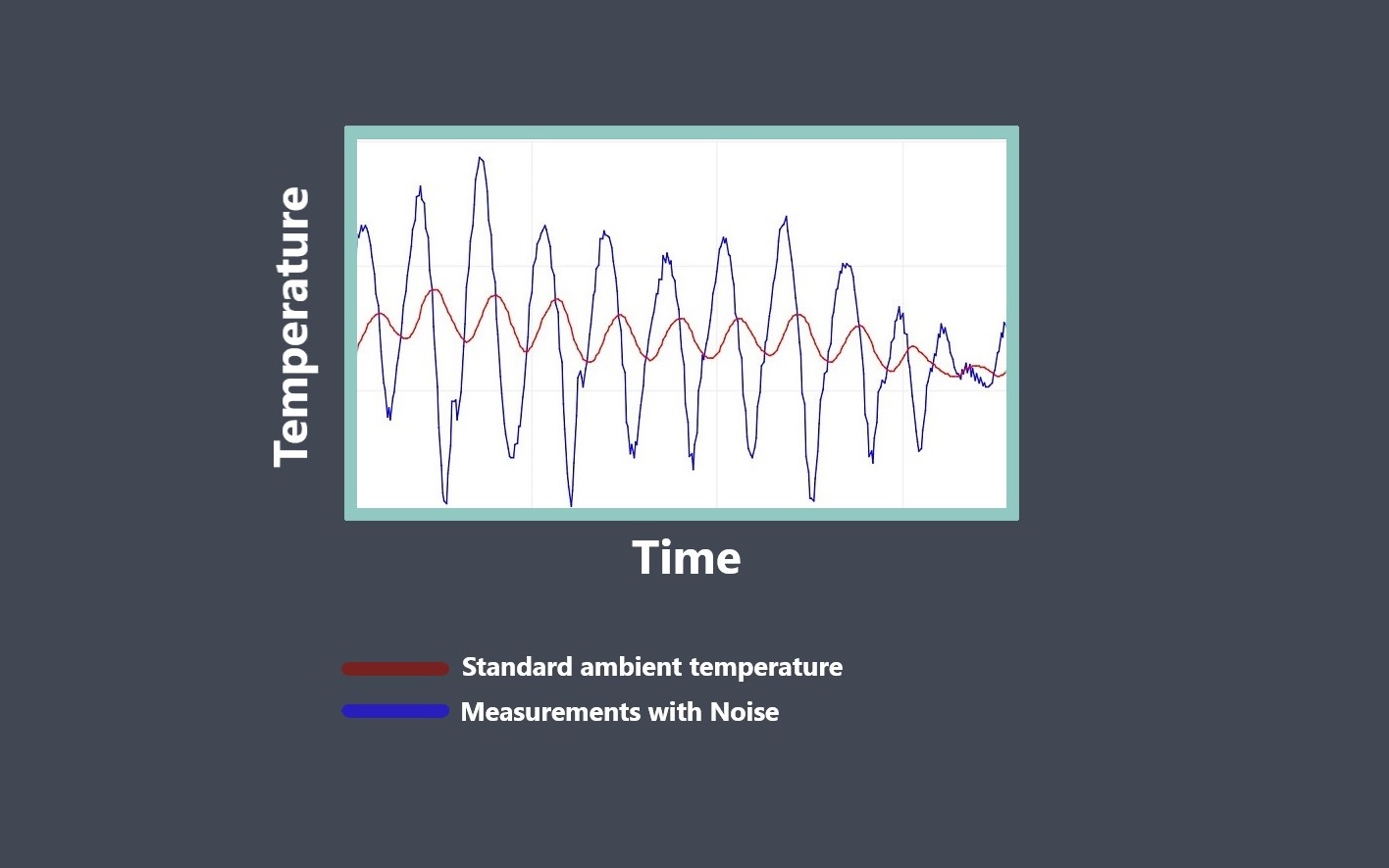
Calibration error can arise due to various factors such as inaccuracies in the reference standard,

variations in the environmental conditions during calibration and measurement, sensor drift or non-linearity, electrical noise, or human error during calibration.
Sensor calibration error types
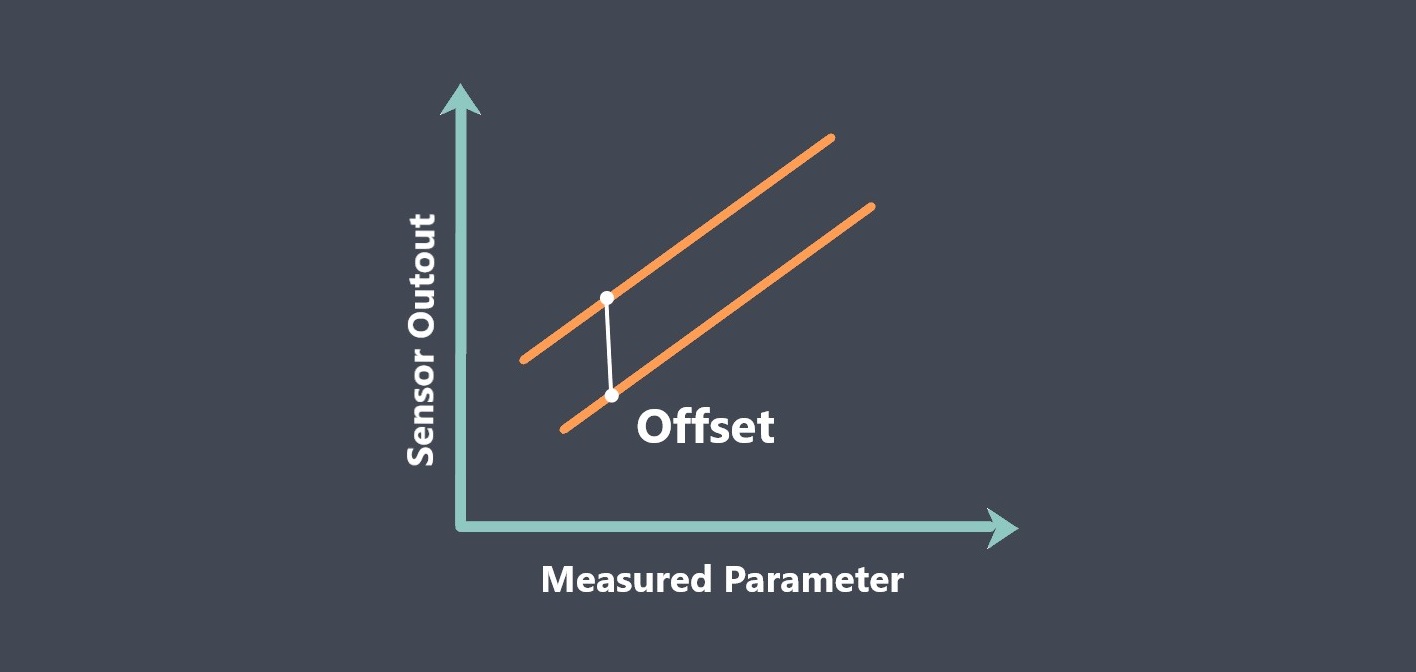
Calibration error can be expressed in absolute or relative terms, depending on the application and the unit of measurement.
- Absolute calibration error: This usually expressed in the same unit as the measured quantity.
- Relative calibration error: It expressed as a percentage of the full-scale measurement range.
To ensure accurate and reliable measurements, calibration error should be minimized and kept within acceptable limits based on the specific application and industry standards. Calibration procedures should be performed periodically and documented to ensure traceability and quality control.