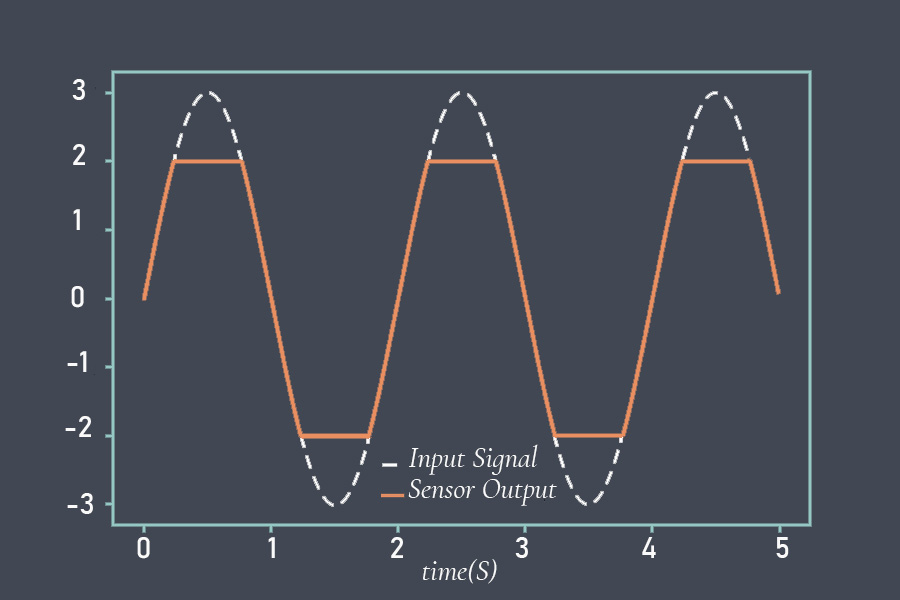
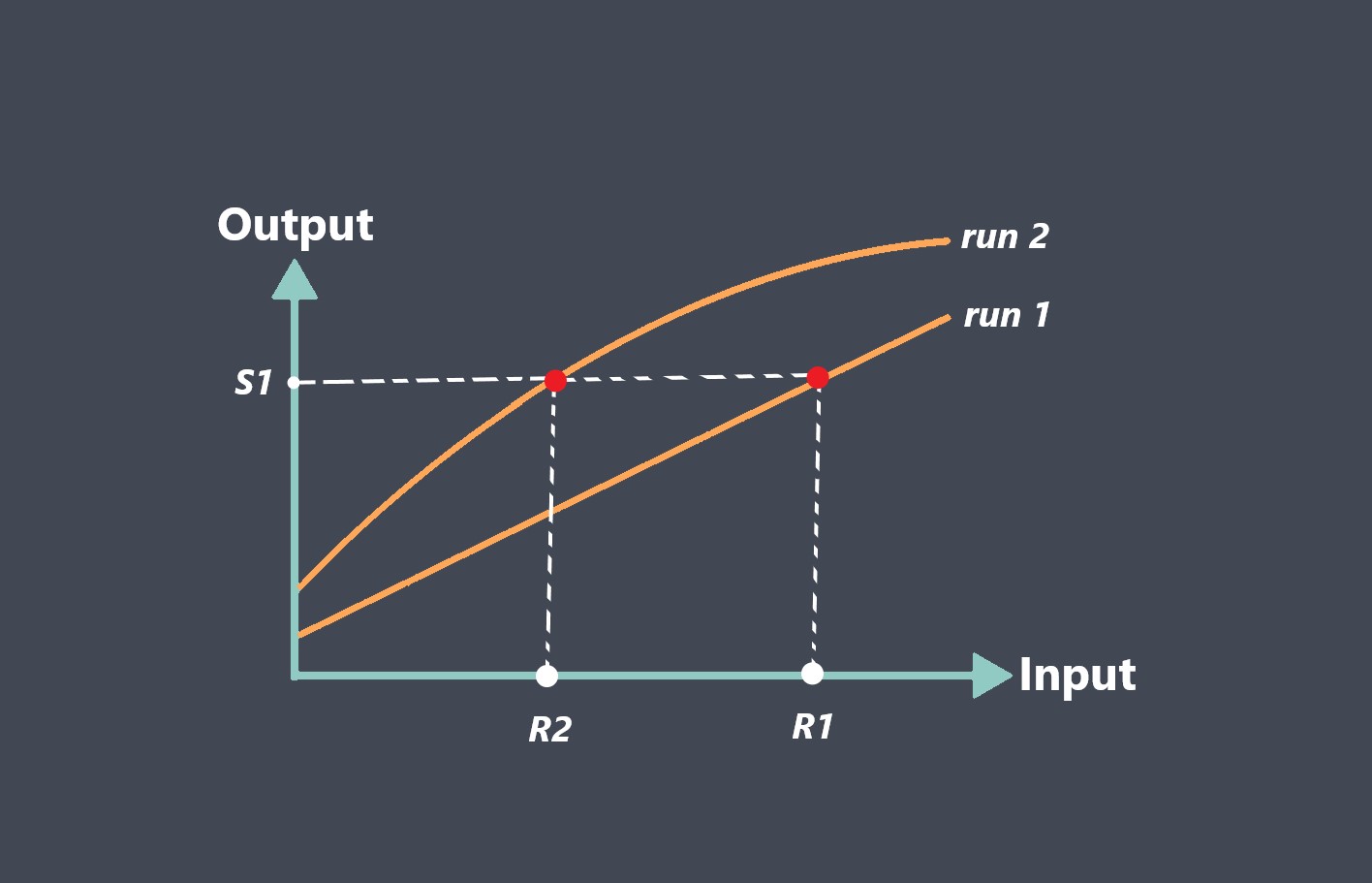
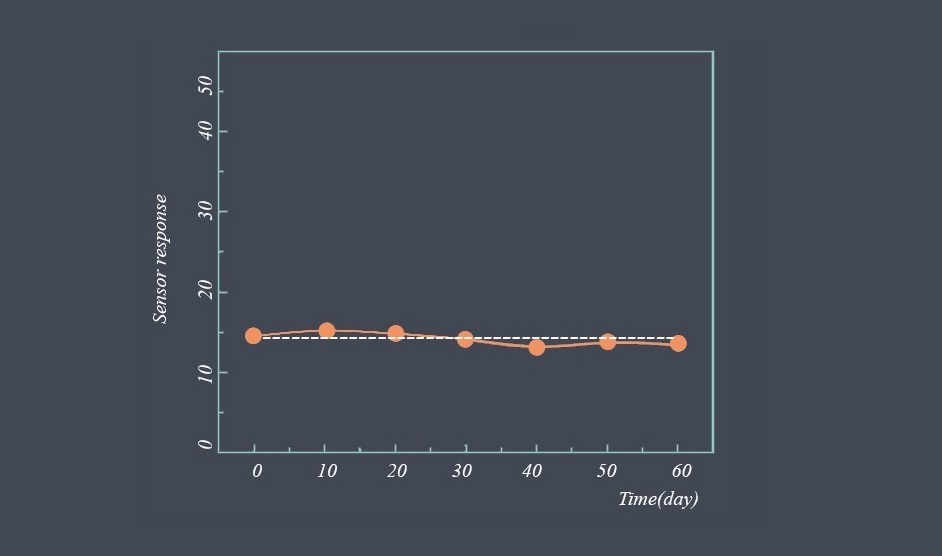
Repeatability is the ability of a sensor to provide the same output signal for the same input signal over multiple measurements. It indicates the consistency and reliability of the sensor’s measurements under identical conditions. A sensor with high repeatability will produce consistent and repeatable output values for a given input signal.
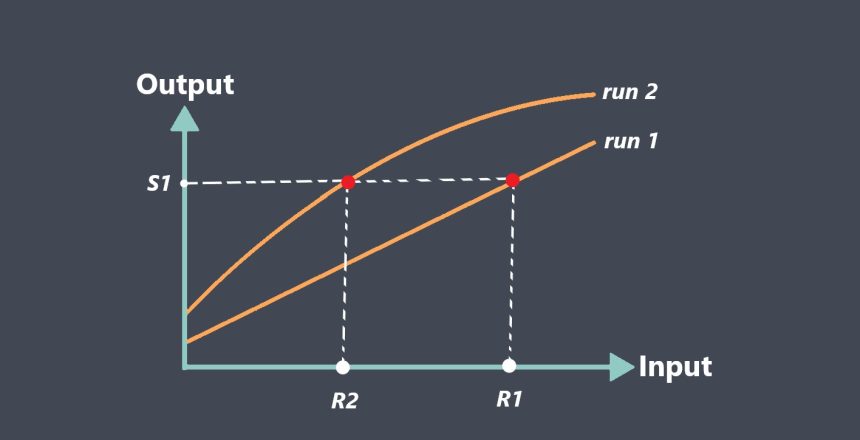
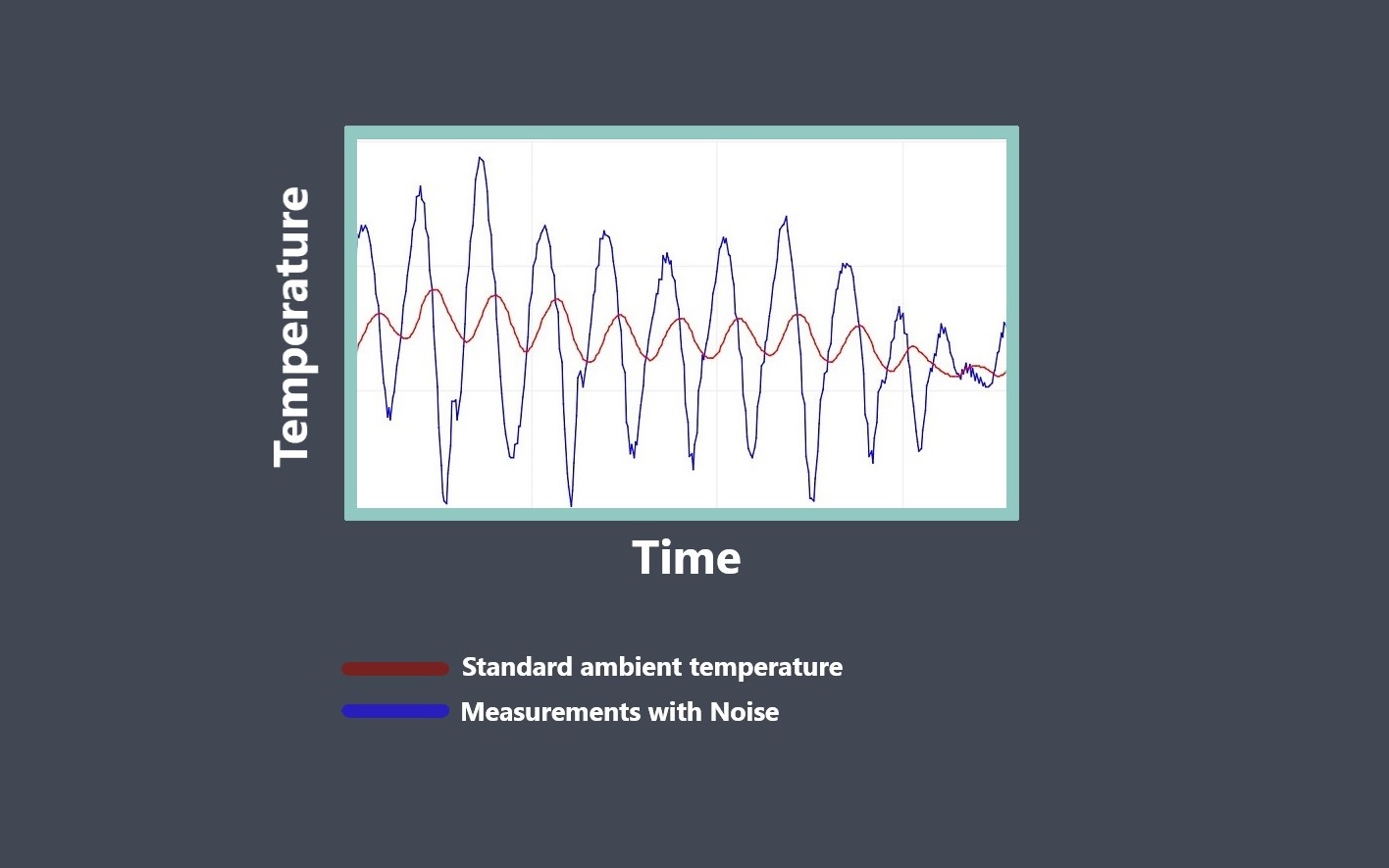
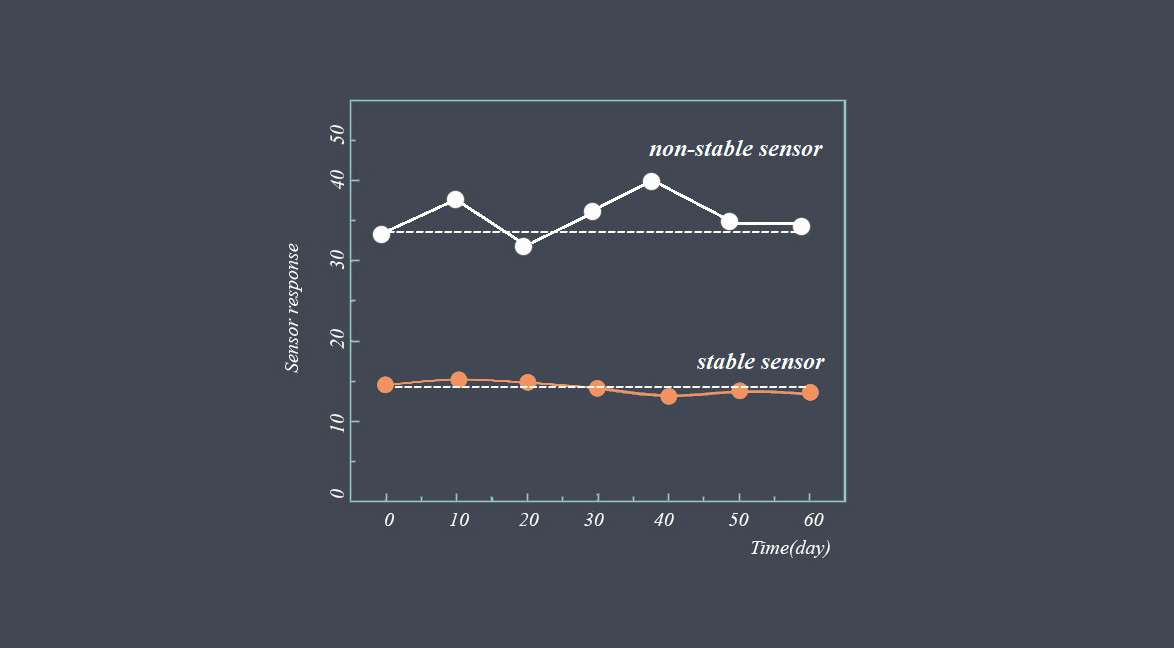
Sensor repeatability refers to the ability of a sensor to produce consistent readings when measuring the same quantity under the same conditions over time. In other words, if a sensor is repeatedly used to measure a particular physical quantity, such as temperature, pressure, or humidity, its repeatability describes how closely the sensor’s measurements agree with each other.
For example, if a temperature sensor is used to measure the temperature of a liquid, and the sensor repeatedly measures the same temperature value when the liquid is at the same temperature and under the same conditions, then the sensor is said to have good repeatability.
Repeatability importance
Repeatability is an important characteristic of a sensor as it ensures that the sensor’s measurements can be trusted and relied upon over time. It is often assessed by performing multiple measurements of the same quantity using the same sensor and comparing the results to determine the degree of variation between them.
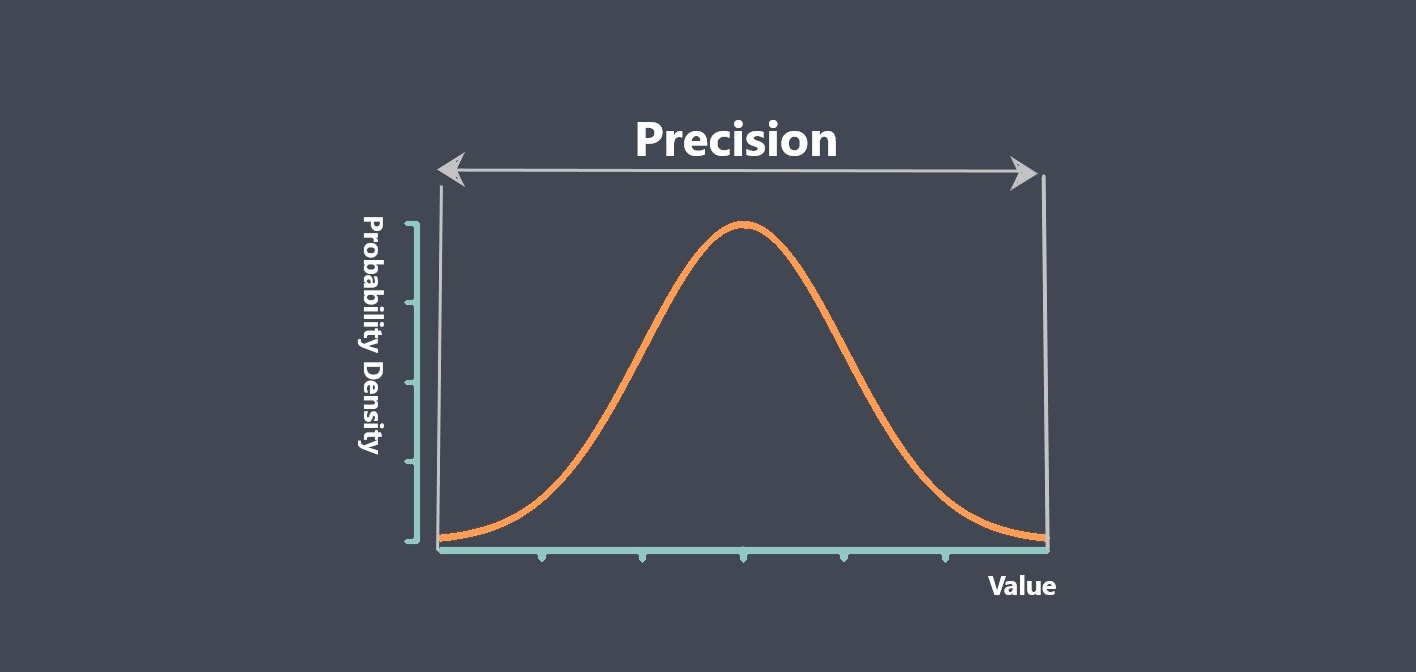
This parameter used to evaluate the quality and reliability of a sensor. It is a measure of the sensor’s precision, which is the ability to produce consistent and accurate measurements over time. Repeatability is particularly important in applications where precise and consistent measurements are critical, such as in scientific research, manufacturing, and quality control.
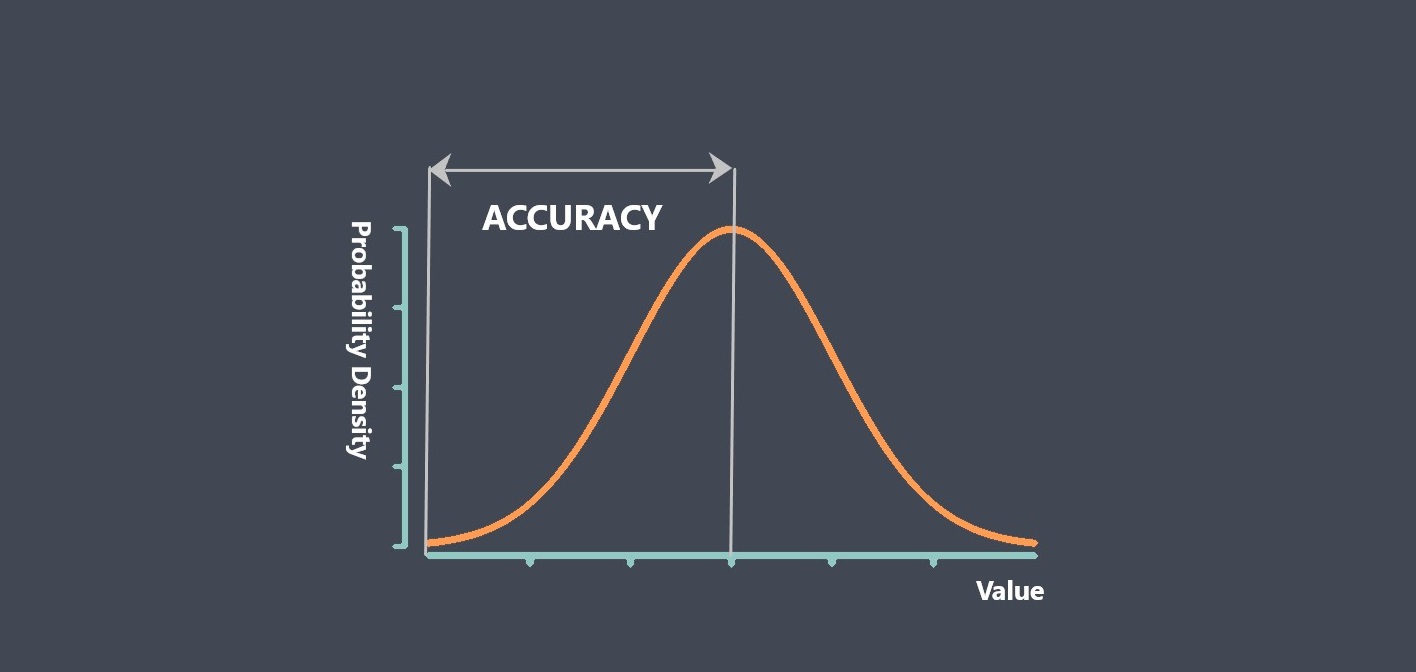
Repeatability VS Accuracy
Repeatability and accuracy are both important performance parameters used to evaluate the quality and reliability of a sensor, but they measure different aspects of a sensor’s performance.
Repeatability refers to the consistency of a sensor’s measurements when measuring the same quantity under the same conditions over time. A sensor with good repeatability will produce consistent measurements with low variation, even if the measurements are not exactly the true value. Repeatability is important when precise and consistent measurements are required, such as in manufacturing, scientific research, or quality control.
Accuracy, on the other hand, refers to how closely a sensor’s measurements agree with the true value of the quantity being measured. A sensor with good accuracy will produce measurements that are close to the true value, even if they are not consistent or repeatable. Accuracy is important when the absolute value of the measurement is critical, such as in medical diagnosis or safety-critical applications.

In summary, repeatability measures the consistency of a sensor’s measurements, while accuracy measures how closely those measurements agree with the true value of the quantity being measured. Both parameters are important for different applications and can be evaluated through different methods, such as statistical analysis or comparison to a known reference standard.
Difference between repeatability and reproducibility
Repeatability and reproducibility may be confused. they are both important sensor parameters to evaluate the quality and reliability of a sensor, but they measure different aspects of the system’s performance.
Reproducibility measures the variation in measurements obtained from the same measurement system, using the same measurement procedure, under different operating conditions or by different operators.
A measurement system with good reproducibility will produce consistent and precise measurements even when used by different operators or in different environments.

Repeatability, on the other hand, measures the variation in measurements obtained from the same measurement system, using the same measurement procedure, and under the same operating conditions.
A measurement system with good repeatability will produce consistent and precise measurements when measuring the same quantity repeatedly.

In other word, repeatability measures the variation in
measurements obtained from a single measurement system under the same conditions, while reproducibility measures the variation in measurements obtained from multiple measurement systems under different conditions. Both parameters are important for evaluating the quality and reliability of a measurement system.
Repeatability is important when precise and consistent measurements are required, such as in scientific research or quality control. Reproducibility is important when the measurement system needs to be used by different operators or in different environments, such as in manufacturing or field testing.
Repeatability error
Repeatability error refers to the variation in measurements obtained from a single measurement system when measuring the same quantity repeatedly under the same conditions. It is a type of random error that can affect the accuracy and precision of a measurement system.
Repeatability error can arise from a variety of sources, including fluctuations in the measurement signal, variations in the measurement system’s operating conditions, and variations in the measurement technique or procedure. For example, a temperature sensor may exhibit repeatability error due to fluctuations in the temperature of the environment or changes in the sensor’s response over time.
Repeatability error can be quantified using statistical measures such as standard deviation, variance, or coefficient of variation (CV). The CV is a useful metric as it expresses the degree of variation in the measurements as a percentage of the average value, making it easier to compare the repeatability error of different measurement systems.

To minimize repeatability error in a measurement system, it is important to properly calibrate and maintain the system over time. Regular calibration can help correct any systematic errors or drift in the measurement system’s output, while proper maintenance can prevent physical damage or contamination that could affect the system’s performance.
Repeatability error formula
The repeatability error formula is typically used to quantify the variation in measurements obtained by the same person or instrument under identical conditions. It is often expressed as the standard deviation of the differences between the repeated measurements. The formula for repeatability error can be written as:
Repeatability error = √(Σ(xi – x̄)²/(n-1))
where
- xi represents the individual measurements
- x̄ represents the mean of the measurements
- n represents the number of repeated measurements
To calculate the repeatability error, you would first take multiple measurements of the same quantity using the same instrument or by the same person under the same conditions. Then, you would calculate the mean of these measurements and the standard deviation of the differences between the individual measurements and the mean. The resulting value would be the repeatability error.