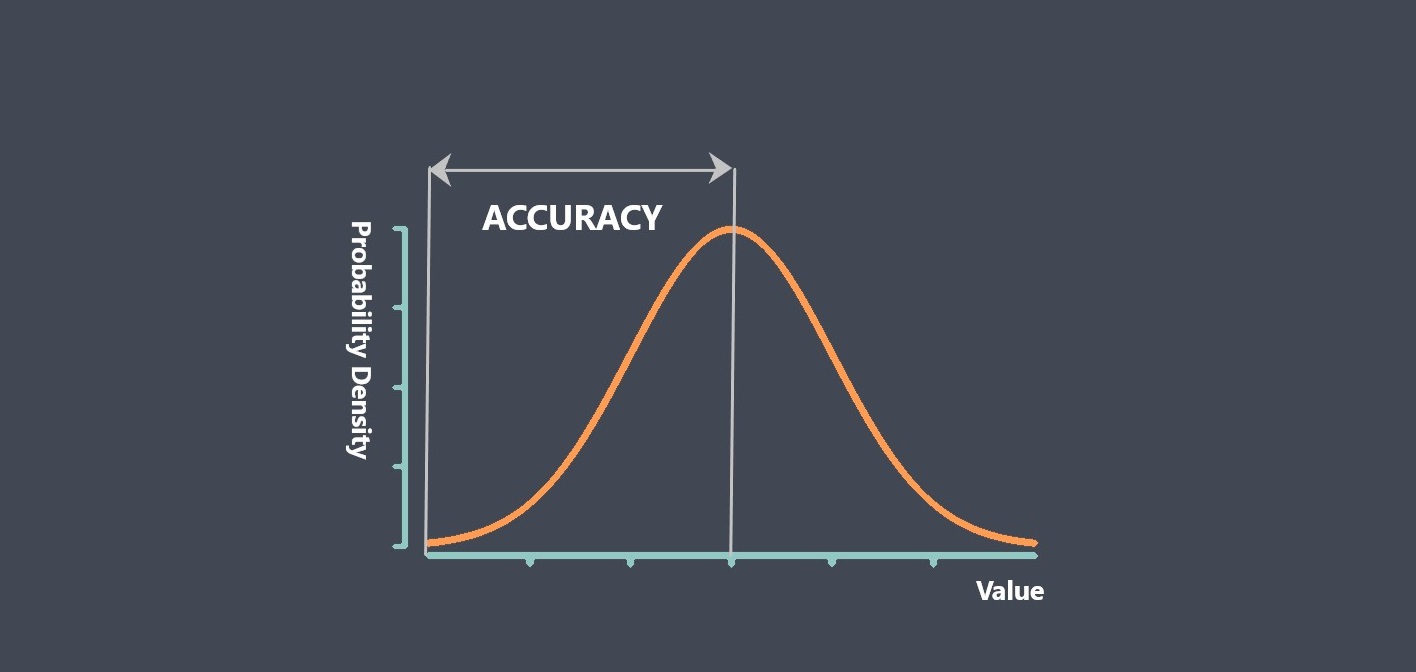
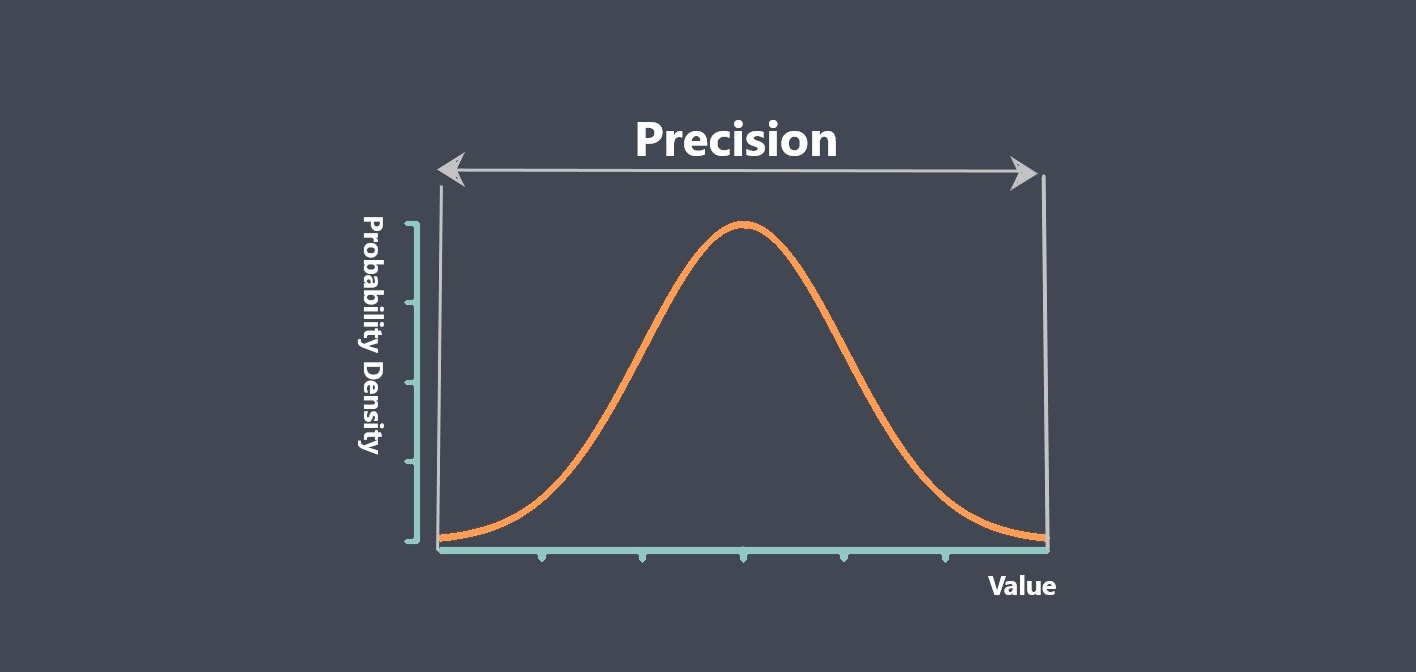
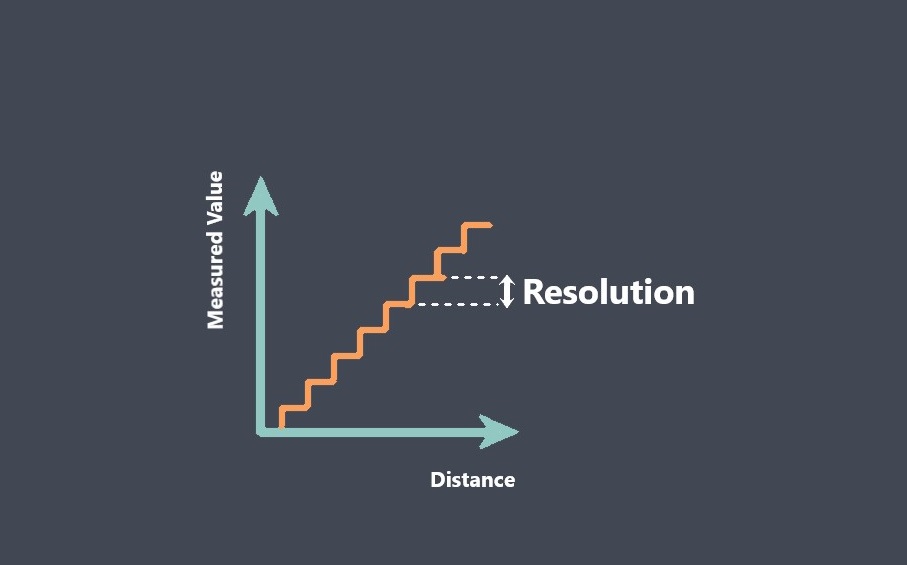
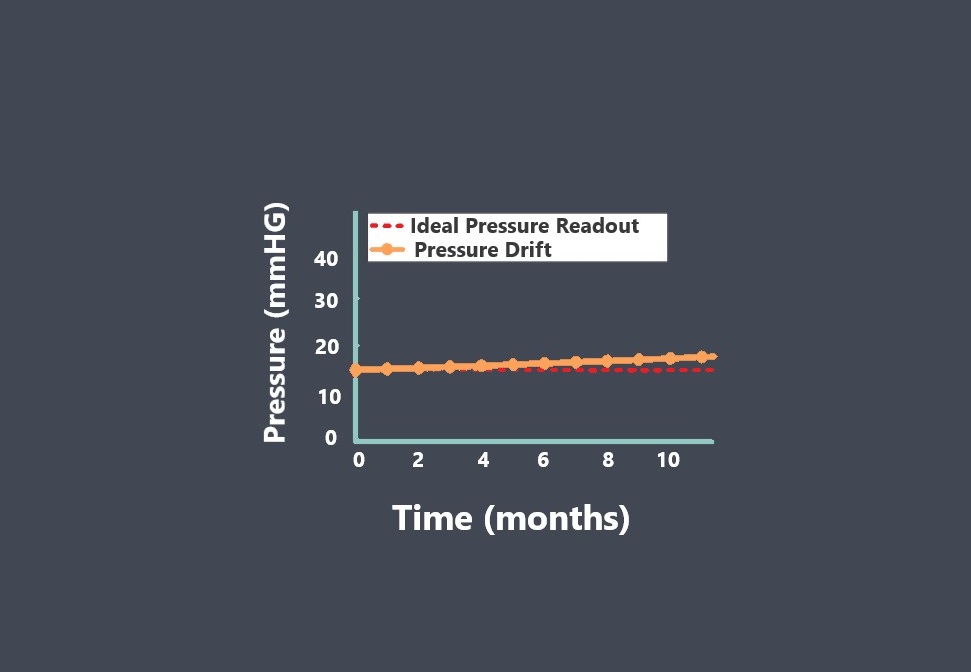
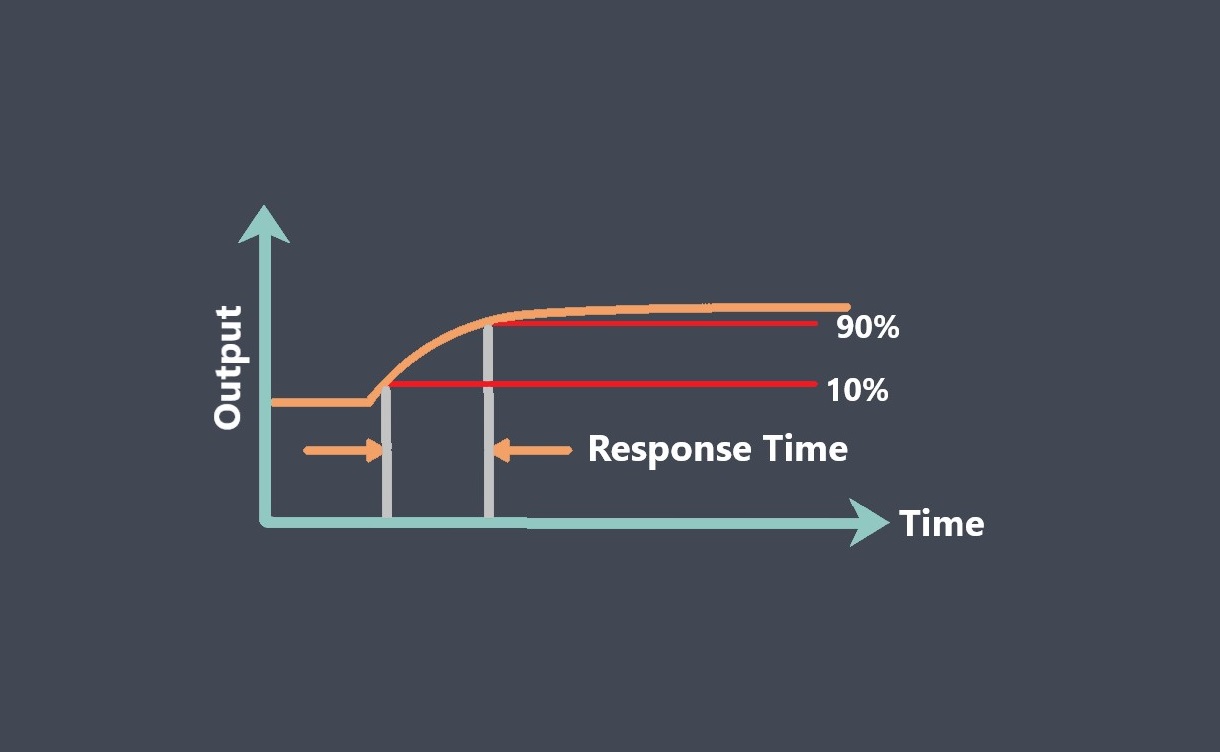
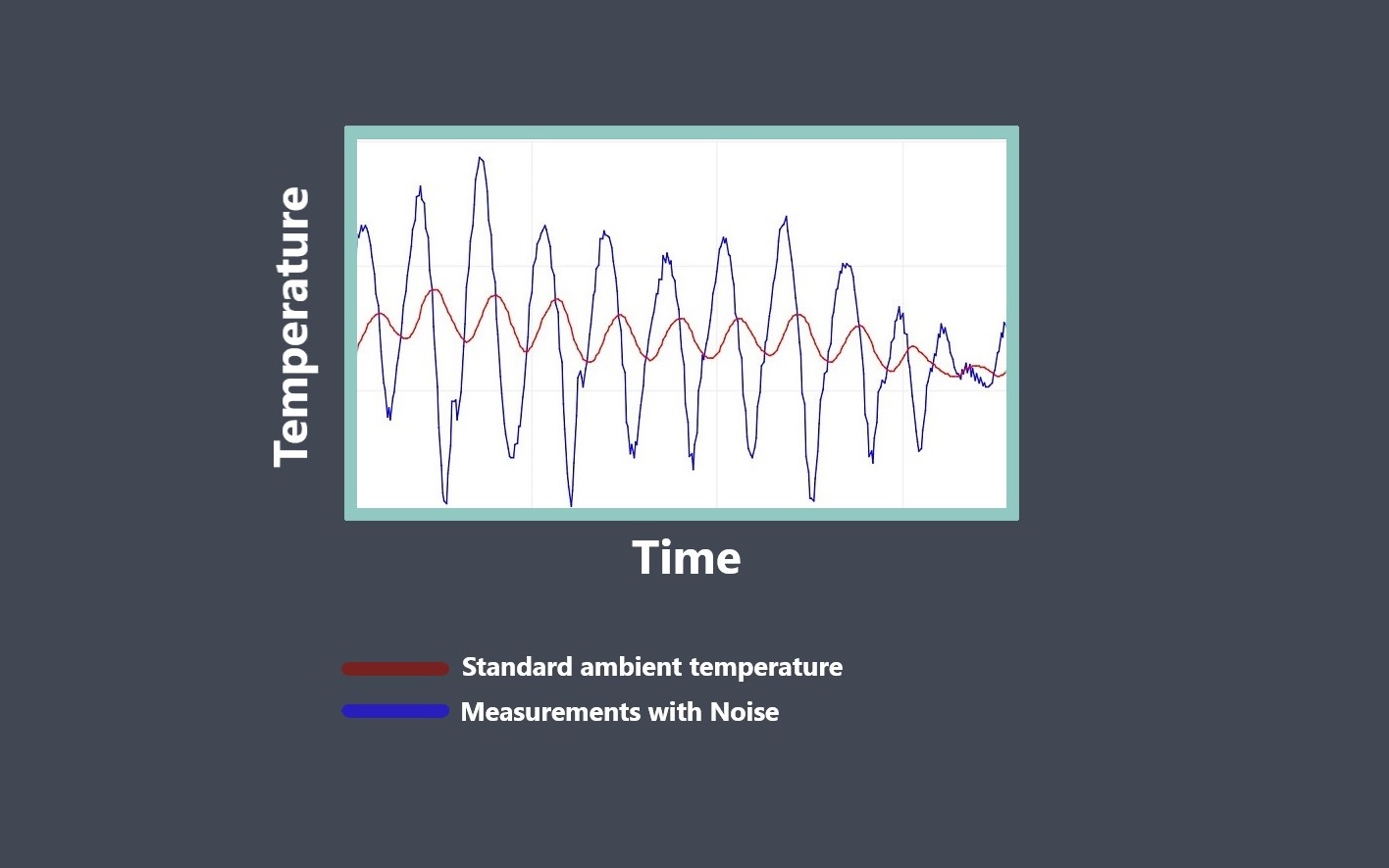
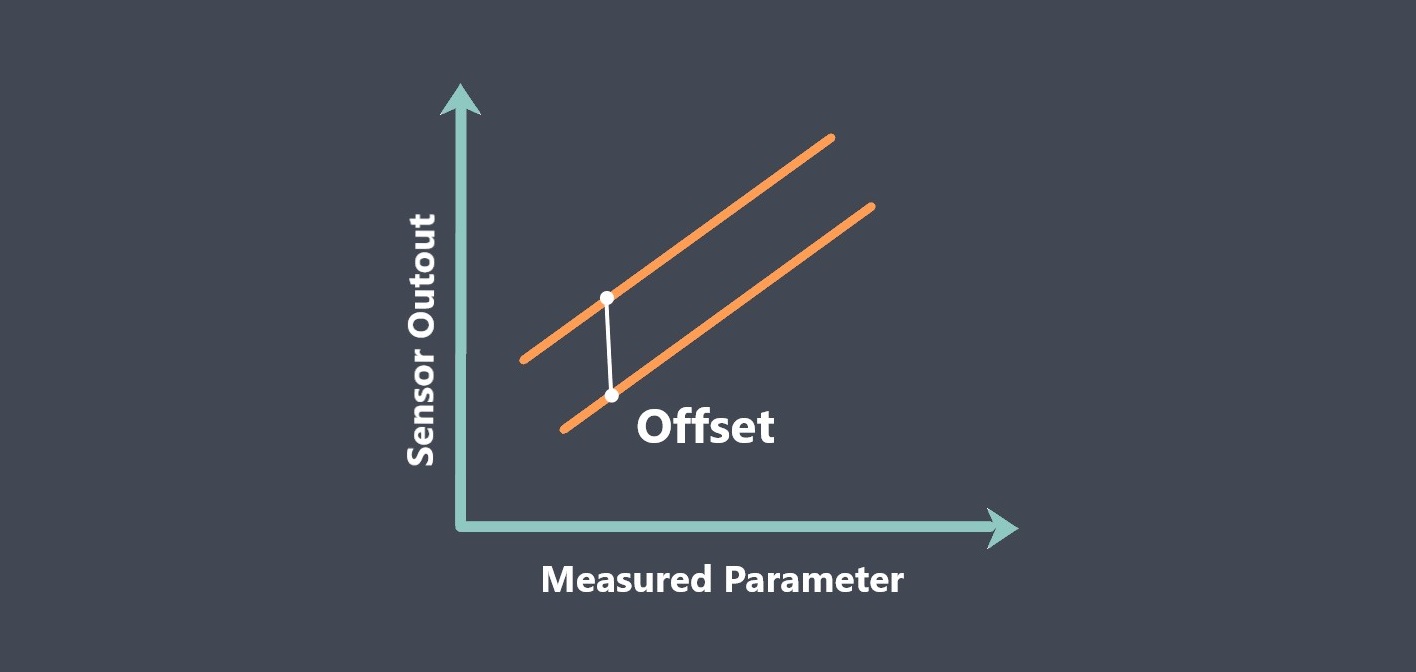
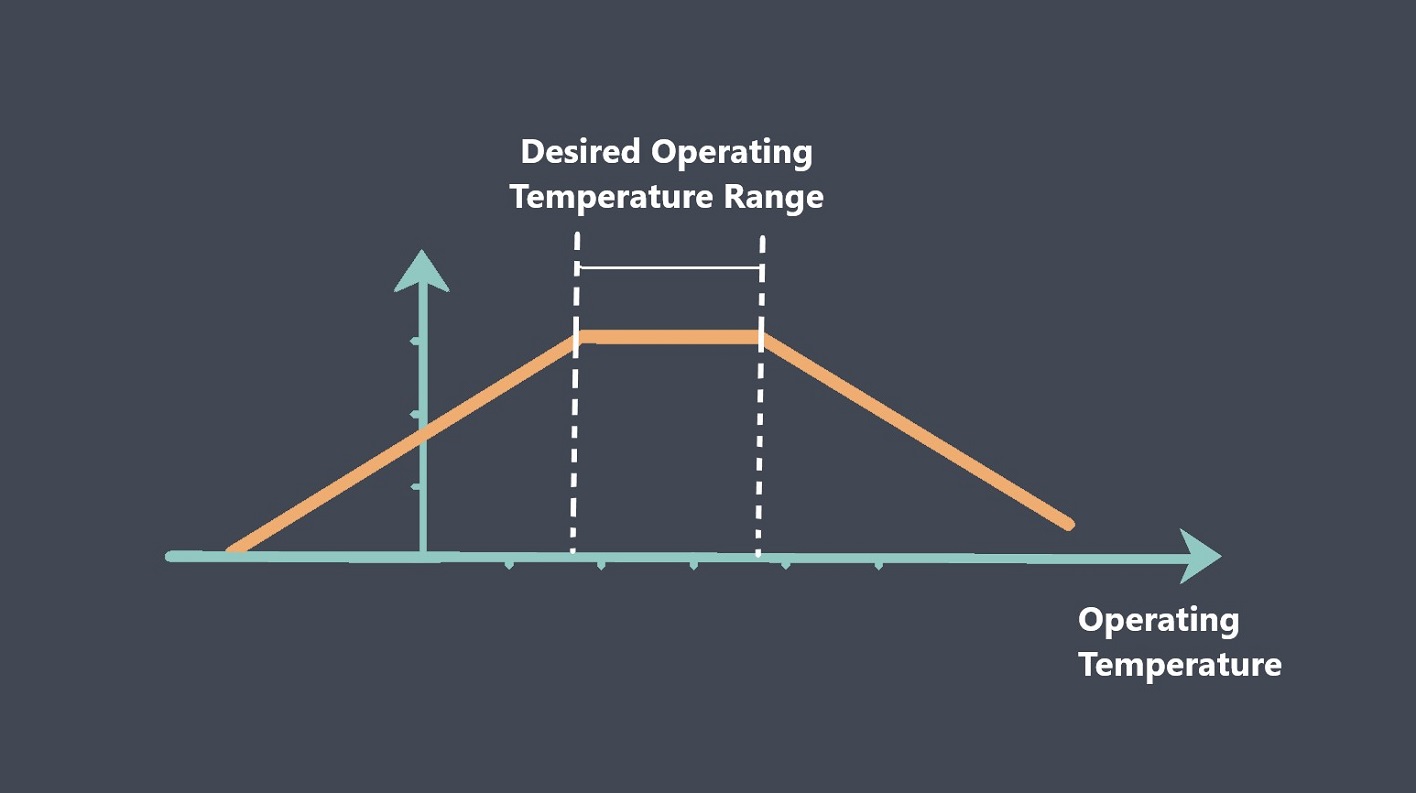
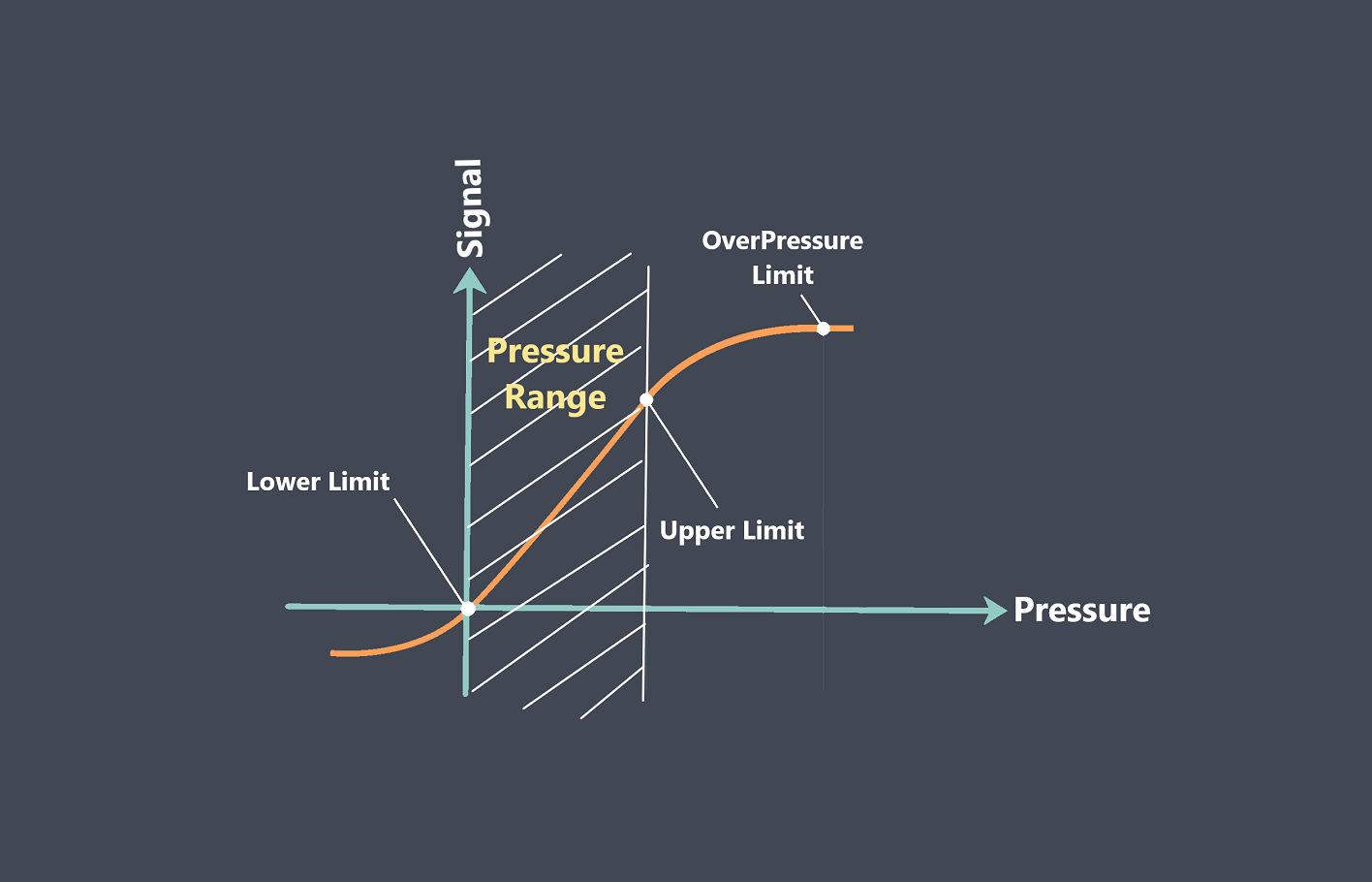
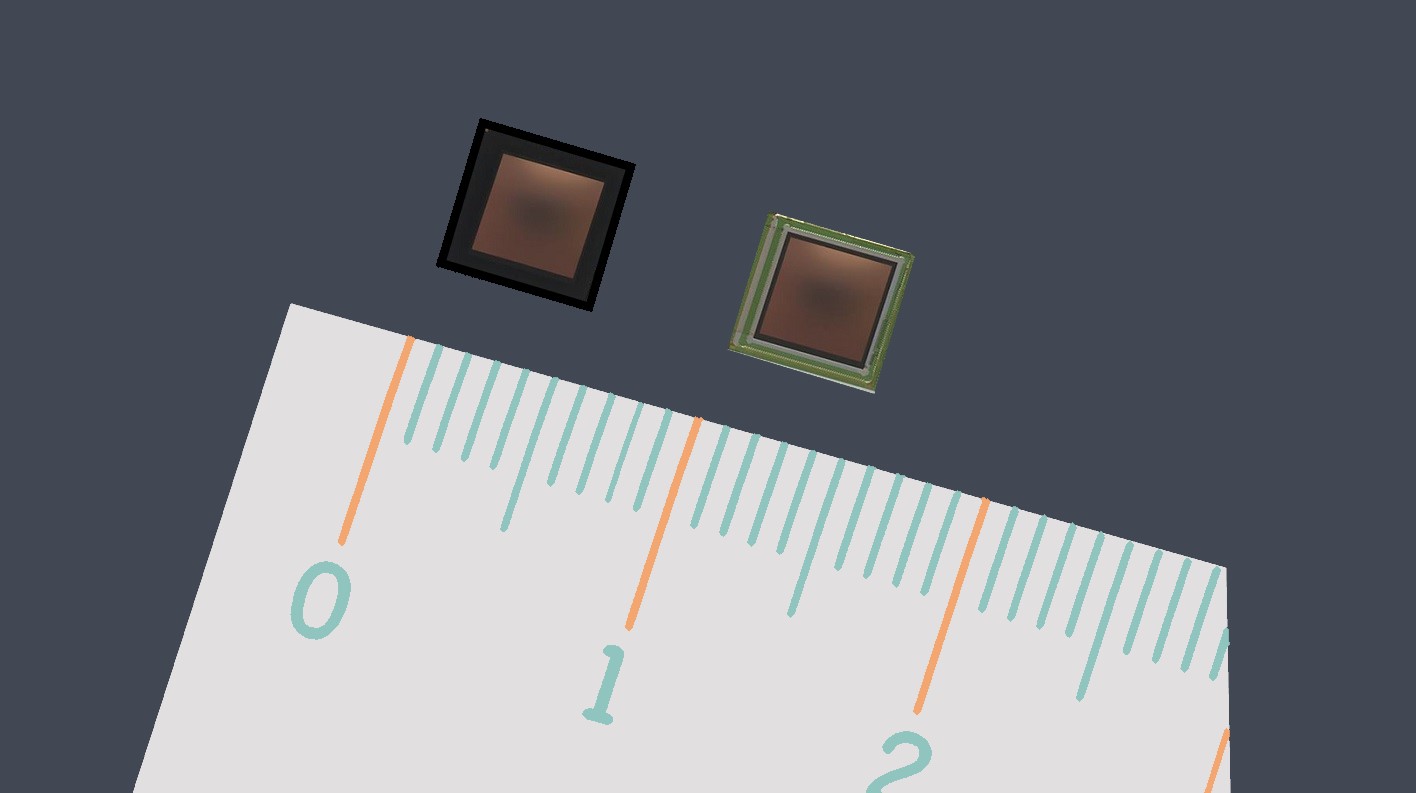
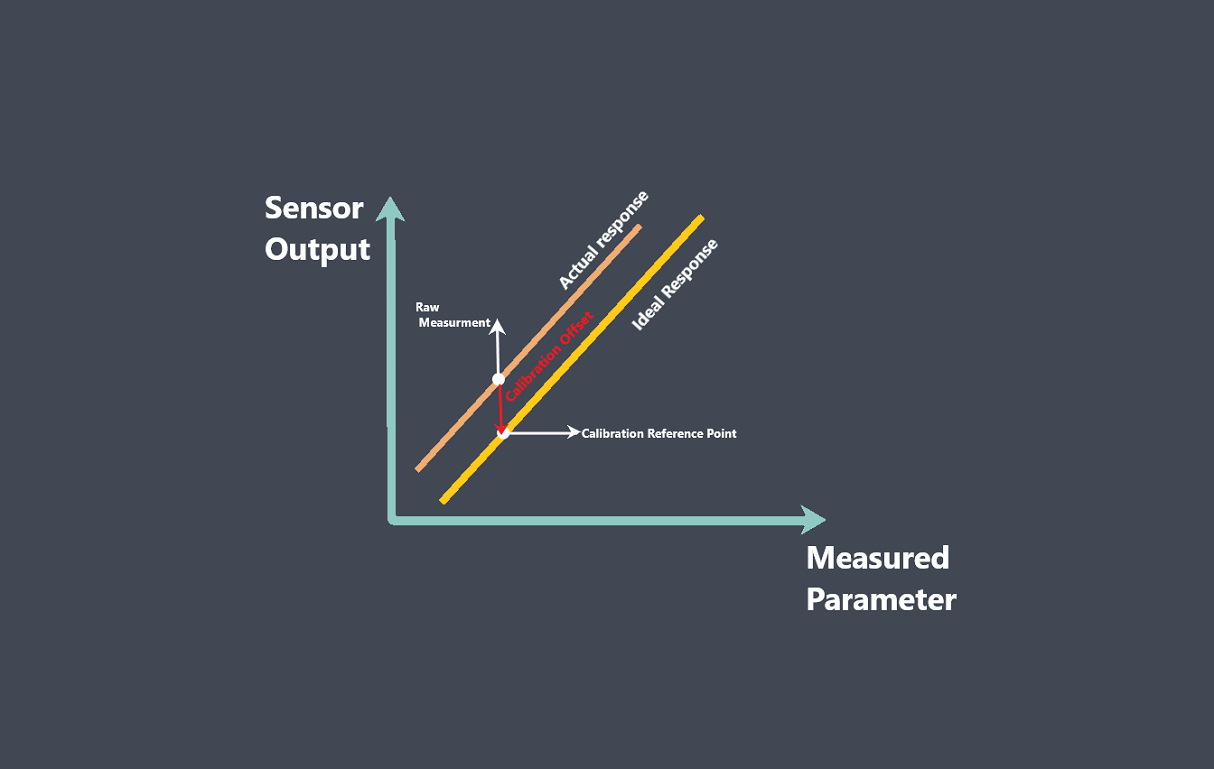
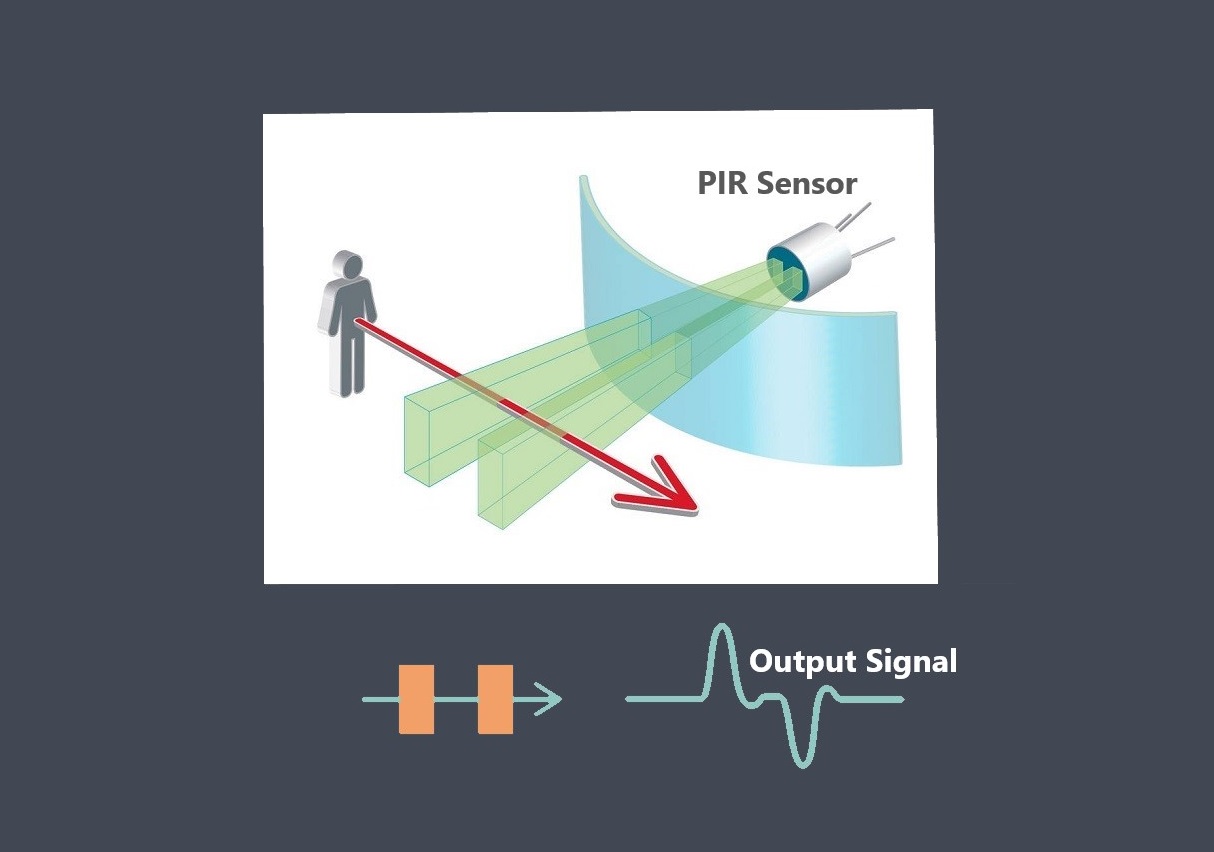
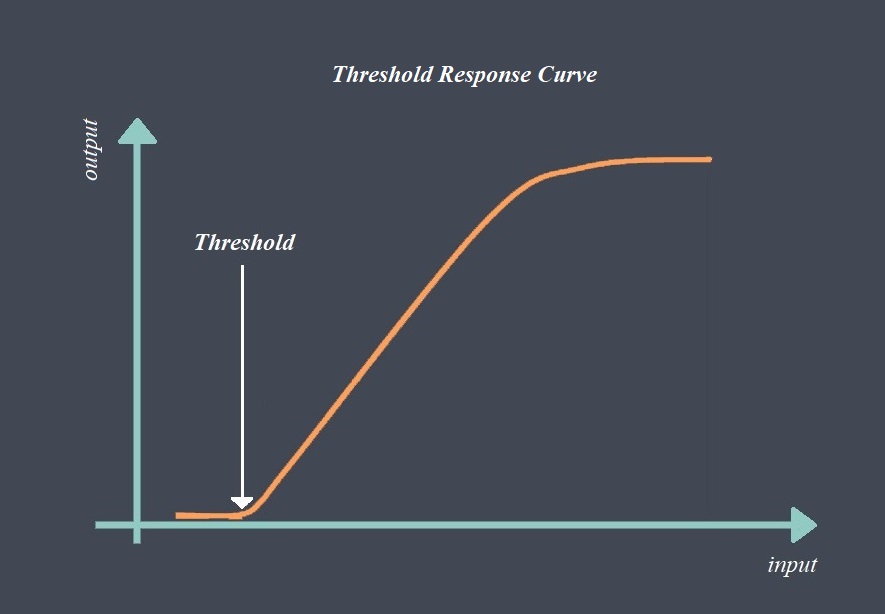
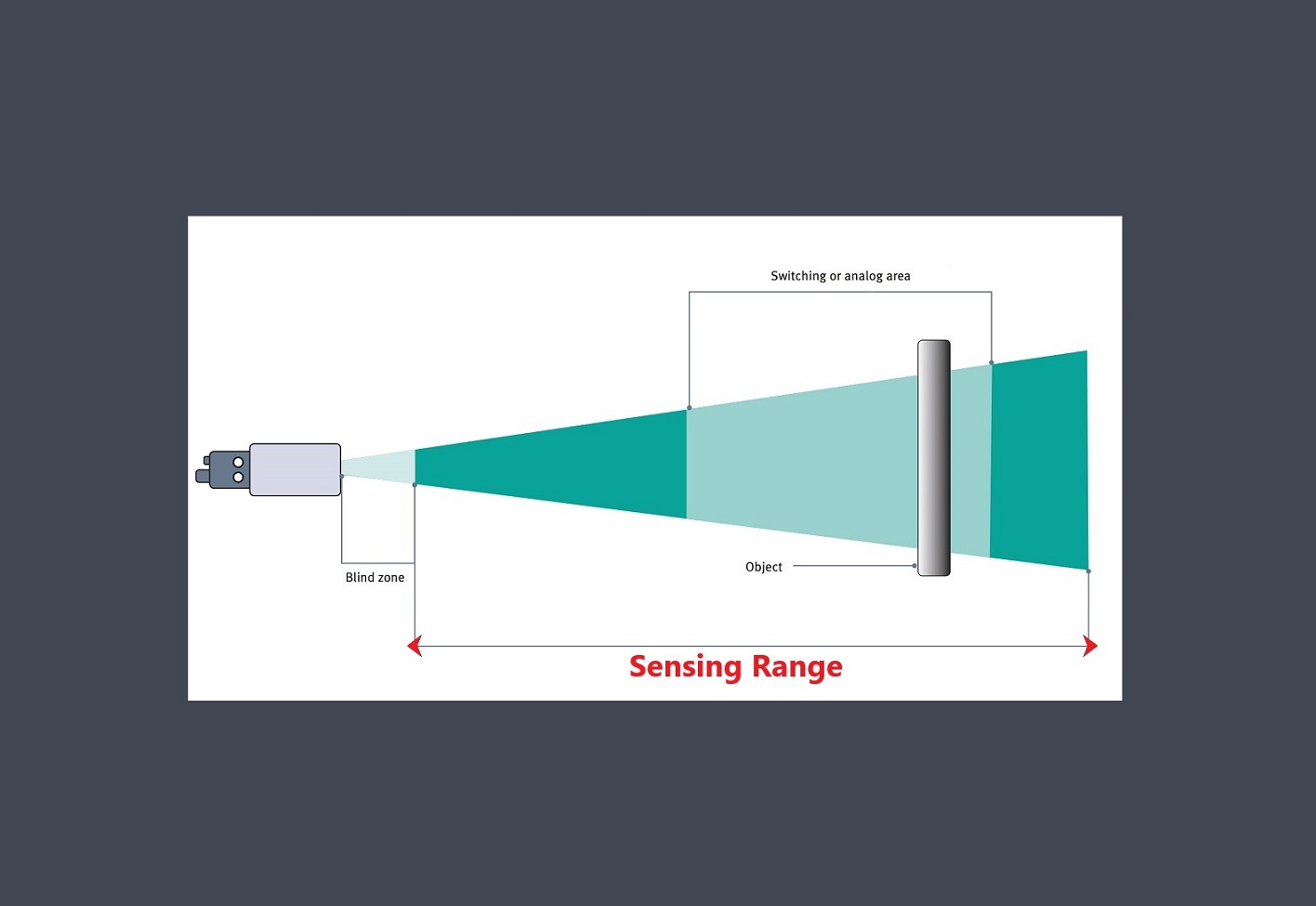
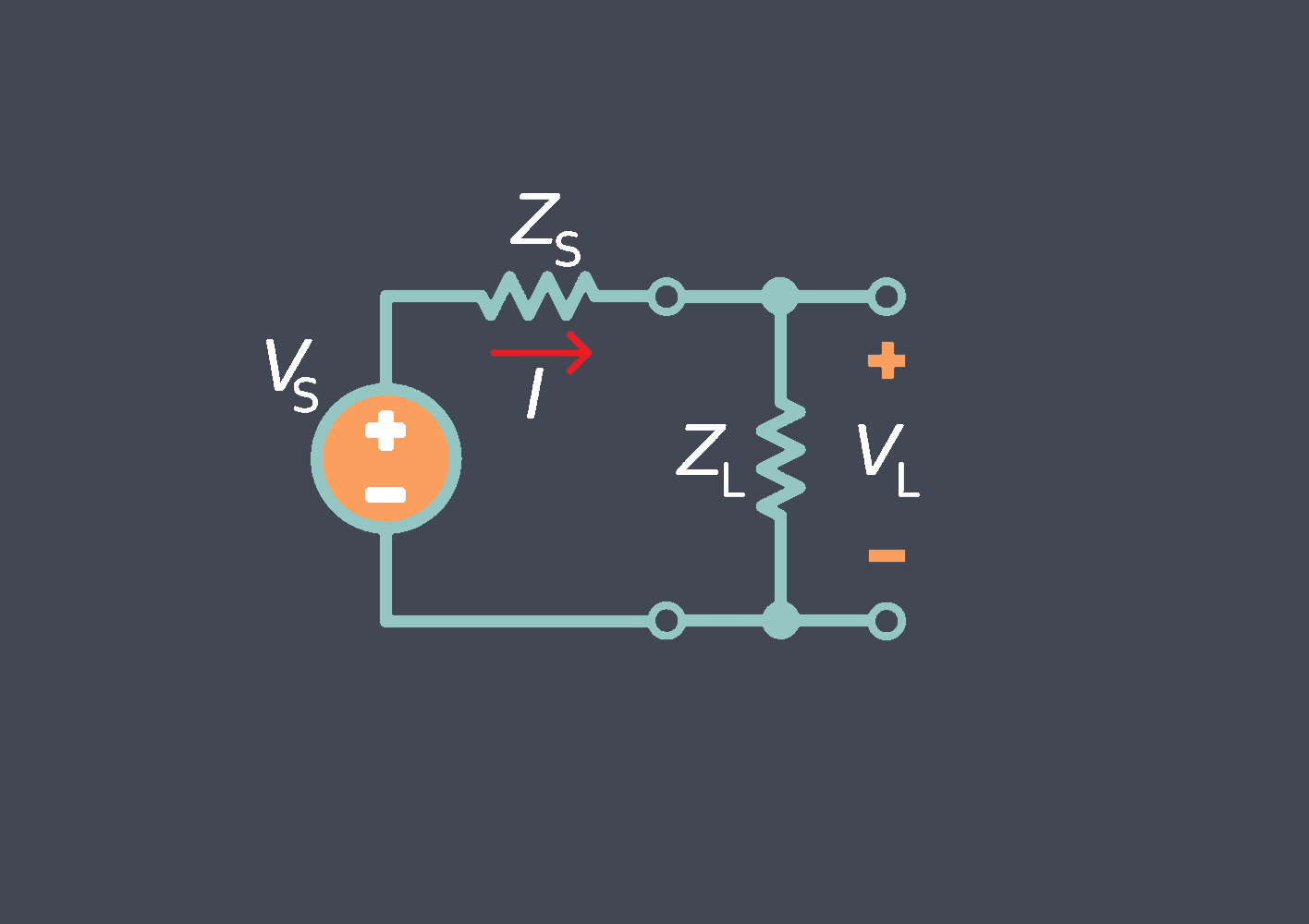
In the context of sensors, the term “sensing element” refers to the specific component within a sensor that directly interacts with the physical stimulus or environmental parameter being measured.
The sensing element is responsible for converting the physical input into a corresponding electrical, mechanical, or optical signal that can be processed and interpreted by the sensor’s electronics or external systems.
For example, in a temperature sensor, the sensing element may be a thermistor or a temperature-sensitive resistor. When exposed to changes in temperature, the resistance of the thermistor varies, allowing the sensor to measure the temperature.
In summary, the sensing element is the part of a sensor that directly interacts with the physical stimulus and initiates the signal conversion process.
Here are some common types of sensors based on their sensing elements:
Resistive Sensors
These sensors use a change in resistance to measure a physical parameter. Examples include thermistors (temperature), strain gauges (strain or pressure), and potentiometers (position).

Capacitive Sensors
These sensors utilize changes in capacitance to measure parameters such as proximity, humidity, or pressure. Capacitive touch sensors are commonly used in touchscreens and touch-sensitive devices.

Piezoelectric Sensors
These sensors generate an electrical charge in response to mechanical pressure or strain. They are used in applications such as vibration sensing, force measurement, and acoustic sensing.

Optical Sensors
Optical sensors use light to measure various parameters. Examples include photodiodes (light intensity), phototransistors (light intensity or proximity), and optical encoders (position or speed).

Magnetic Sensors
Magnetic sensors detect changes in magnetic fields and are commonly used for position, speed, or proximity sensing. Examples include Hall effect sensors and magneto resistive sensors.

Thermal Sensors
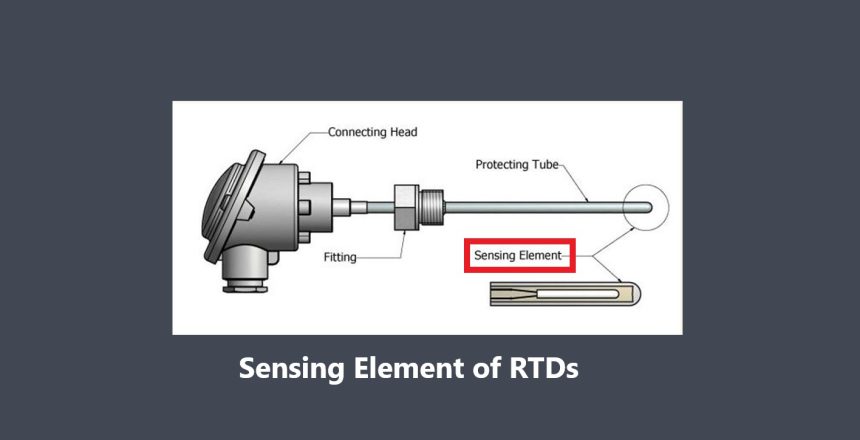
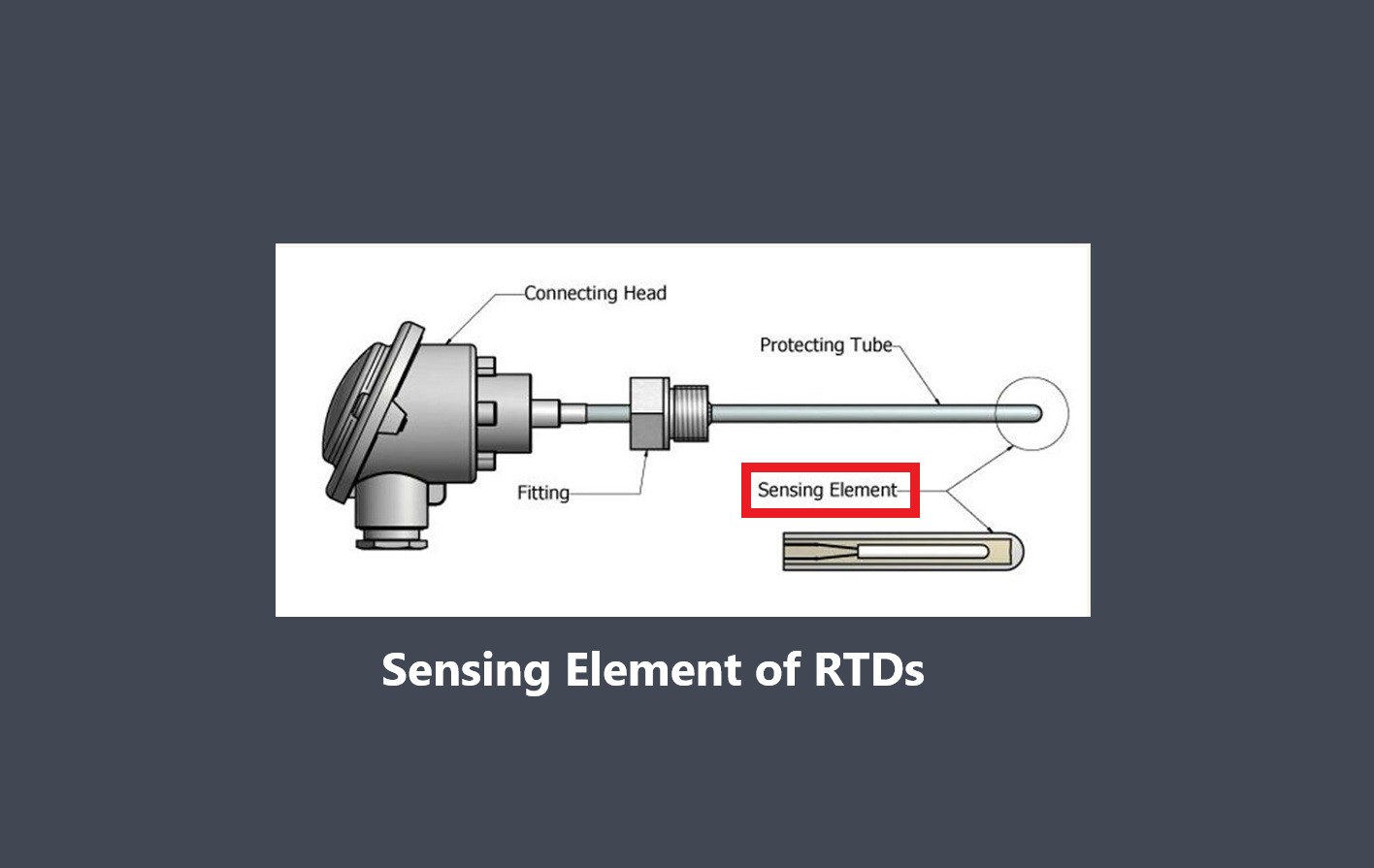
These sensors detect changes in temperature and utilize principles such as thermocouples or resistance temperature detectors (RTDs) to measure temperature variations.

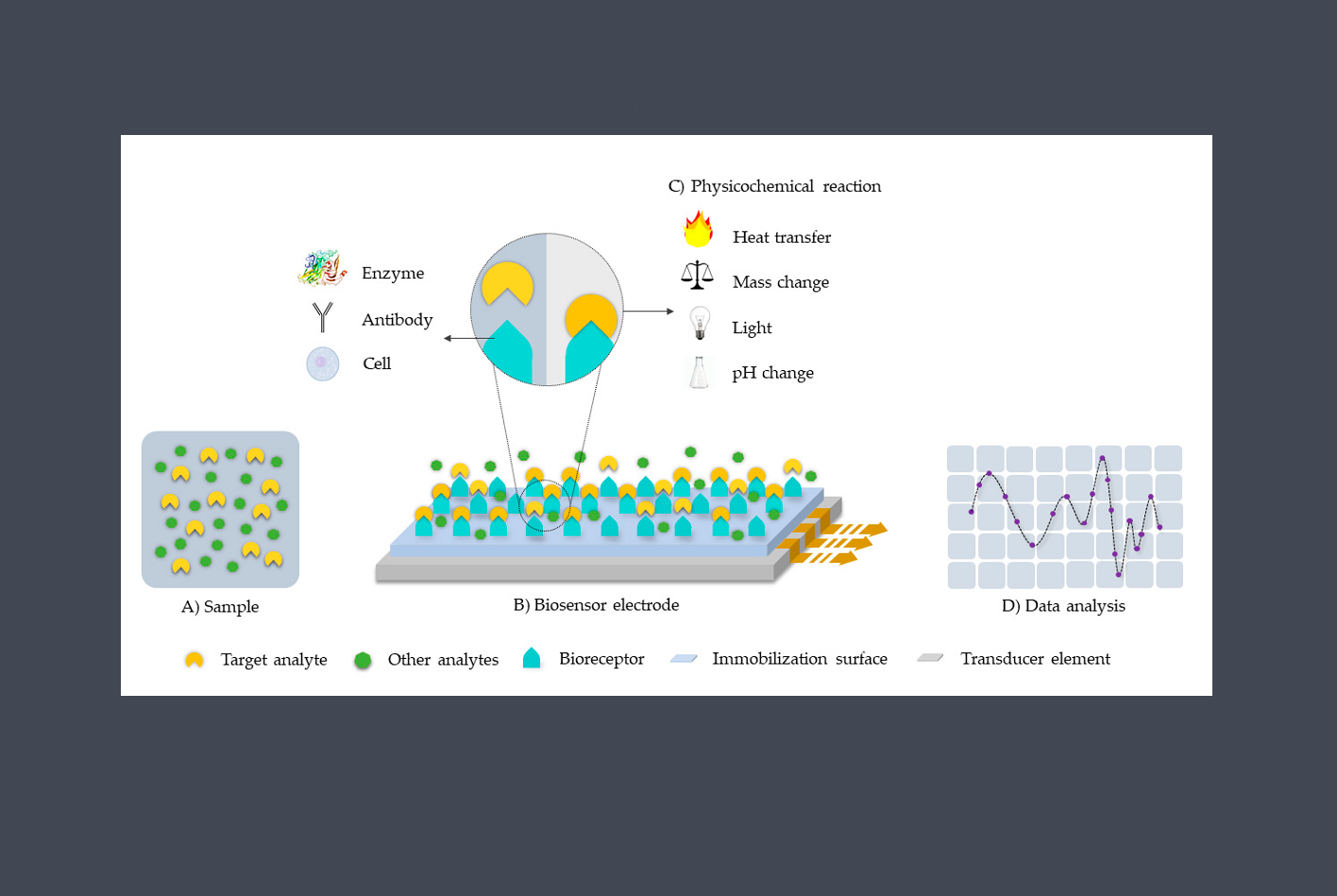
Chemical Sensors
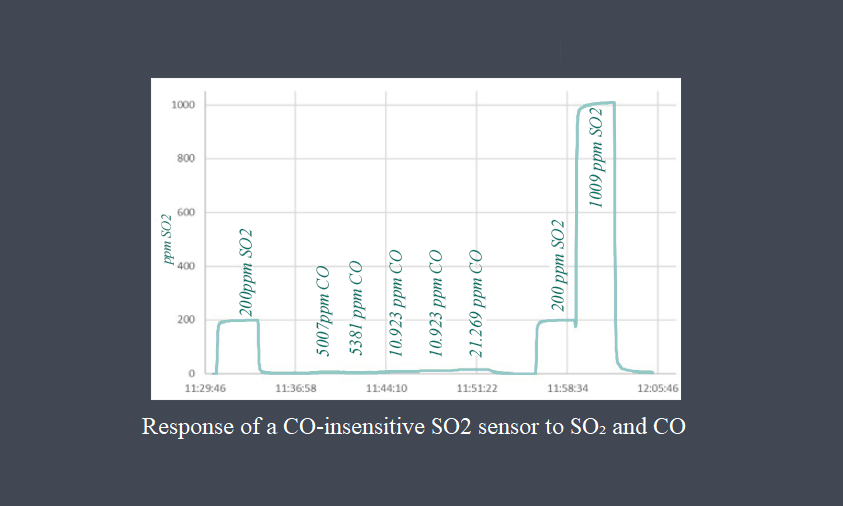
Chemical sensors are used to detect and measure the presence or concentration of specific chemicals or gases. Examples include gas sensors, pH sensors, and biosensors.

These are just a few examples of the types of sensors based on their sensing elements. There are many other specialized sensors available for specific applications, each utilizing different principles for measuring various physical or chemical parameters.
The specific design and type of sensing element used in a sensor depend on the target parameter to be measured and the desired sensitivity, accuracy, and range of the sensor.