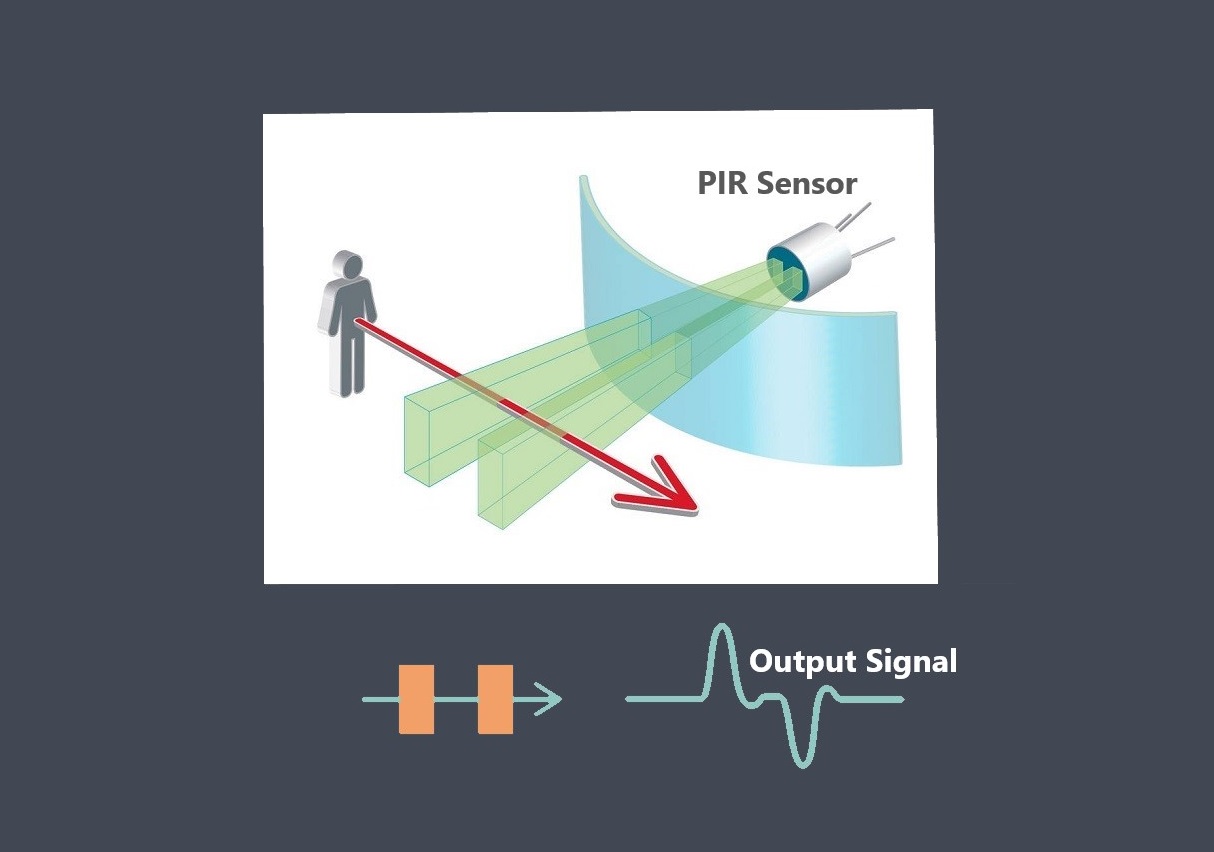
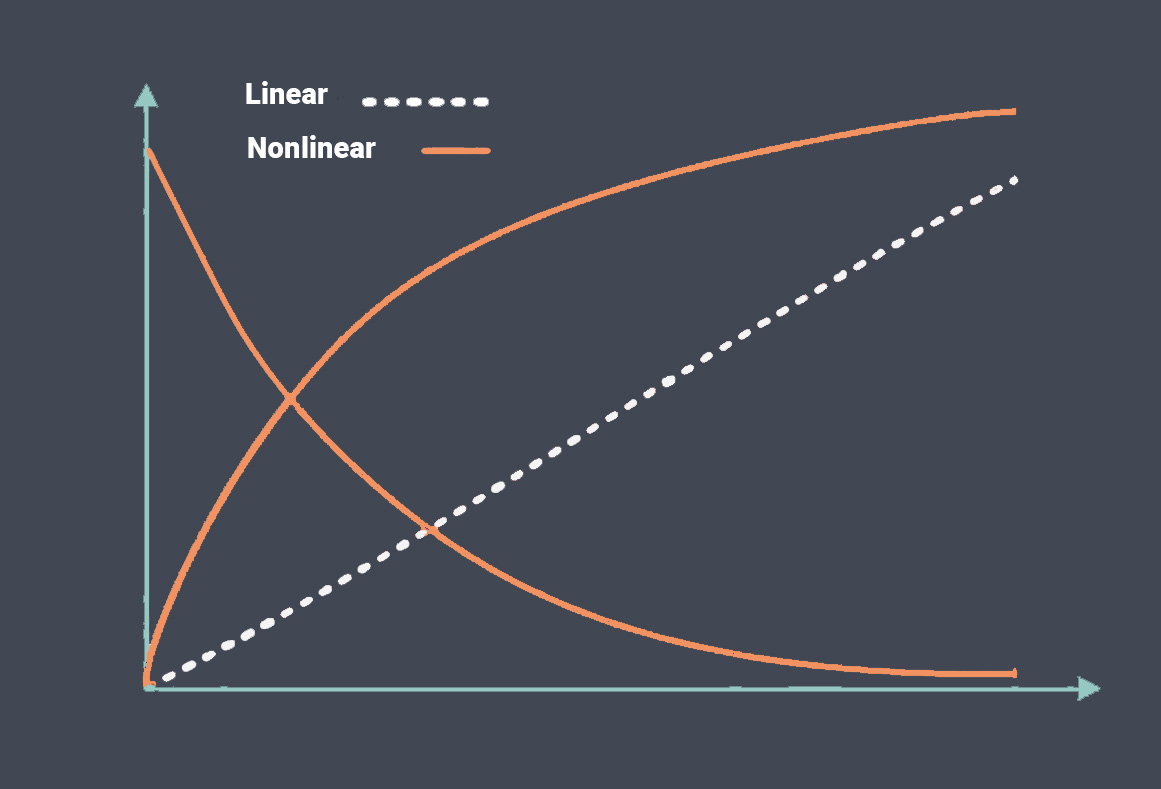
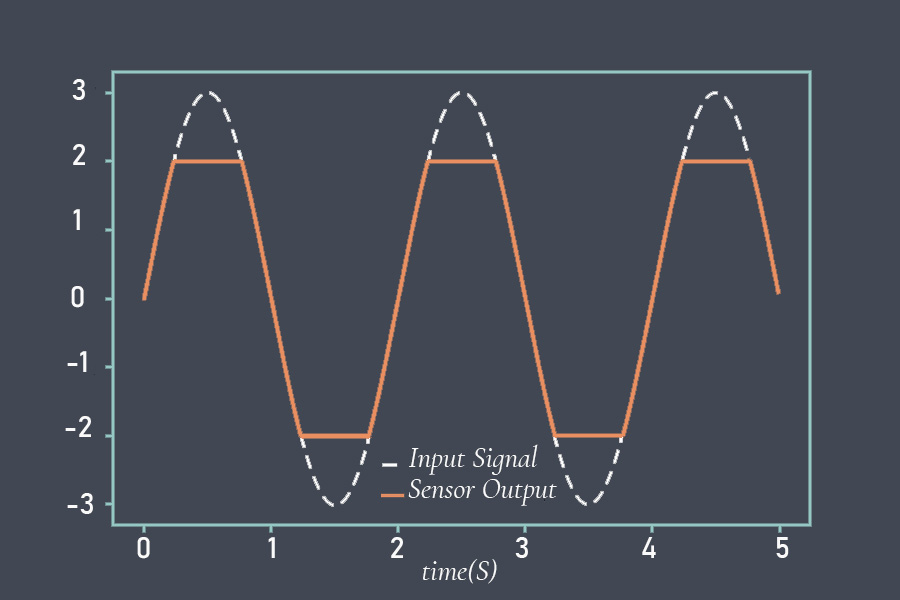
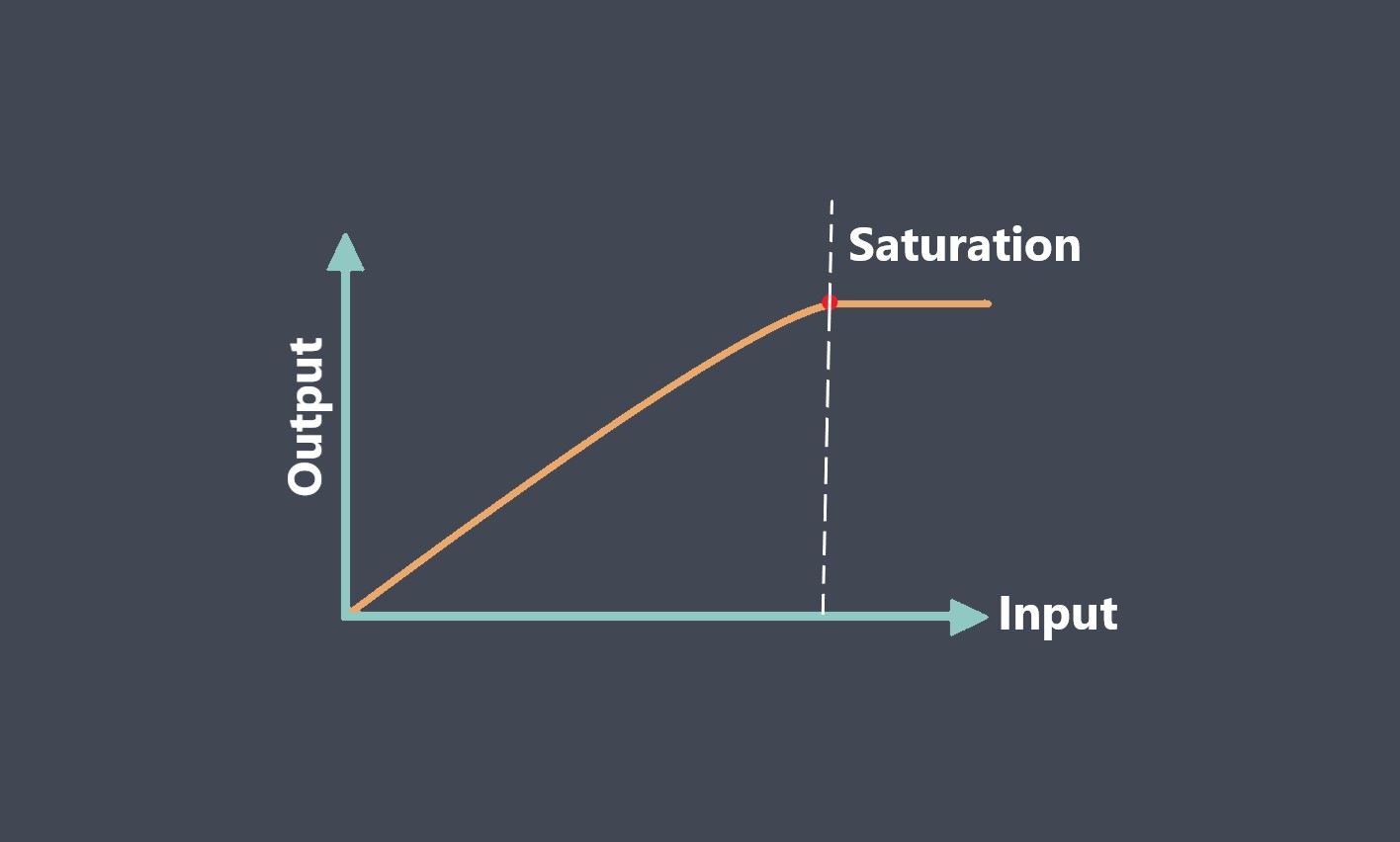
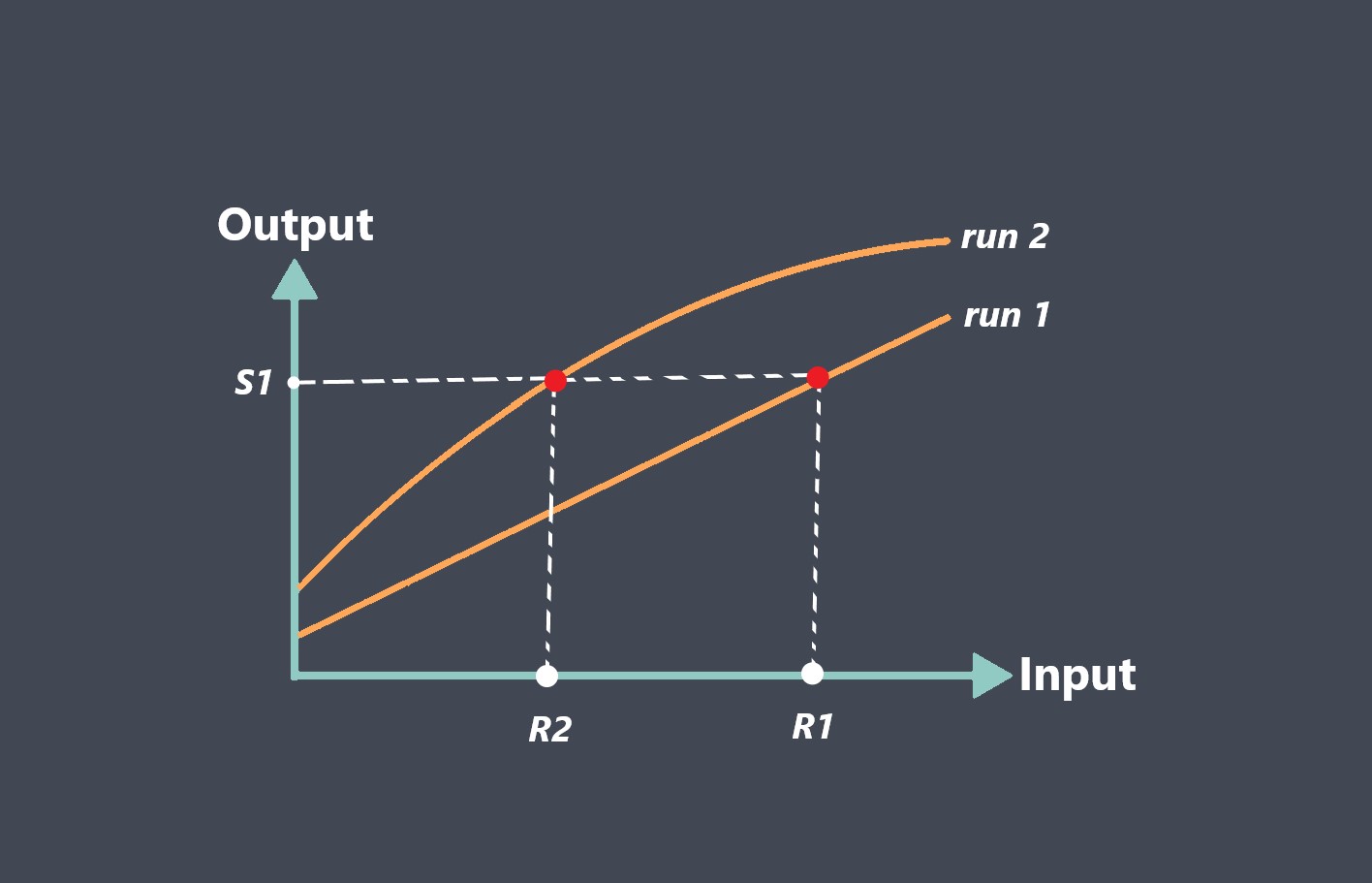
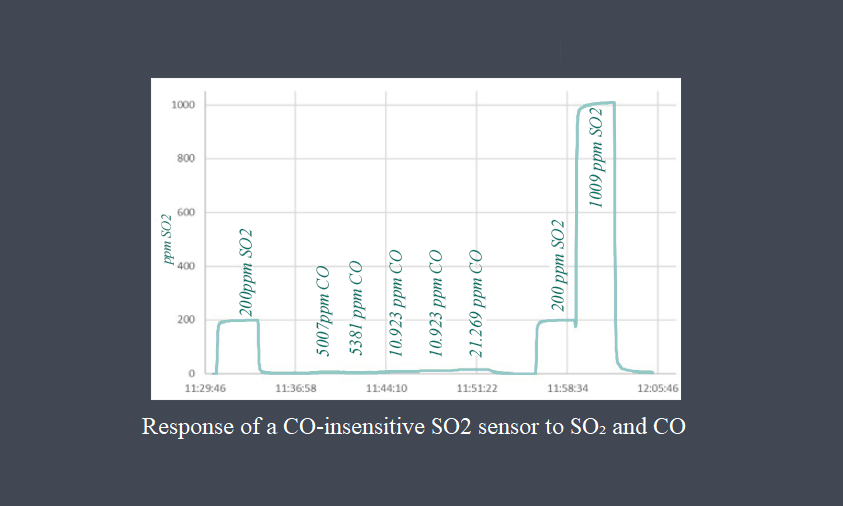
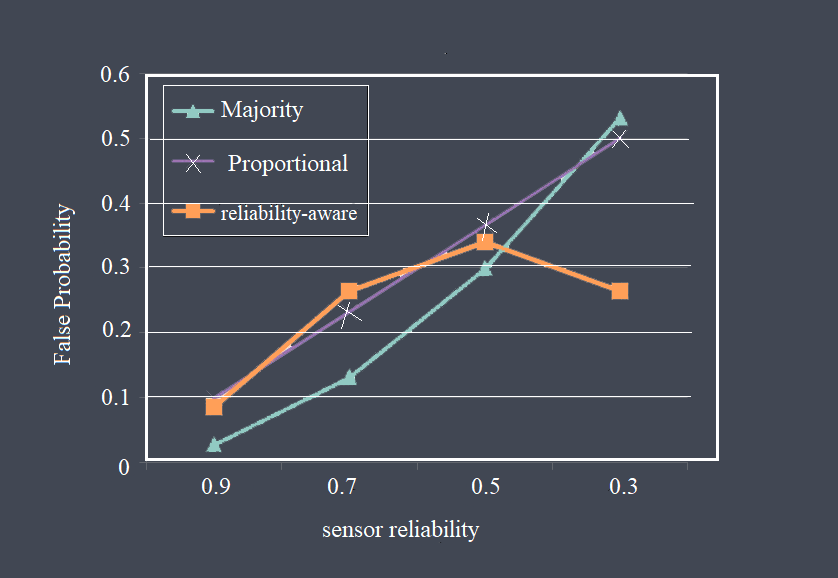
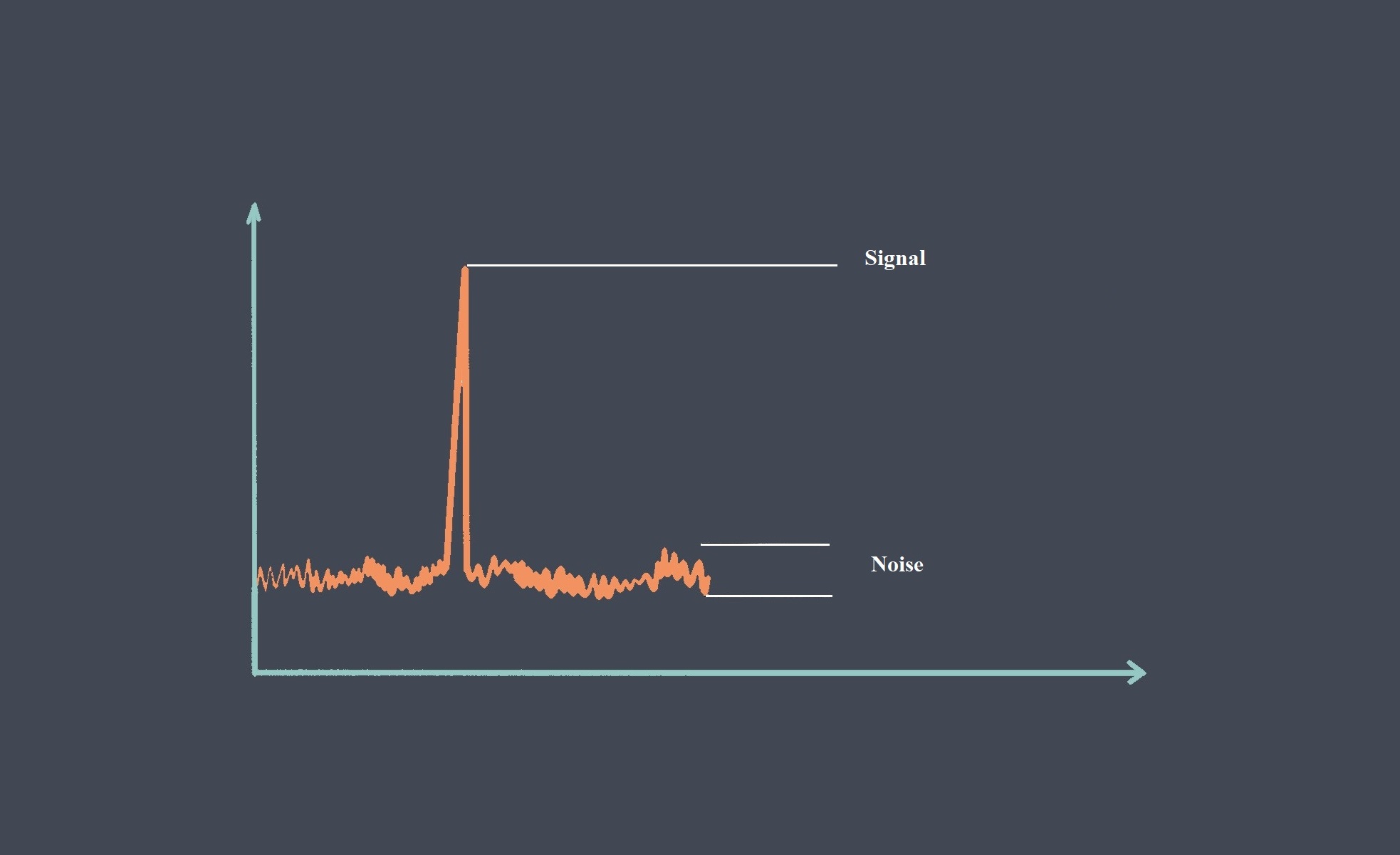
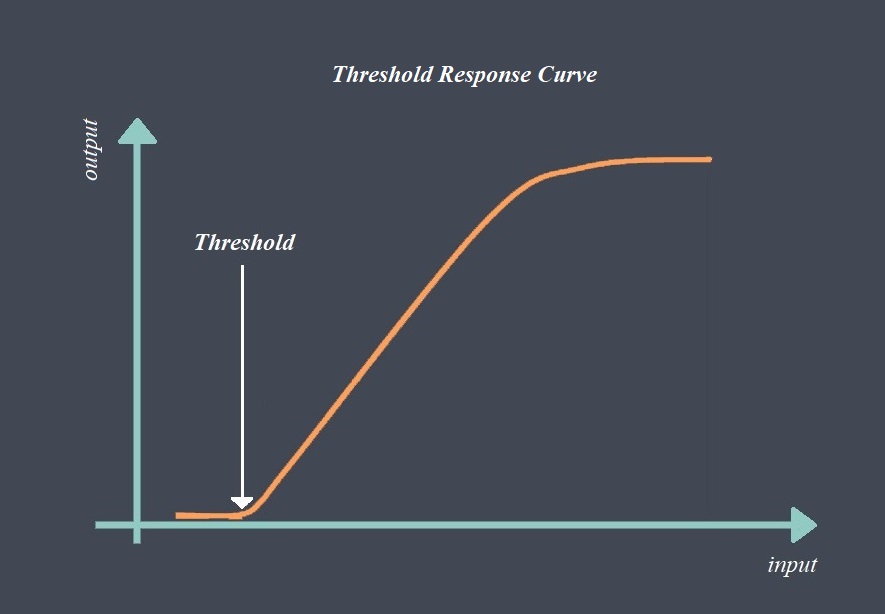
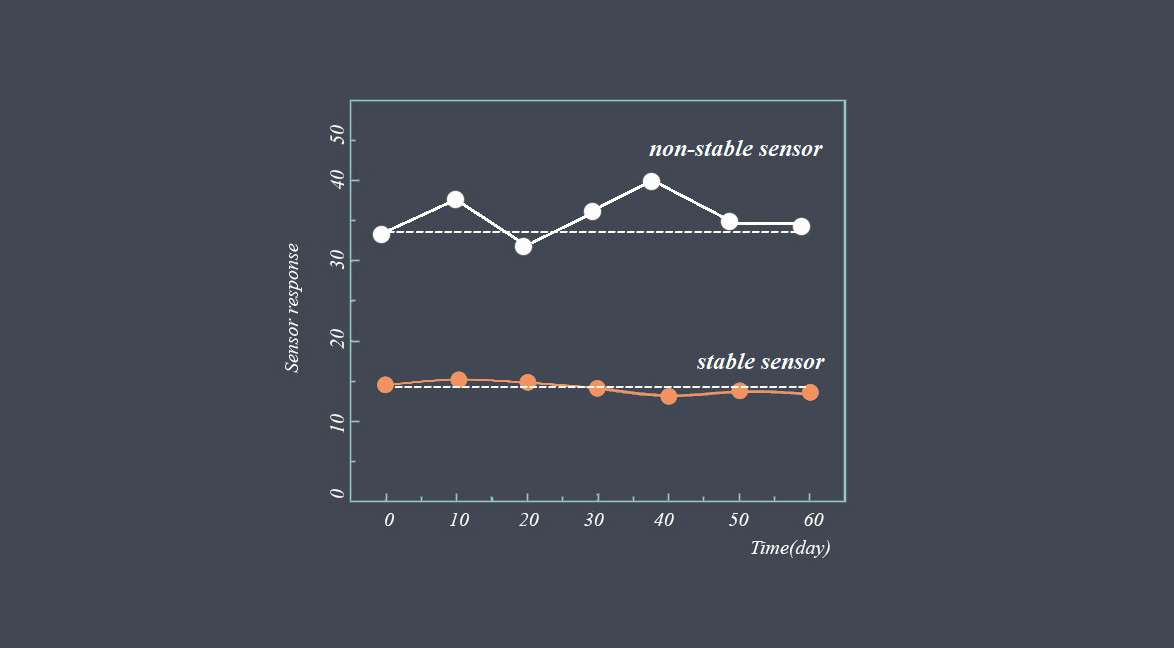
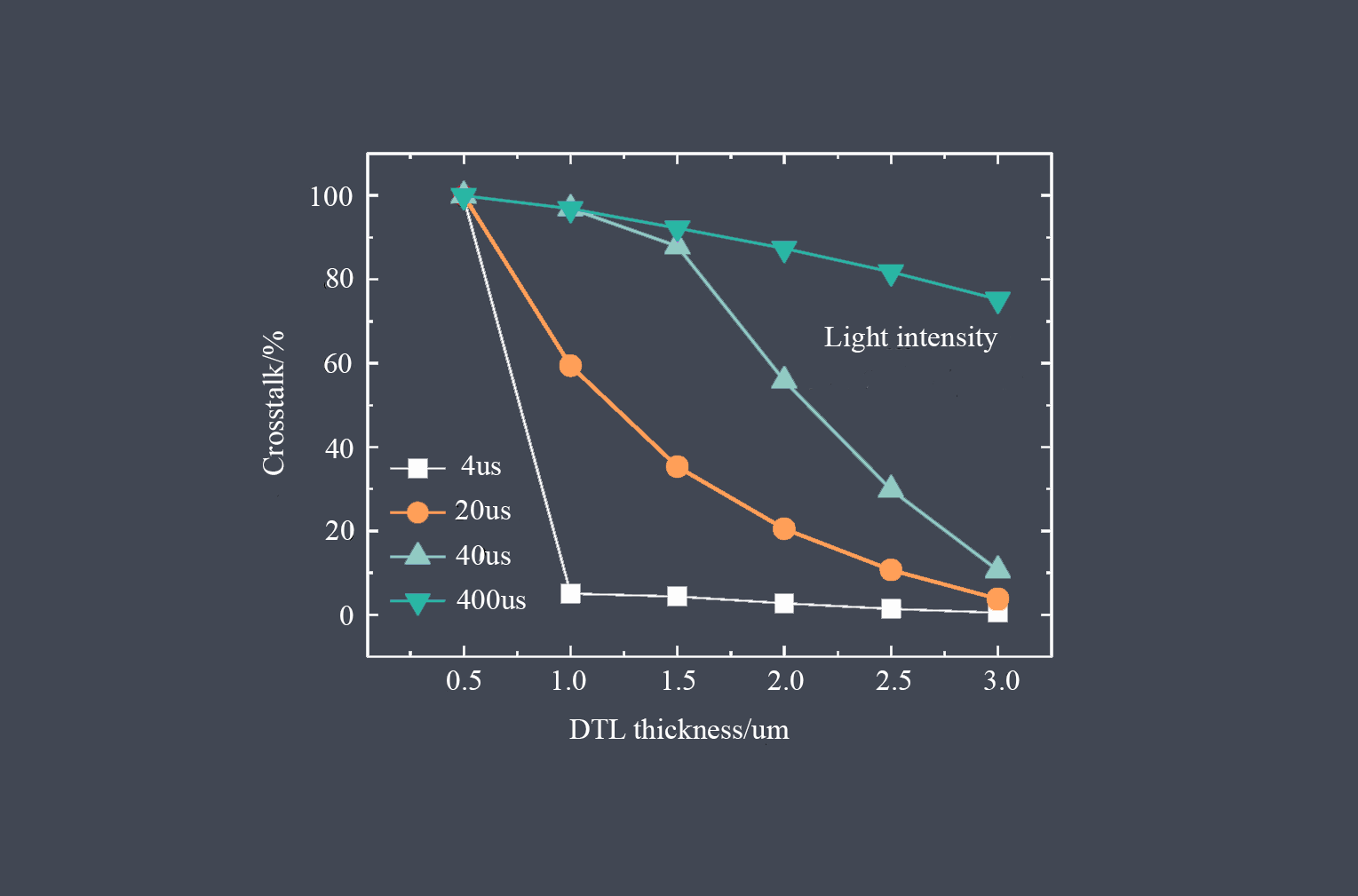
Response time is a critical parameter in sensor technology that measures how quickly a sensor can detect and react to changes in the input signal. It represents the time taken by the sensor to reach a specified percentage of its final output value in response to a step change in the input signal. Response time is essential in applications where real-time monitoring and fast detection of events are required.
Sensor response time refers to the time it takes for a sensor to register a change in the input signal and produce a corresponding output signal. It is a measure of how quickly the sensor can respond to changes in the quantity being measured and is an important specification to consider when selecting a sensor for a particular application.
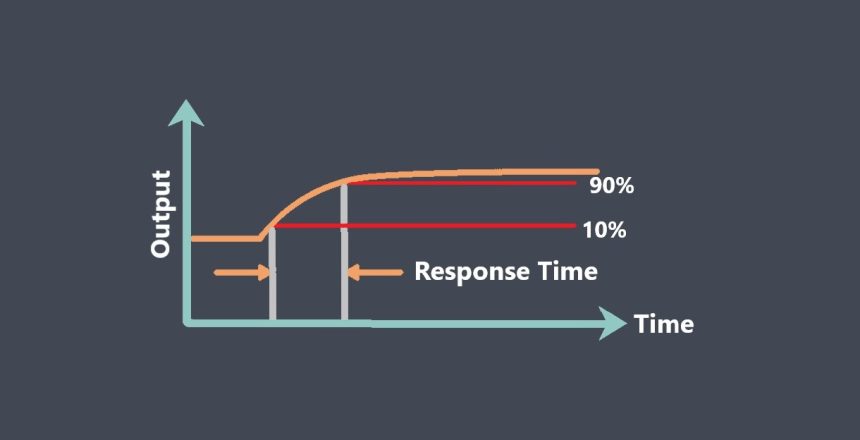
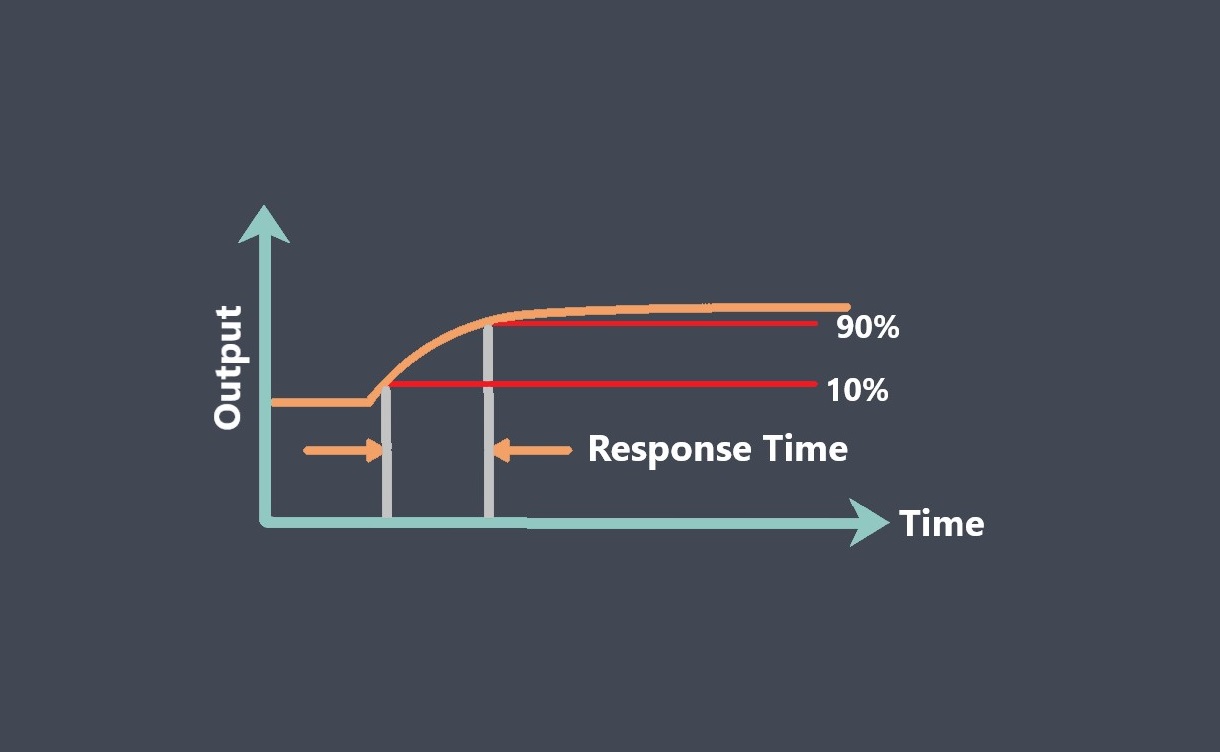
The response time of a sensor is typically specified by the manufacturer and represents the time it takes for the output signal to reach a certain percentage of its final value after a step change in the input signal. For example, a temperature sensor may have a response time of 90% in 5 seconds, meaning that the output signal will reach 90% of its final value within 5 seconds after a step change in temperature.
Why the sensor response time is important?
The response time of a sensor is important for several reasons:
Real-Time Monitoring and Control
In many applications, sensors are used to monitor and control processes in real-time. For example, in industrial automation, sensors detect changes in temperature, pressure, or other variables and trigger appropriate actions. In such scenarios, a fast response time is crucial to ensure timely and accurate monitoring and control of the system.
Safety and Emergency Situations
In certain applications, sensors play a vital role in ensuring safety and responding to emergency situations. For instance, in fire detection systems, smoke sensors need to quickly detect the presence of smoke and activate alarms or sprinkler systems. A fast response time can help minimize response delays and improve overall safety.
Dynamic Environments
Sensors may be used in environments where the measured parameters change rapidly. In these cases, a sensor with a fast response time enables capturing and reacting to those changes promptly. This is particularly important in applications like robotics, automotive systems, or environmental monitoring, where real-time adjustments are necessary.
Process Optimization
In various industries, sensors are employed to optimize processes and improve efficiency. By providing quick feedback on relevant parameters, sensors enable precise adjustments and fine-tuning of operations. A faster response time allows for enhanced process control, reducing waste, energy consumption, and improving overall productivity.
System Integration and Compatibility
Sensors are often part of larger systems or networks. When integrating sensors into a system, it’s important to consider their response time to ensure compatibility with other components. Mismatches in response times can lead to synchronization issues, data inaccuracies, or delays in system-wide processes.
Performance Comparison and Selection
Comparing the response times of different sensors helps in selecting the most suitable sensor for a specific application. By evaluating response times, you can determine which sensor meets the timing requirements of your system and choose accordingly.
Overall, the response time of a sensor directly impacts the accuracy, reliability, and efficiency of the system or process it is involved in. It determines how quickly the sensor detects changes, provides output signals, and contributes to real-time decision-making and control.
It’s important to note that the significance of response time can vary depending on the specific application and requirements. Some applications may prioritize accuracy over speed, while others may demand both fast response and high precision. Therefore, it’s crucial to consider the specific context and requirements when evaluating the importance of response time for a particular sensor application.
Factors affecting sensor response time
The response time of a sensor can be affected by factors such as the sensor’s design, sensitivity, signal processing capabilities, and environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity. In general, sensors with faster response times are more suitable for applications where rapid changes in the quantity being measured need to be detected and responded to quickly, such as in control systems or real-time monitoring applications. Here are some common factors affecting sensor response time:
Sensor Technology
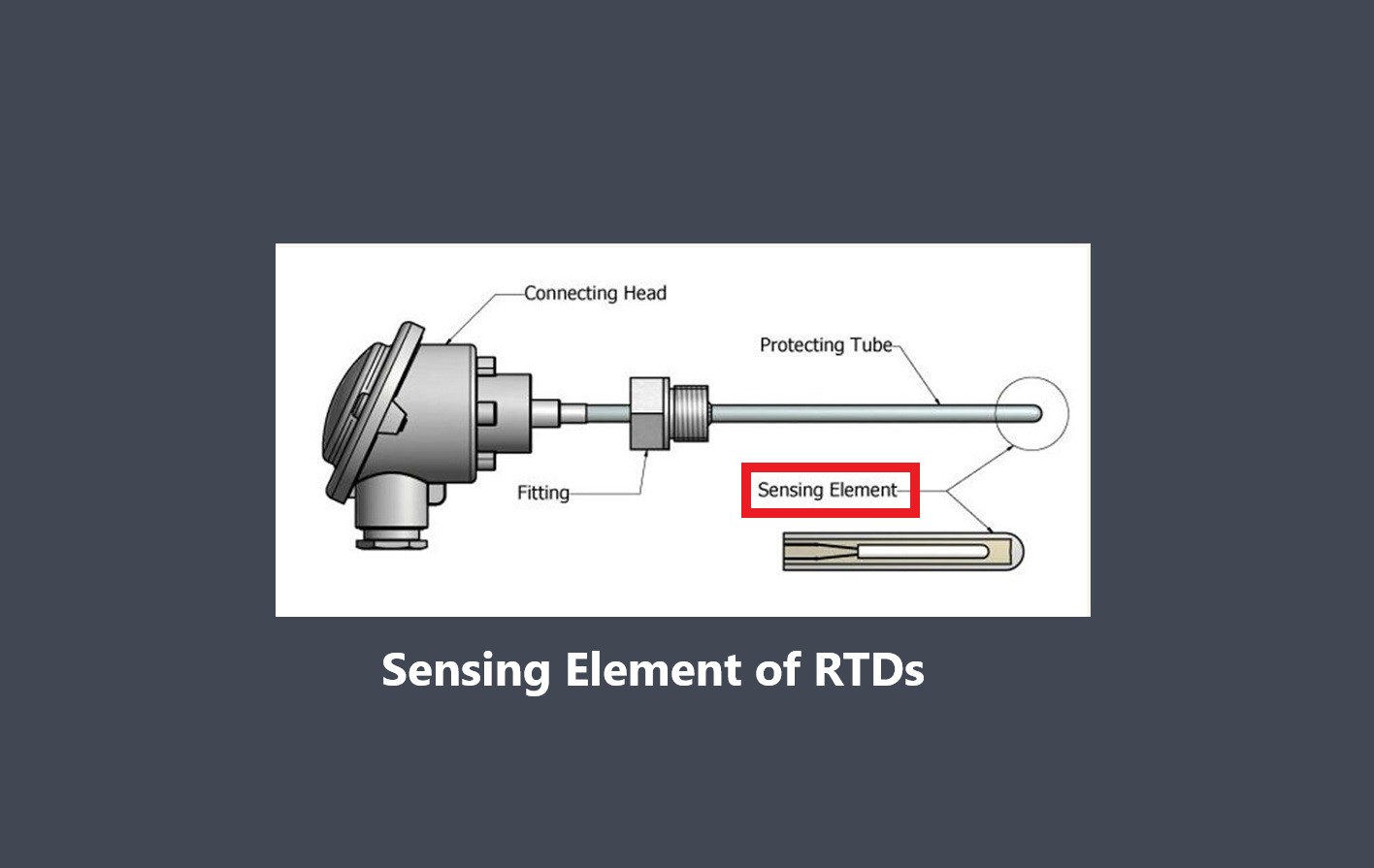
Different types of sensors have different response times based on their underlying technology. For example, some types of sensors, such as thermocouples or RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors), have slower response times compared to semiconductor-based sensors like thermistors or integrated circuit sensors.
Sensor Design
The design of the sensor itself can affect its response time. Factors such as the size and mass of the sensing element, the geometry of the sensor structure, and the materials used can impact how quickly the sensor can detect changes and provide a response.
Environmental Conditions
The environmental conditions in which the sensor operates can influence its response time. Variables like temperature, humidity, pressure, and electromagnetic interference can affect the sensor’s performance and response time. Extreme environmental conditions may cause delays or inaccuracies in sensing the target quantity.
Signal Processing
The signal processing circuitry connected to the sensor can also contribute to the overall response time. Analog-to-digital conversion, filtering, amplification, and other signal conditioning processes can introduce delays, especially if the circuitry is not optimized for high-speed operation.
Sensor Calibration
Proper calibration of the sensor ensures accurate measurements, but it can also impact the response time. In some cases, calibration procedures may involve additional steps or settling time that can affect the overall sensor response time.
Mechanical Factors
If the sensor requires physical movement or mechanical components to operate, factors like inertia, friction, and mechanical damping can influence the response time. These factors are particularly relevant in devices such as accelerometers or force sensors.
Electrical Factors
Electrical considerations such as resistance, capacitance, and inductance in the sensor circuitry can affect the time it takes for the sensor to respond. High resistance or capacitance values, for instance, may introduce delays in signal transmission and processing.
Power Supply
The stability and quality of the power supply provided to the sensor can impact its response time. Inadequate power supply voltage or current can lead to slower response times or introduce noise into the sensor’s output.
It’s important to note that the specific influence and significance of these factors can vary depending on the type of sensor and application context. Manufacturers often provide specifications related to response time for their sensors, which can help users choose the most appropriate sensor for their requirements.
How to evaluate and compare the response time of sensors?
To evaluate and compare the response time of sensors, standardized metrics like rise time, settling time, or time constant are often used.
Rise time measures the time taken for the output signal to rise from a specified lower percentage(10%) to a higher percentage(90%) of its final value.
Settling time represents the time required for the output signal to stabilize within a specified tolerance after a step change.

Time constant characterizes the speed of response and is defined as the time taken for the output signal to reach approximately 63.2% of its final value.
In summary, response time is a crucial parameter that determines how quickly a sensor can detect and react to changes in the input signal. It plays a vital role in applications that require real-time monitoring and fast event detection. Understanding the response time of a sensor helps in selecting the appropriate sensor for time-critical applications and ensures accurate and timely measurements.