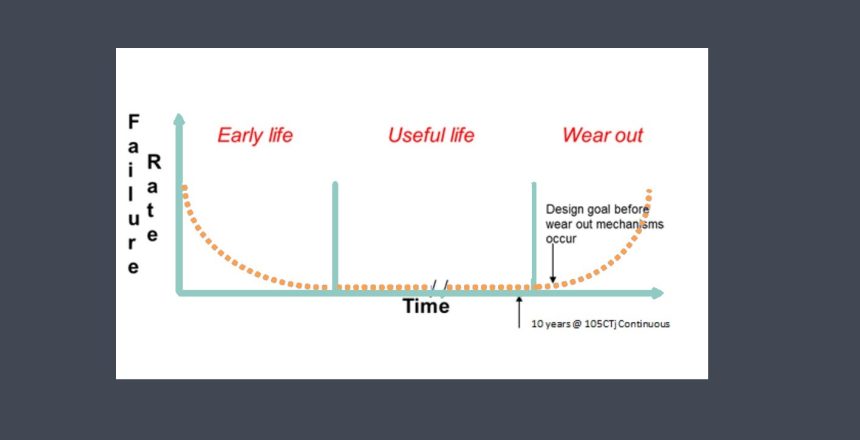
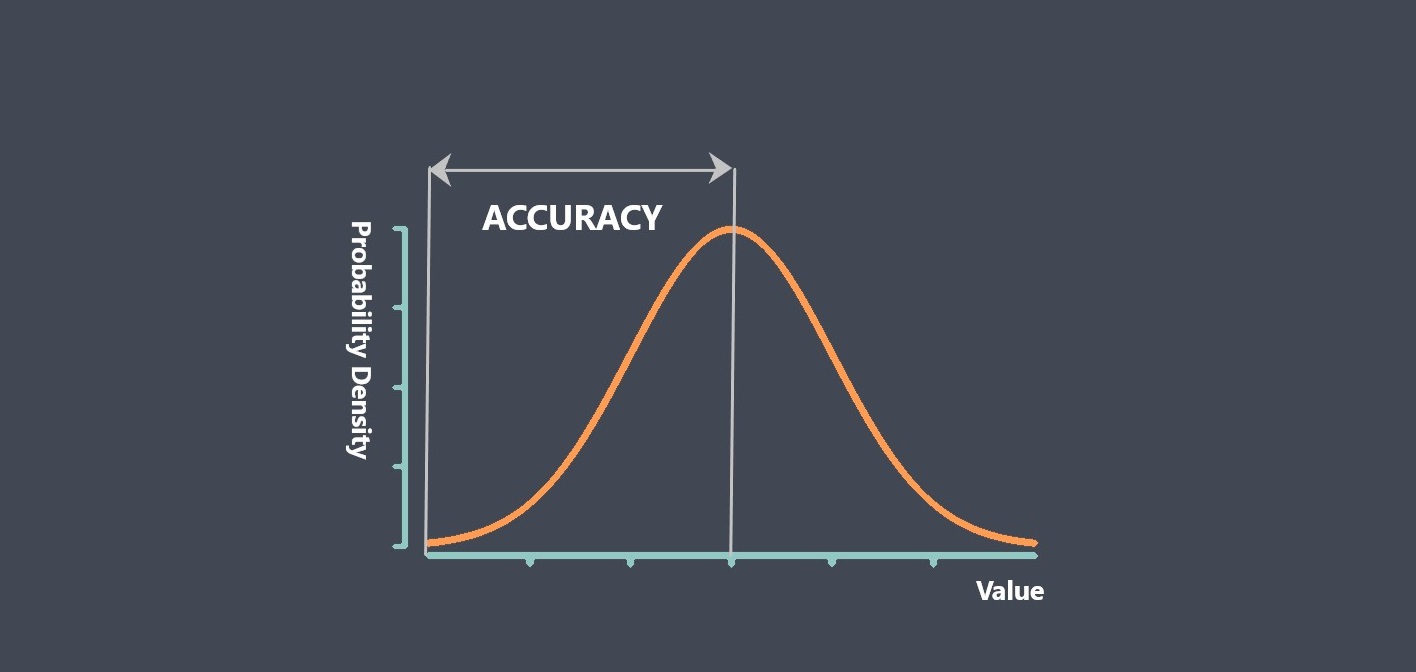
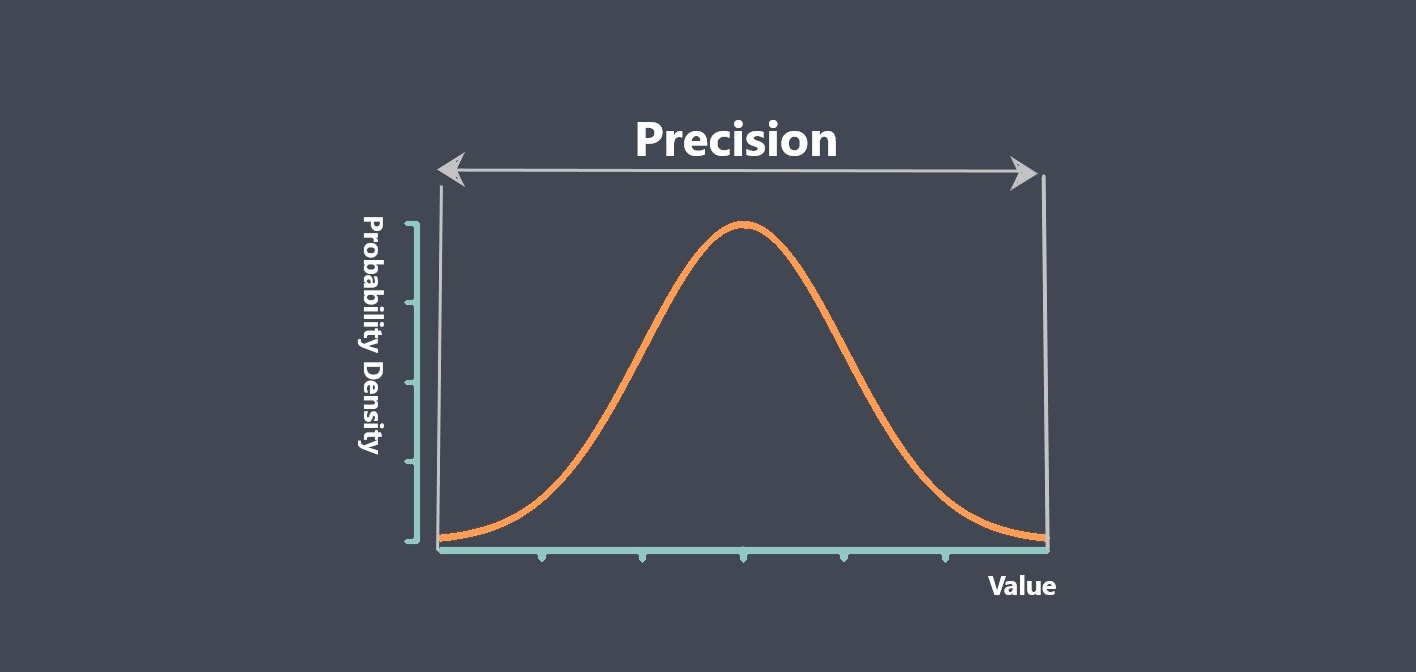
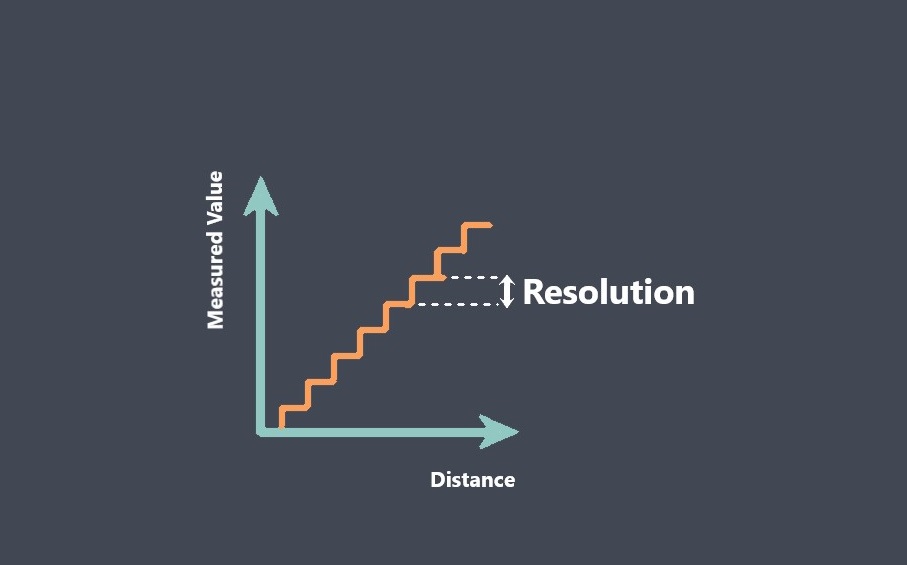
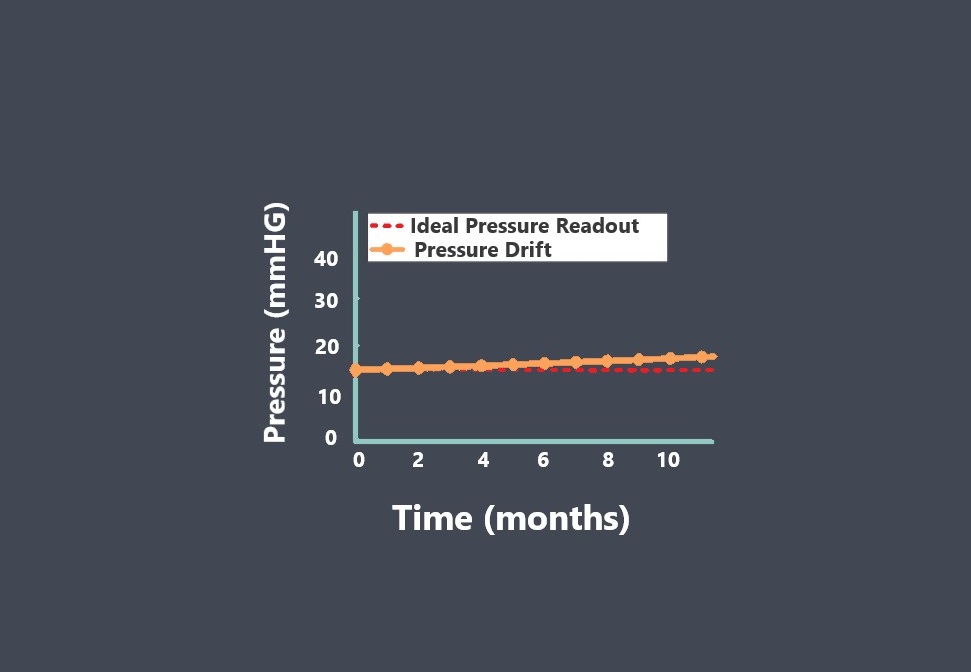
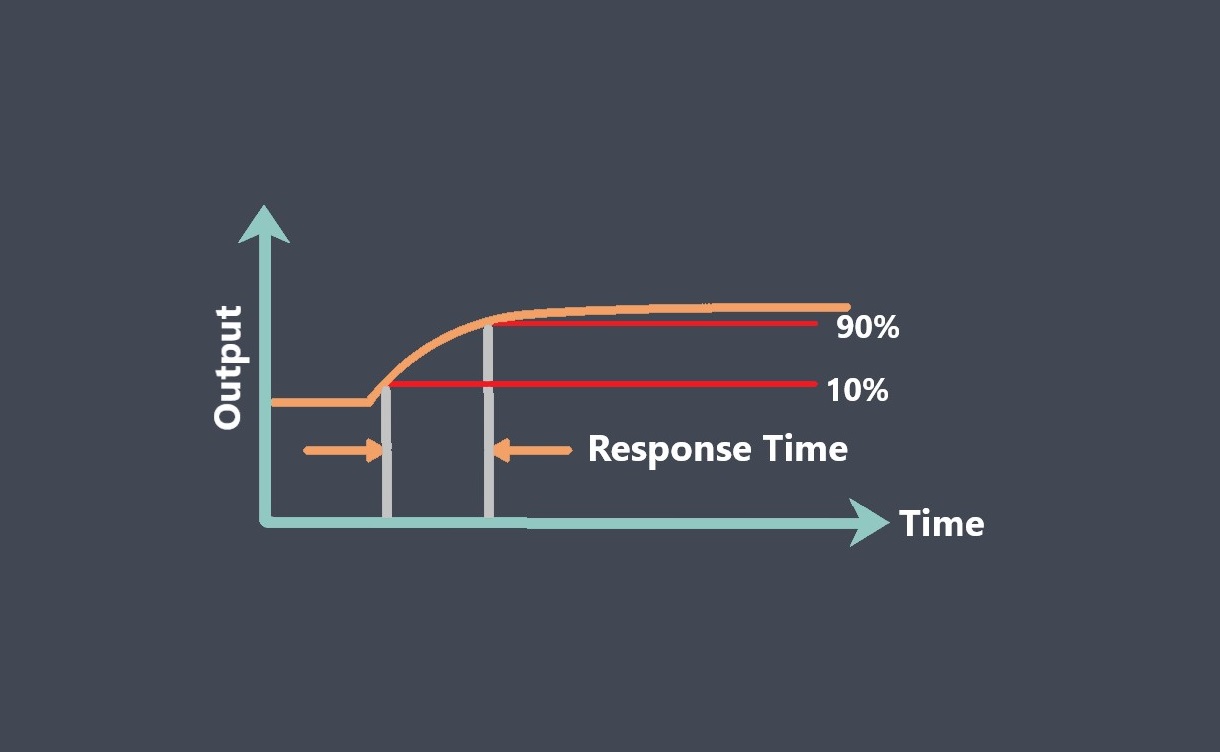
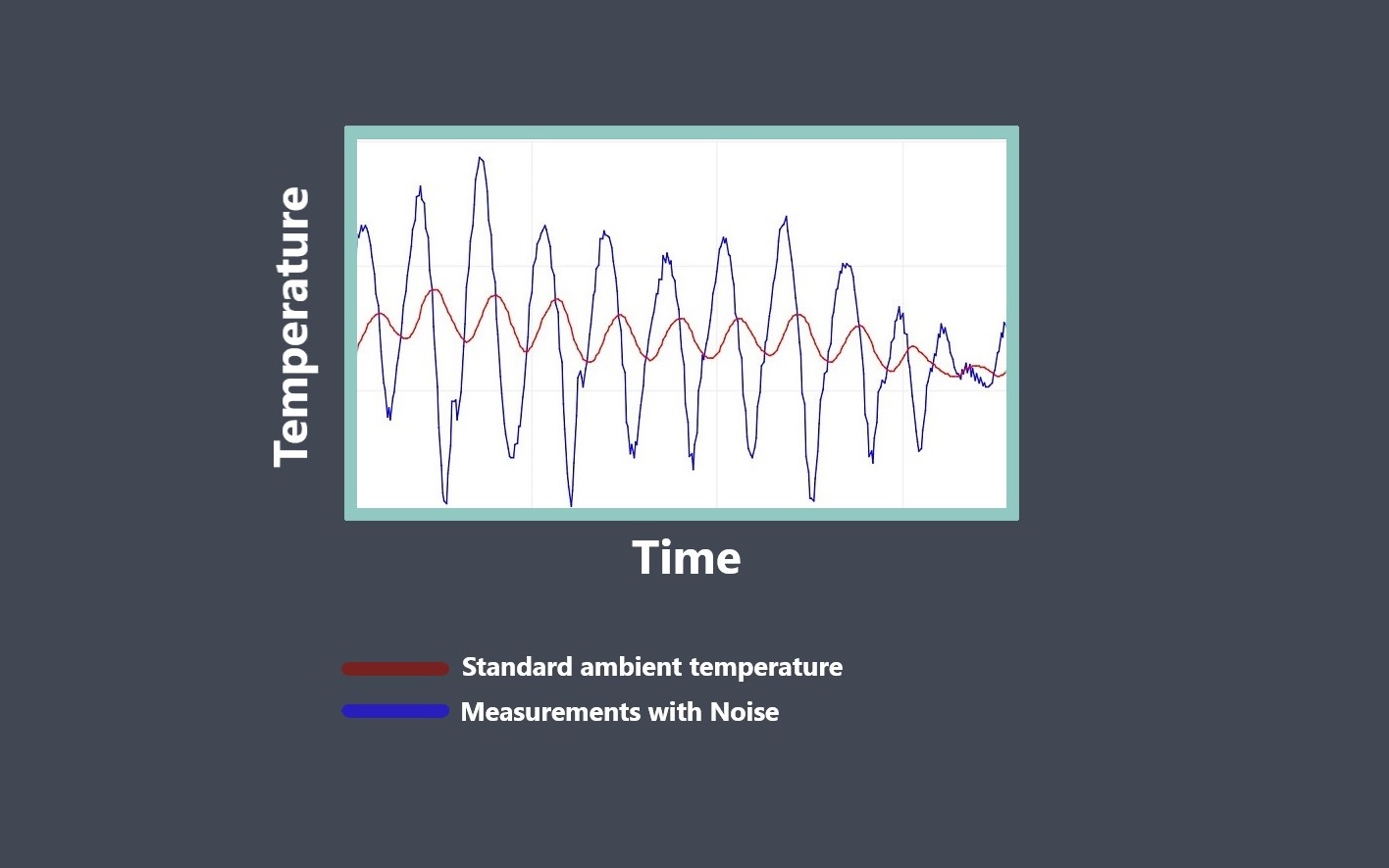
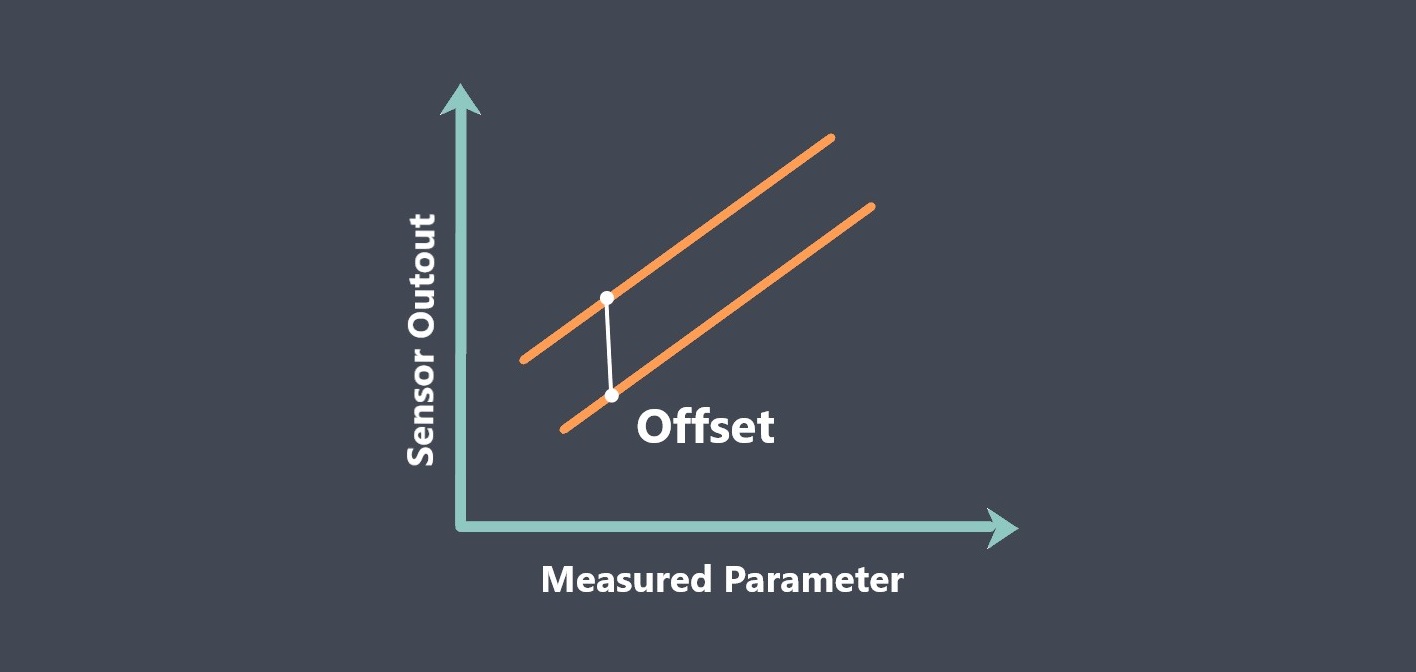
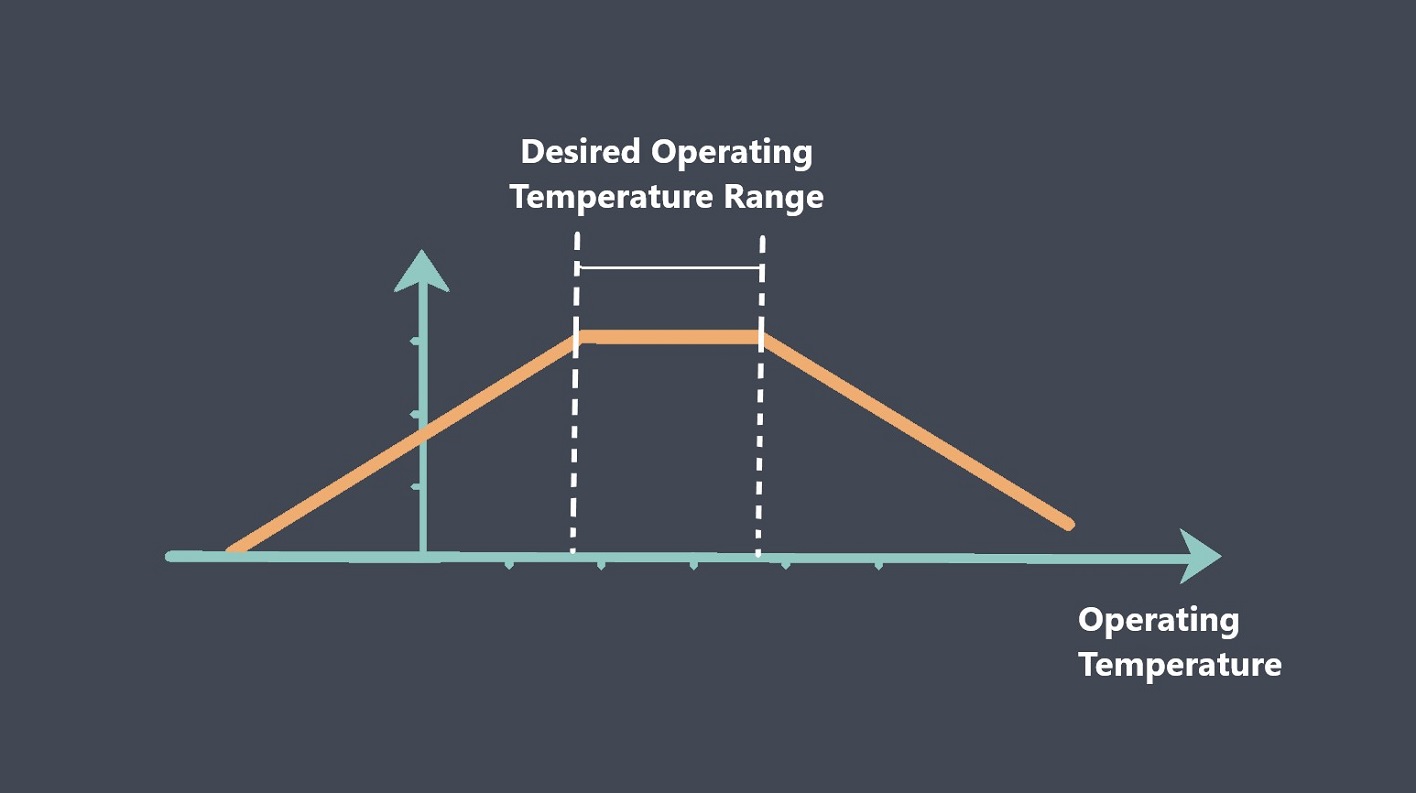
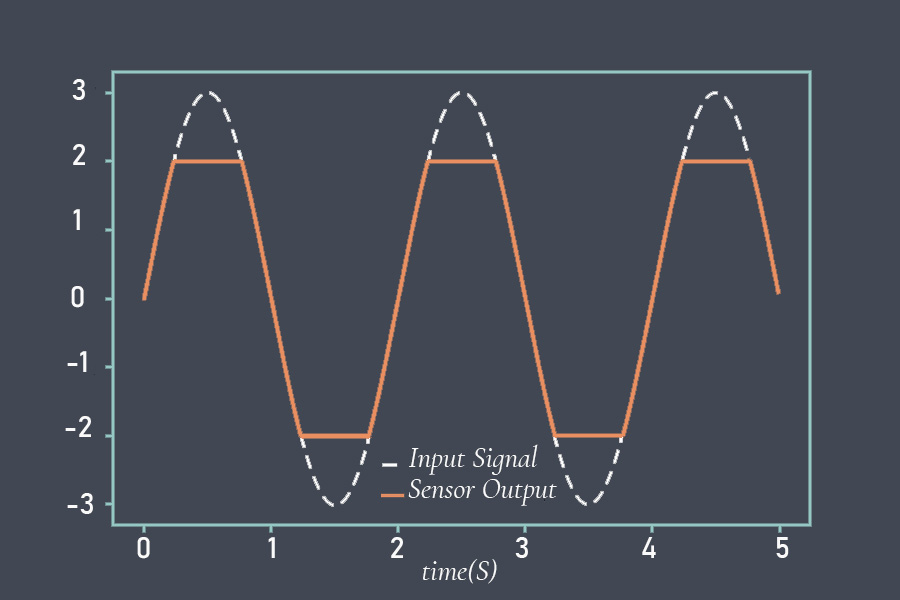
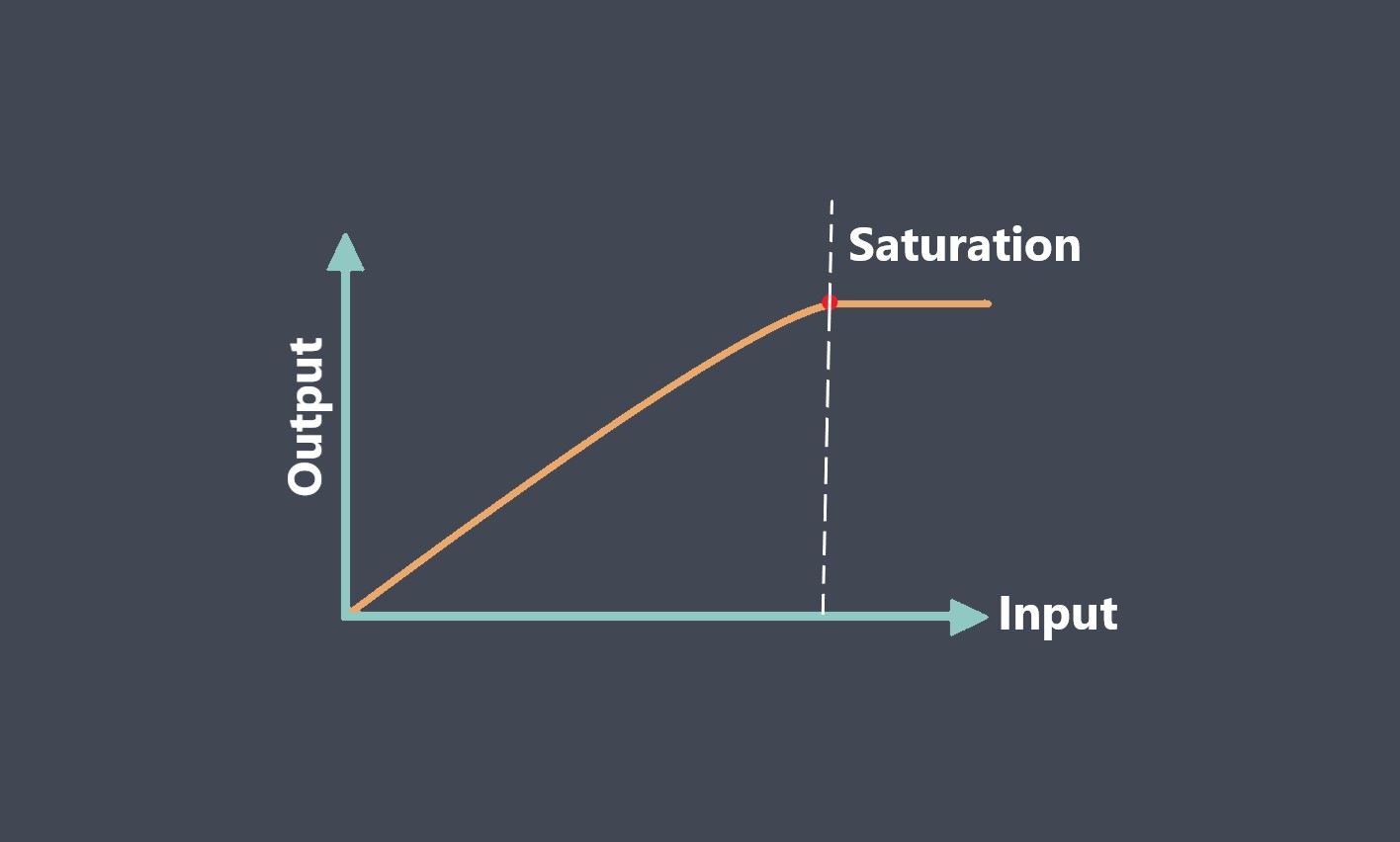
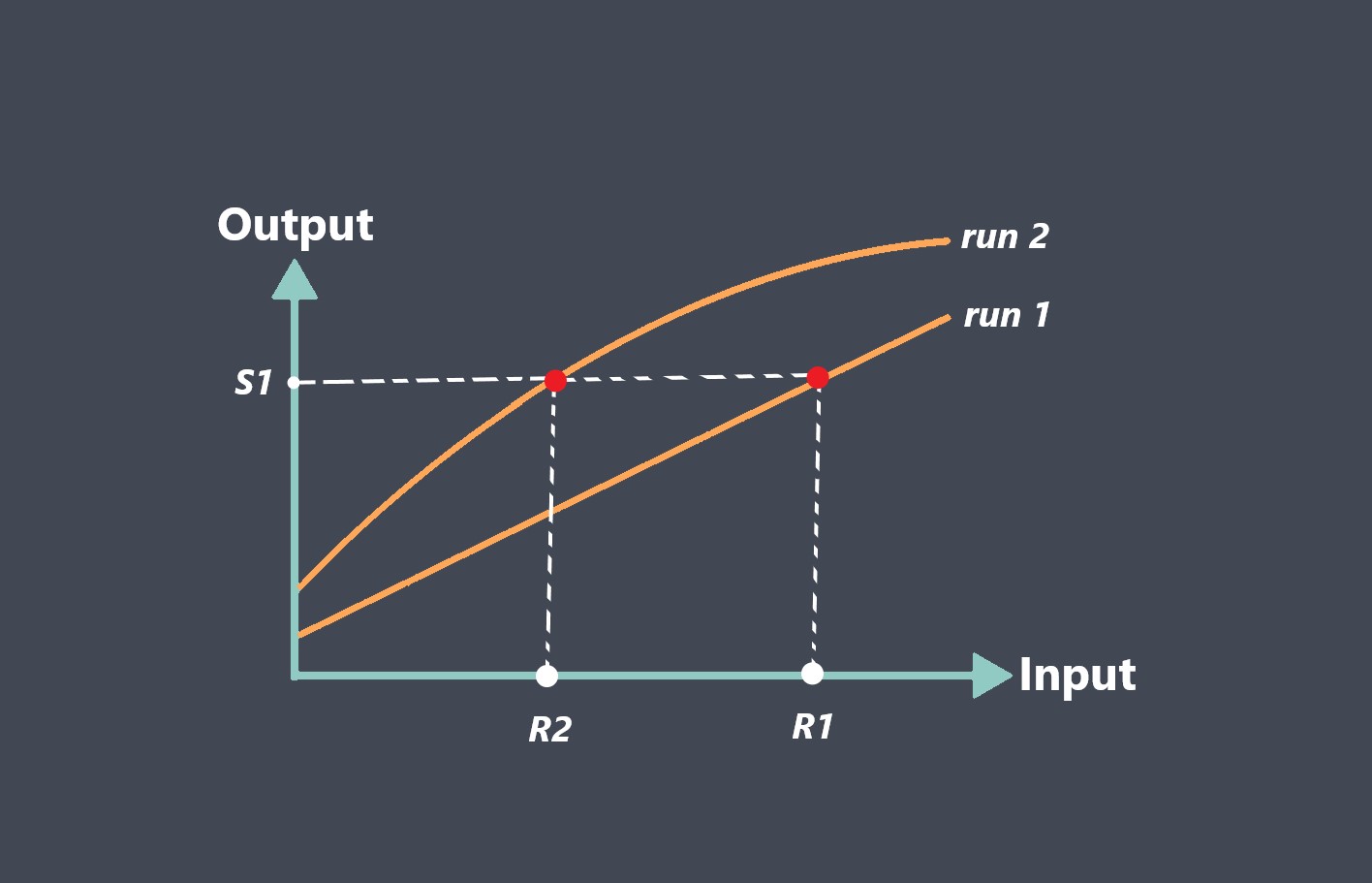
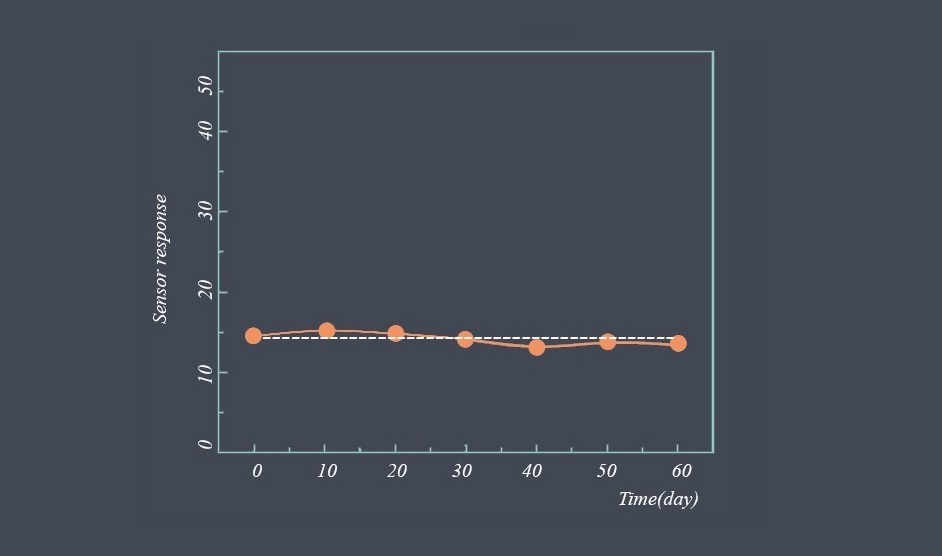
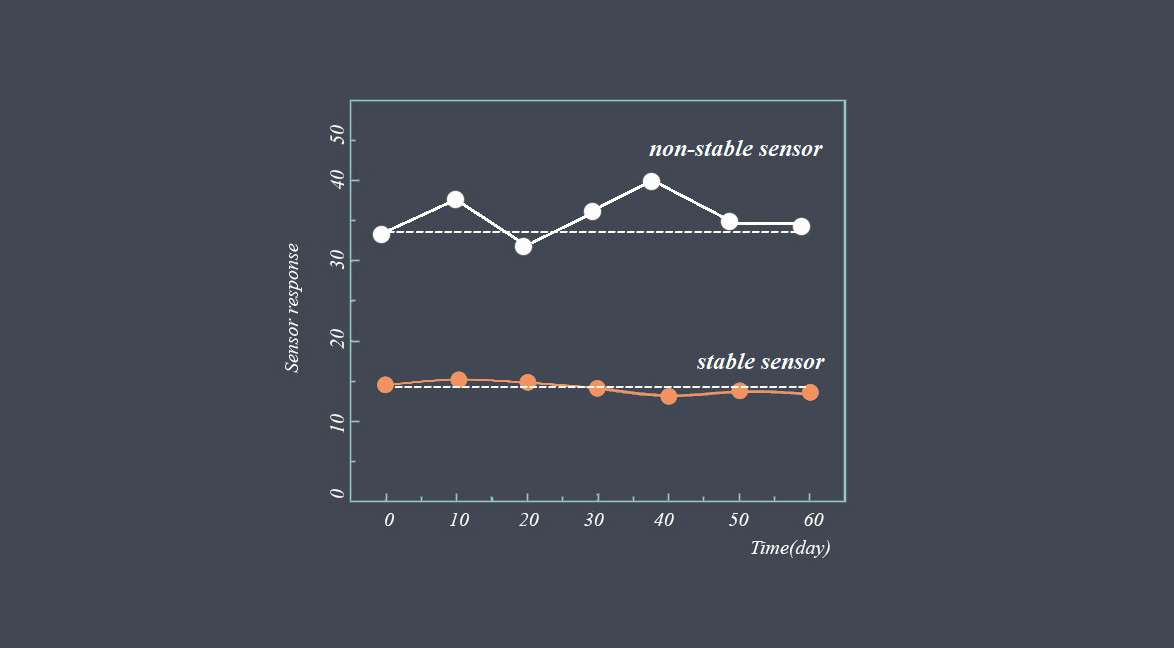
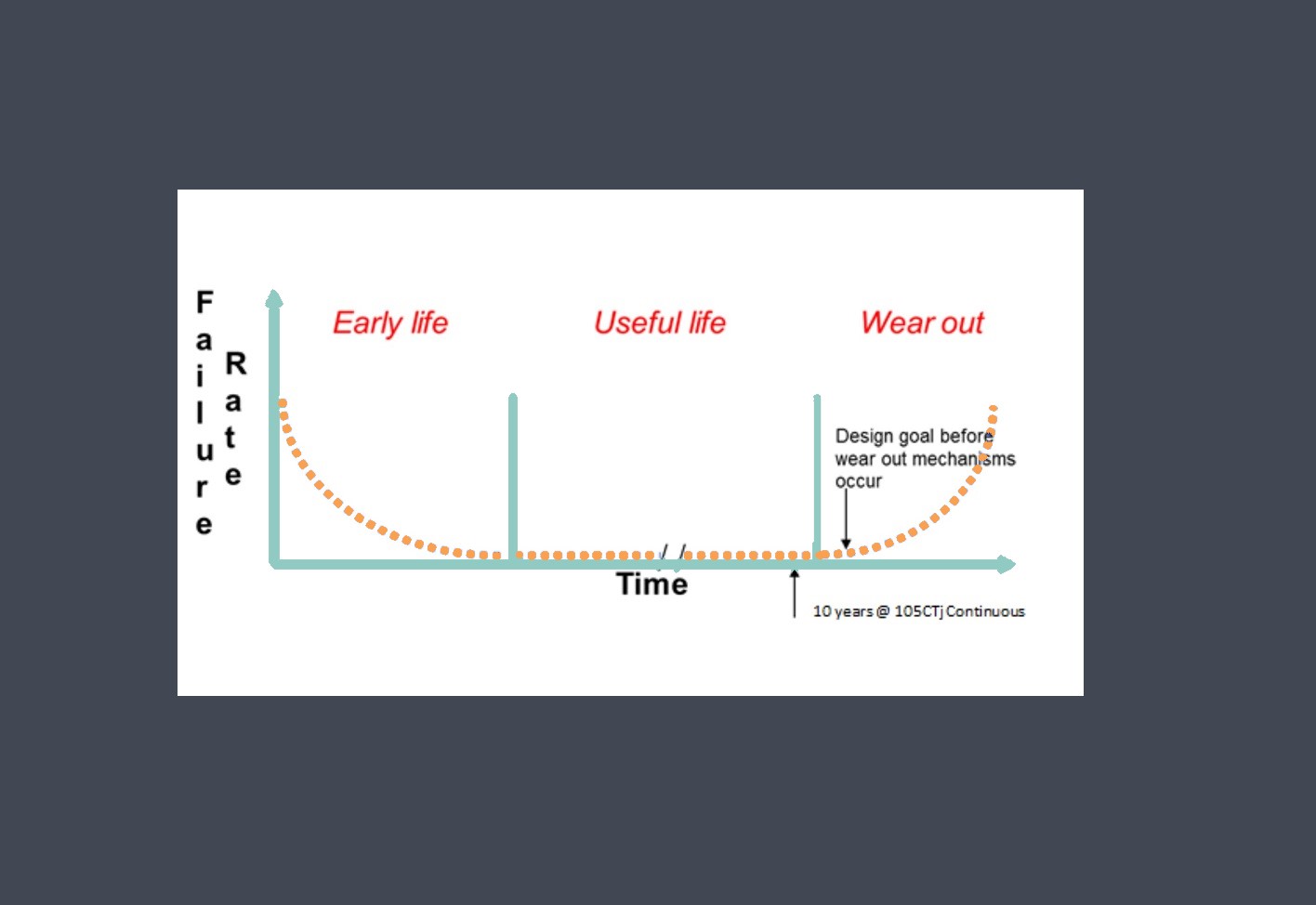
Operating lifetime refers to the expected duration or lifespan of a sensor under normal operating conditions. It indicates how long the sensor is expected to perform reliably and accurately before experiencing degradation or failure.
The operating lifetime of a sensor refers to the duration for which the sensor can consistently and reliably perform its intended function. It represents the period during which the sensor’s performance remains within acceptable specifications or tolerances.
Factors affect sensor operating lifetime
The operating lifetime of a sensor can vary depending on several factors:
Quality and manufacturing
The quality of the sensor and the manufacturing process used can greatly impact its operating lifetime. Sensors that are well-designed, built with high-quality materials, and manufactured using robust processes tend to have longer lifetimes.
Environmental conditions
The operating environment in which the sensor is deployed plays a significant role in its lifetime. Factors such as temperature variations, humidity, corrosive substances, vibrations, shock, and exposure to dust or contaminants can affect the longevity of a sensor. Some sensors are specifically designed for harsh environments and have extended operating lifetimes compared to others.
Usage patterns
The frequency and duration of sensor usage can influence its operating lifetime. Sensors that are subjected to continuous operation or frequent cycling may experience more wear and tear, potentially leading to a shorter lifespan. On the other hand, sensors used intermittently or for shorter durations may last longer.
Maintenance and care
Proper maintenance and care can contribute to extending the operating lifetime of a sensor. Regular cleaning, calibration, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines for handling and storage can help ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Stress and workload
Sensors that are subjected to high levels of stress or heavy workloads may have shorter lifetimes. For example, sensors used in demanding industrial applications or high-impact environments may experience accelerated wear and degradation.
It’s important to note that the operating lifetime of a sensor is typically specified by the manufacturer based on their testing and evaluation procedures. This specification provides an estimate of the sensor’s expected lifespan under normal operating conditions.
How to maximize sensor operating lifetime
To maximize the operating lifetime of a sensor, it is advisable to choose a sensor that is suitable for the specific application requirements, follow proper installation and usage guidelines, regularly inspect and maintain the sensor.
Here are some key practices to follow to maximize sensor operating lifetime:
Proper installation
Ensure that the sensor is installed correctly according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. This includes proper alignment, mounting, and connection. Avoid excessive strain on the sensor and use suitable protection, such as housings or covers, to shield it from environmental factors like dust, moisture, or extreme temperatures.
Regular maintenance
Implement a scheduled maintenance program for the sensors to keep them in optimal condition. This includes cleaning, inspection, and calibration. Cleaning should be done using appropriate methods and materials to avoid damaging the sensor.
Calibration
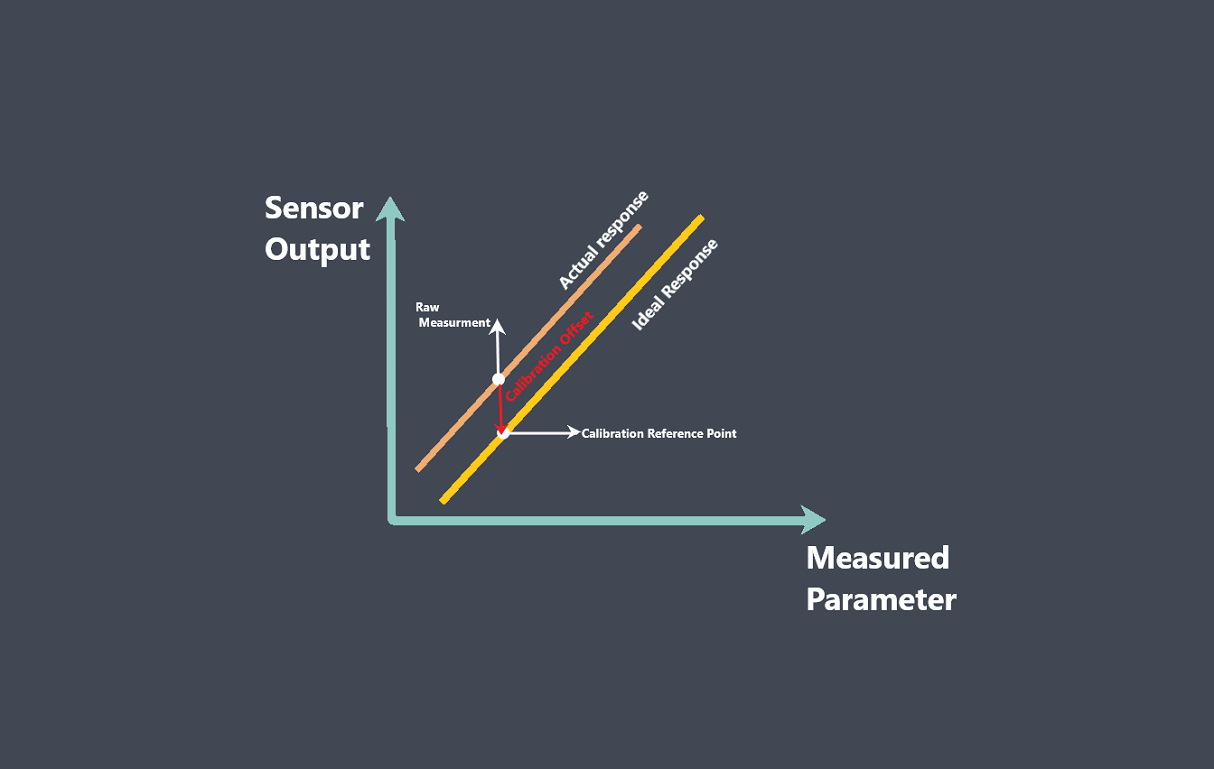
Regularly calibrate the sensors to ensure accurate and reliable measurements. Calibration helps in detecting any drift or deviation in sensor readings, allowing for adjustments or replacements as needed. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for calibration frequency and procedures.
Monitoring operating conditions
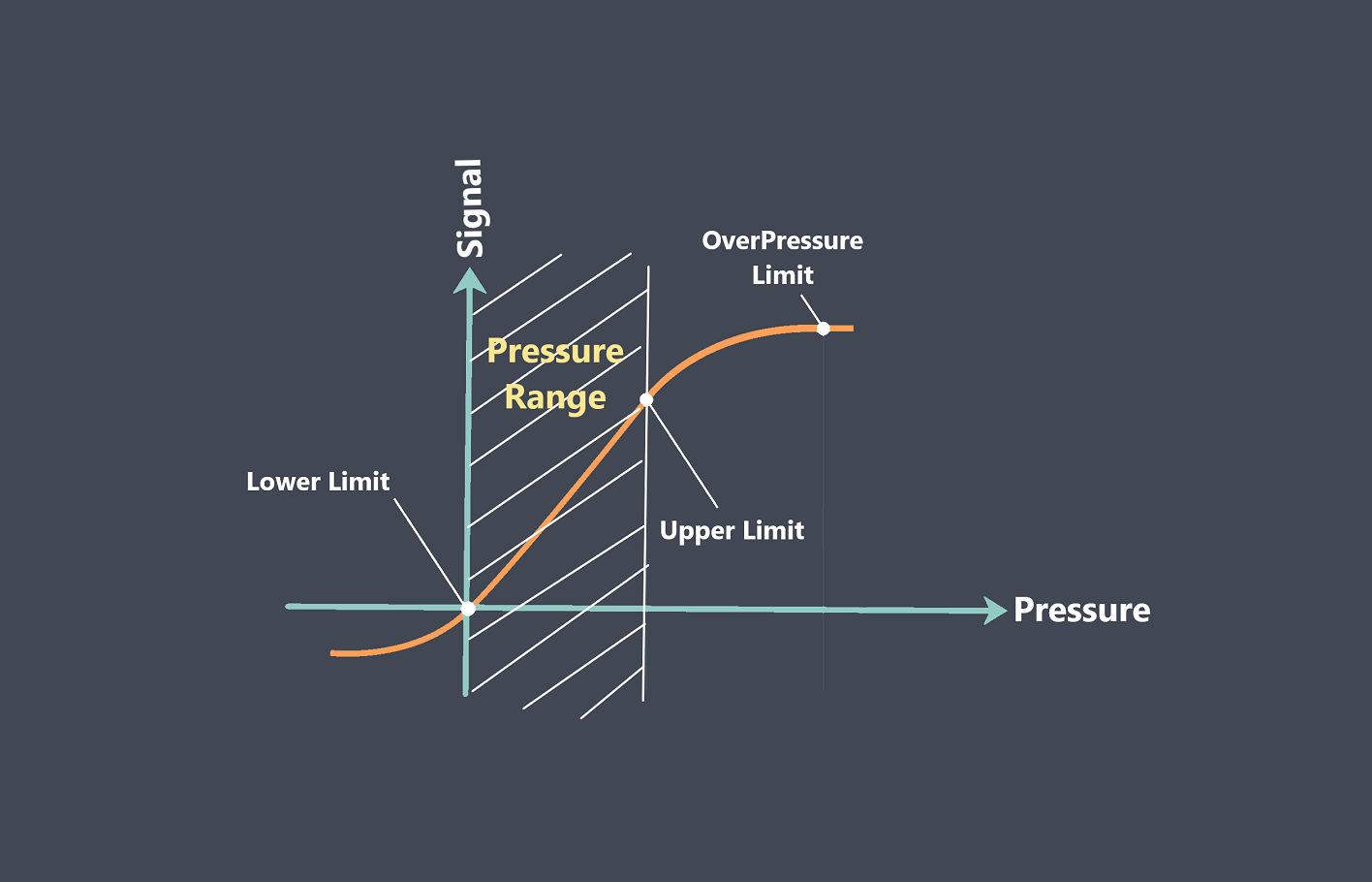
Sensors have specific operating conditions, such as temperature range, humidity levels, or pressure limits. Monitor these parameters and ensure that the sensors are operating within their specified ranges. Exceeding these limits can shorten the sensor’s lifespan.
Avoid overloading or straining
Do not subject the sensors to excessive force, vibration, or overload. This can cause premature wear and damage to the sensor components, leading to reduced operating lifetime. Consider using protective measures, such as shock absorbers or buffers, if the sensor is exposed to high impact or vibration.
Quality sensors
Invest in sensors from reputable manufacturers known for their quality and durability. High-quality sensors are designed and manufactured to withstand harsh conditions and provide longer operating lifetimes. Consider factors like reliability, certifications, and warranty when choosing sensors.
Continuous monitoring and analysis
Implement a system to monitor and analyze sensor data continuously. This allows for early identification of any abnormalities or deviations in readings, enabling timely action to prevent further damage or failure. Regular data analysis can aid in proactive maintenance and optimize sensor performance.
By following these best practices, you can significantly maximize sensor operating lifetime, resulting in improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and cost savings in the long run.