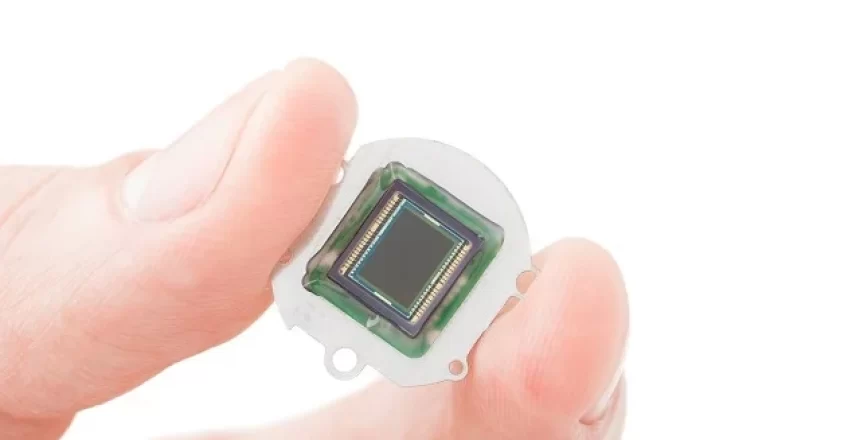
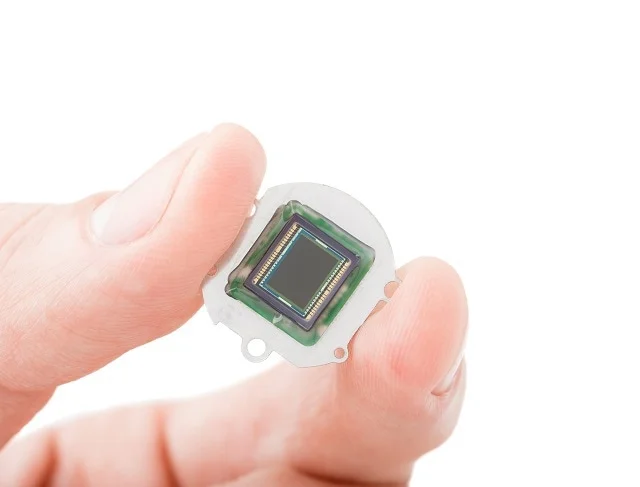
These sensors convert optical images into electrical signals, and are commonly used in digital cameras, surveillance systems, and machine vision.
Image sensors are electronic devices that capture and convert optical images into digital signals. They are used in a wide range of imaging devices, including digital cameras, smartphones, surveillance cameras, and scientific equipment.
Image sensors types
There are two main types of image sensors: charge-coupled devices (CCD) and complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) sensors. Both types function by converting light photons into an electrical signal, but they employ different technologies to do so.
charge coupled devices (CCD)
Charge-coupled devices (CCD) are a type of image sensor that convert light photons into electrical charge. They consist of an array of pixels, where each pixel is capable of accumulating and transferring charge.

The basic working principle of charge-coupled devices (CCD)
It involves three main stages: exposure, transfer, and readout.
During the exposure stage, the pixels collect and store electrical charge proportional to the intensity of the incident light. This charge is trapped within potential wells located beneath each pixel.
After the exposure stage, the charge is transferred from pixel to pixel within the CCD chip using a series of specialized registers. This charge transfer is achieved by applying clock signals that create electric fields, allowing the charge packets to move across the chip. The most common transfer technique is known as a bucket-brigade shift register.

Once the charge has been transferred to the output register, it can be read out sequentially from each pixel. This is accomplished by converting the accumulated charge into a voltage signal. The voltage signal can then be further amplified and digitized for processing or storage.
charge coupled devices (CCD) advantages and disadvantages:
CCD sensors are known for their excellent image quality, high sensitivity, and low noise characteristics. They offer good dynamic range, meaning they can capture both bright and dim details in a scene. CCDs are particularly useful in applications that require accurate color reproduction, such as professional cameras and scientific imaging systems.
However, CCDs do have some drawbacks. They tend to consume more power and generate more heat compared to other types of image sensors like CMOS. CCD sensors also have a slower readout speed, making them less suitable for applications that require fast continuous shooting or video recording.
complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) sensors
Complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) sensors are a type of image sensor widely used in digital cameras, smartphones, and other imaging devices. They are known for their low power consumption, fast readout speeds, and the ability to integrate additional functionalities on the same chip.

CMOS sensors work on the principle of converting light photons into electrical charge, similar to CCDs.
However, their underlying technology and operational characteristics differ significantly.
In CMOS sensors, each pixel has its own amplifier, which allows for parallel readout of the pixel data.
This parallel readout capability leads to faster overall readout speeds compared to CCDs.

complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) sensors advantages:
- One of the key advantages of CMOS sensors is their low power consumption. Unlike CCDs, which require high voltage to transfer charge across the chip, CMOS sensors operate at lower voltages, resulting in reduced power consumption. This makes CMOS sensors ideal for battery-powered devices like smartphones.
- Another advantage of CMOS sensors is their ability to integrate additional functionalities on the same chip. Because CMOS sensors use active transistors in each pixel, it is easier to incorporate features such as on-chip analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), image processing algorithms, and even wireless communication capabilities. This integration can simplify the overall system design and reduce the number of external components required.
- Furthermore, CMOS sensors offer flexibility in terms of pixel design. CMOS pixels can be made smaller, which enables higher resolution images. Additionally, CMOS sensors can implement various pixel architectures, such as backside-illuminated (BSI) pixels, which improve light sensitivity and allow for better image quality, especially in low-light conditions.
complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) sensors limitations:
While CMOS sensors have numerous advantages, they do have some limitations. Compared to CCD sensors, CMOS sensors generally exhibit higher noise levels and lower dynamic range. However, significant advancements have been made in reducing these limitations, and modern CMOS sensors now offer competitive image quality.
Overall, the adoption of CMOS sensors has grown rapidly due to their low power consumption, fast readout speeds, integration capabilities, and improved performance. They have become the dominant image sensor technology in most consumer electronics devices, playing a crucial role in advancing digital imaging technology.
Complementary metal oxide semiconductor sensors VS charge-coupled devices
Both CCD and CMOS sensors have their own advantages and are suitable for different applications. CCD sensors are commonly used in professional cameras and applications where image quality is paramount. CMOS sensors, on the other hand, are widely used in consumer electronics like smartphones and digital cameras due to their lower cost, faster processing capabilities, and ability to integrate additional functionalities on the sensor chip.

In recent years, CMOS technology has made significant advancements, closing the gap in image quality compared to CCD sensors. As a result, many manufacturers have shifted towards using CMOS sensors in their imaging devices due to the benefits they offer in terms of efficiency, cost, and versatility.