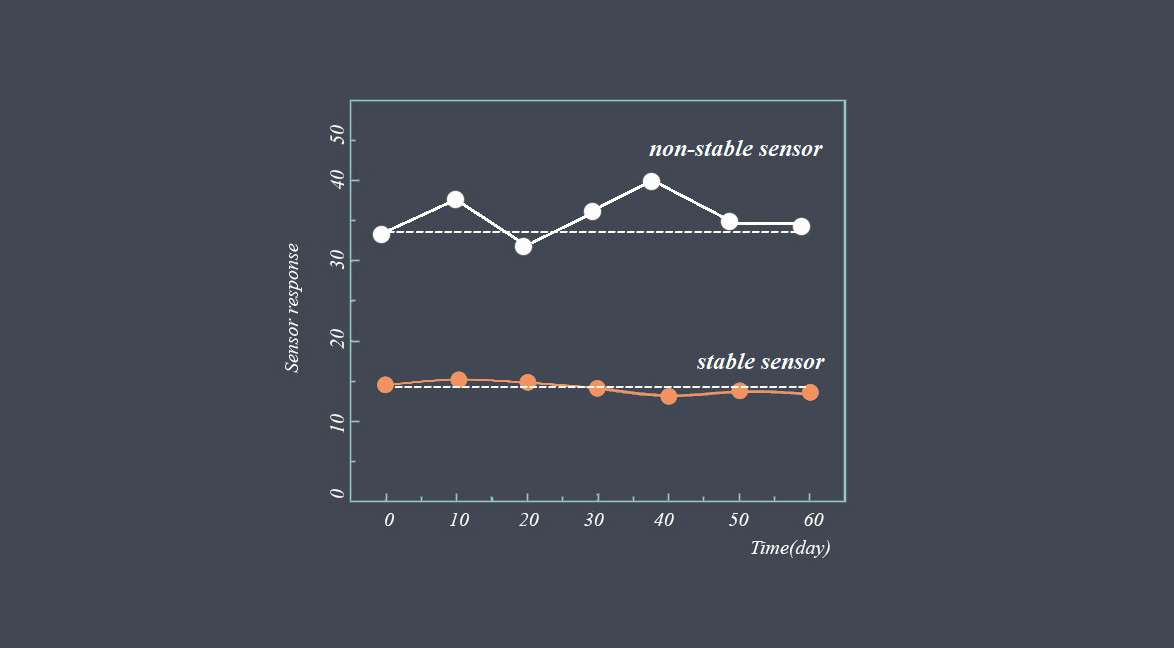
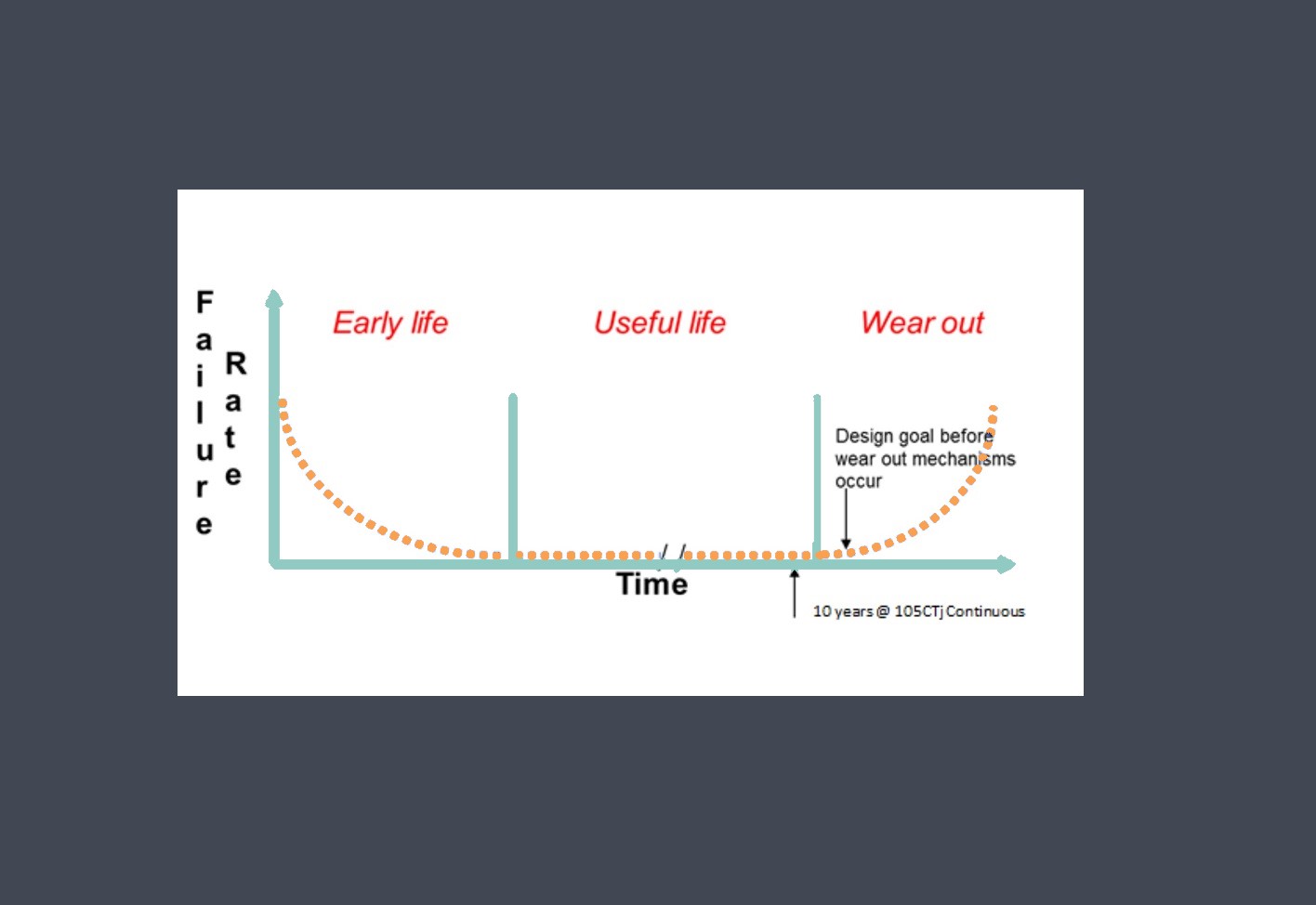
Stability refers to the ability of a sensor to maintain its performance over time. It is a measure of the sensor’s consistency and reliability in providing accurate measurements under constant operating conditions. A stable sensor will exhibit minimal changes in its output signal over an extended period.
Sensor stability one of the sensor abilities to maintain its accuracy and precision over time, as well as under varying environmental conditions. In other words, a stable sensor will consistently provide reliable and accurate measurements even after extended use and exposure to different environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and vibration.
This is an important consideration in many applications where accurate and reliable measurements are critical, such as in industrial process control, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnostics. If a sensor is not stable, it can lead to inaccurate readings, which can result in faulty decisions or actions.
Factors affect sensor stability
There are several factors that can affect sensor stability. Here are some of the most common ones:
Environmental conditions
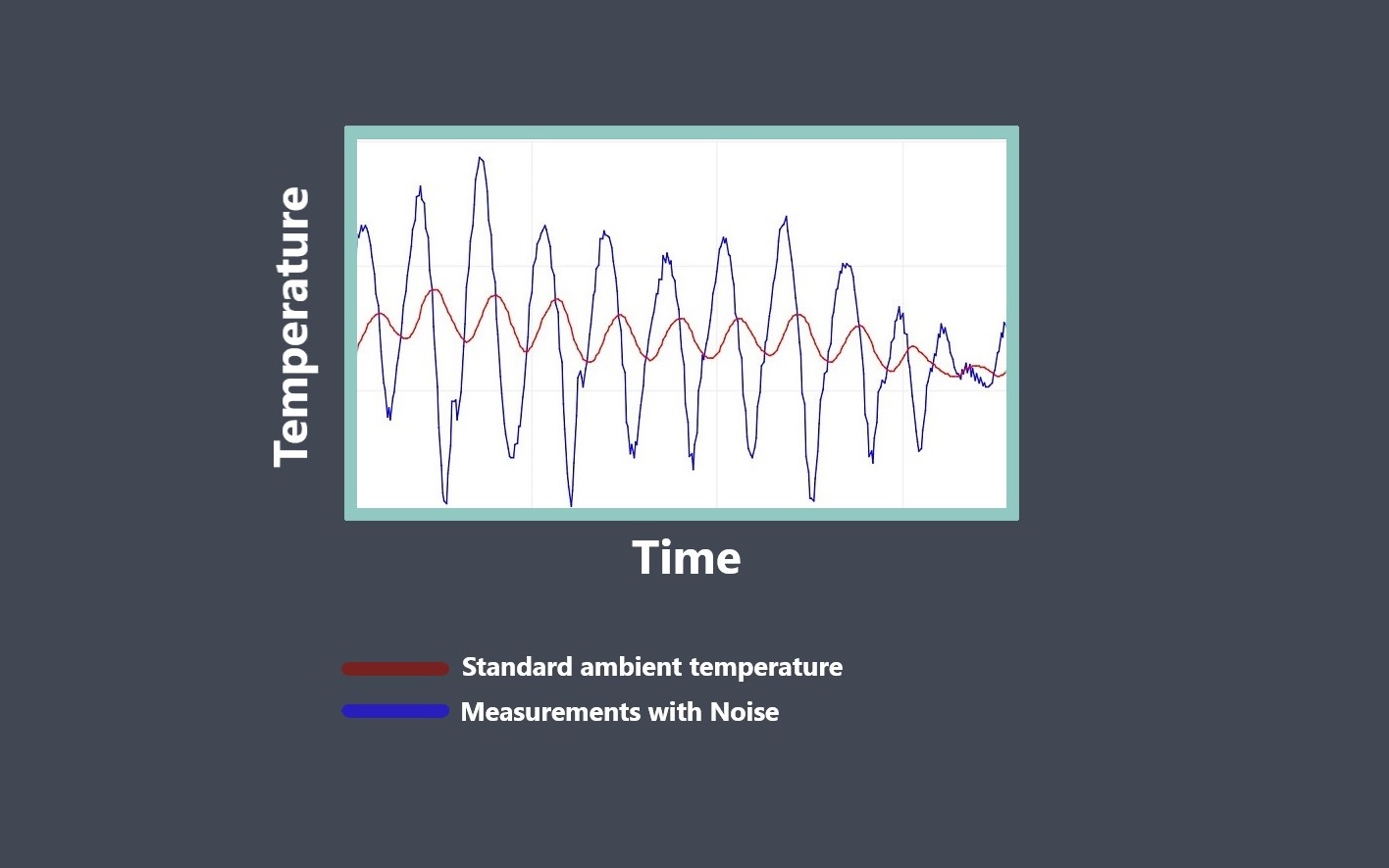
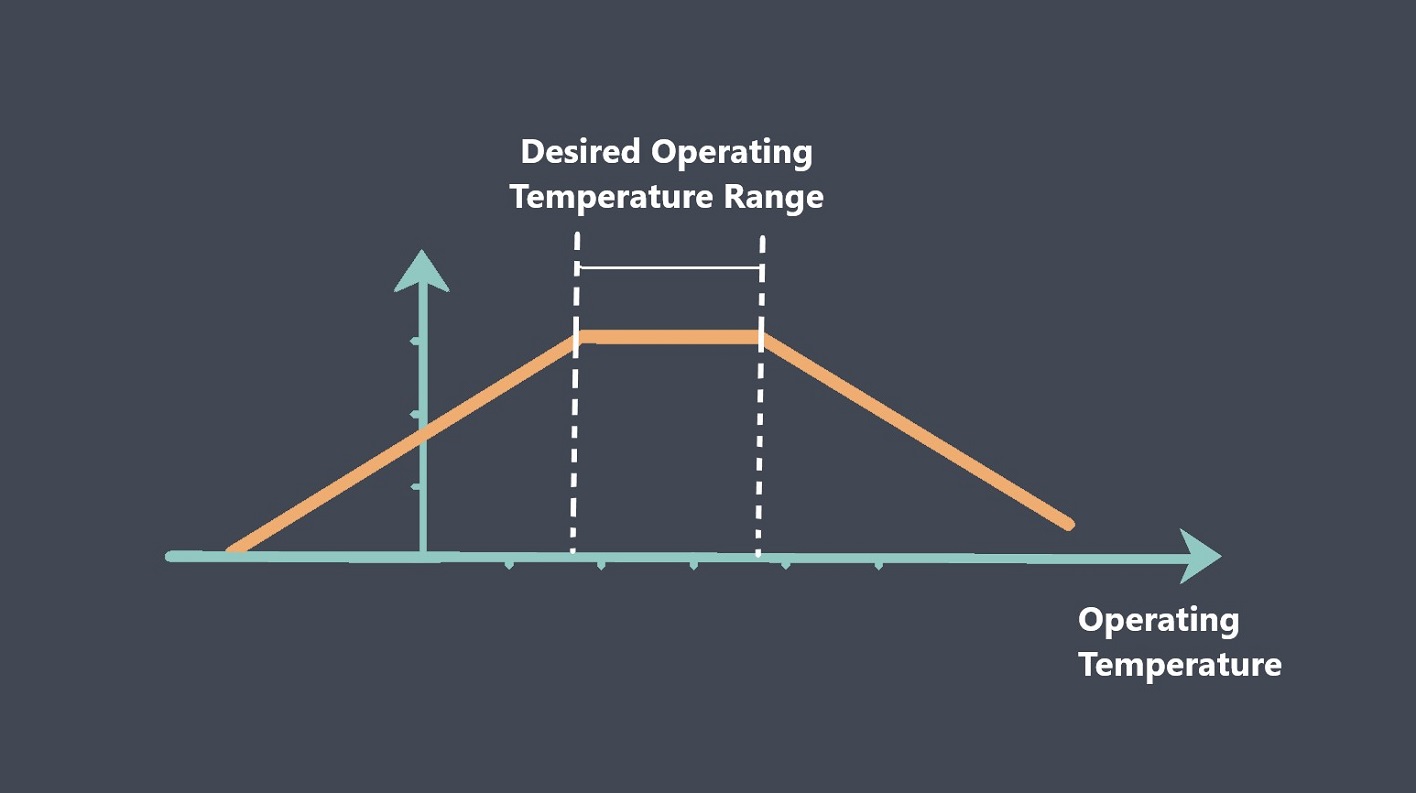
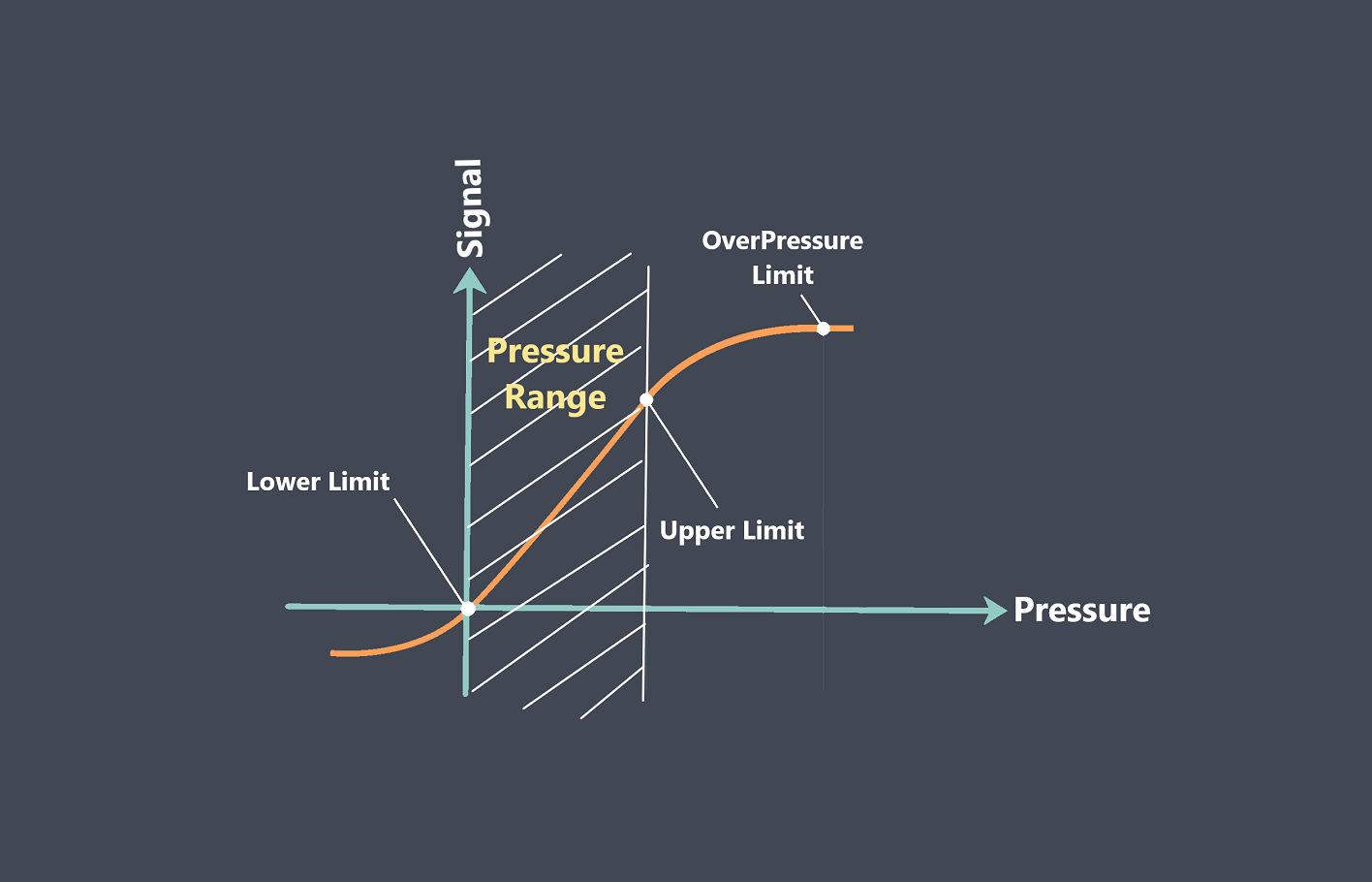
The environmental conditions to which the sensor is exposed can affect its stability. Factors like temperature, humidity, vibration, and electromagnetic interference can all impact the accuracy and reliability of the sensor. Manufacturers typically test sensors under a range of environmental conditions to determine their performance limits and to develop appropriate compensation techniques.
Physical design and construction
The physical design and construction of the sensor can also affect its stability. The materials used in the sensor can impact its stability over time, particularly when exposed to environmental factors. The quality of the signal processing and amplification circuitry used in the sensor can also impact its stability.
Calibration
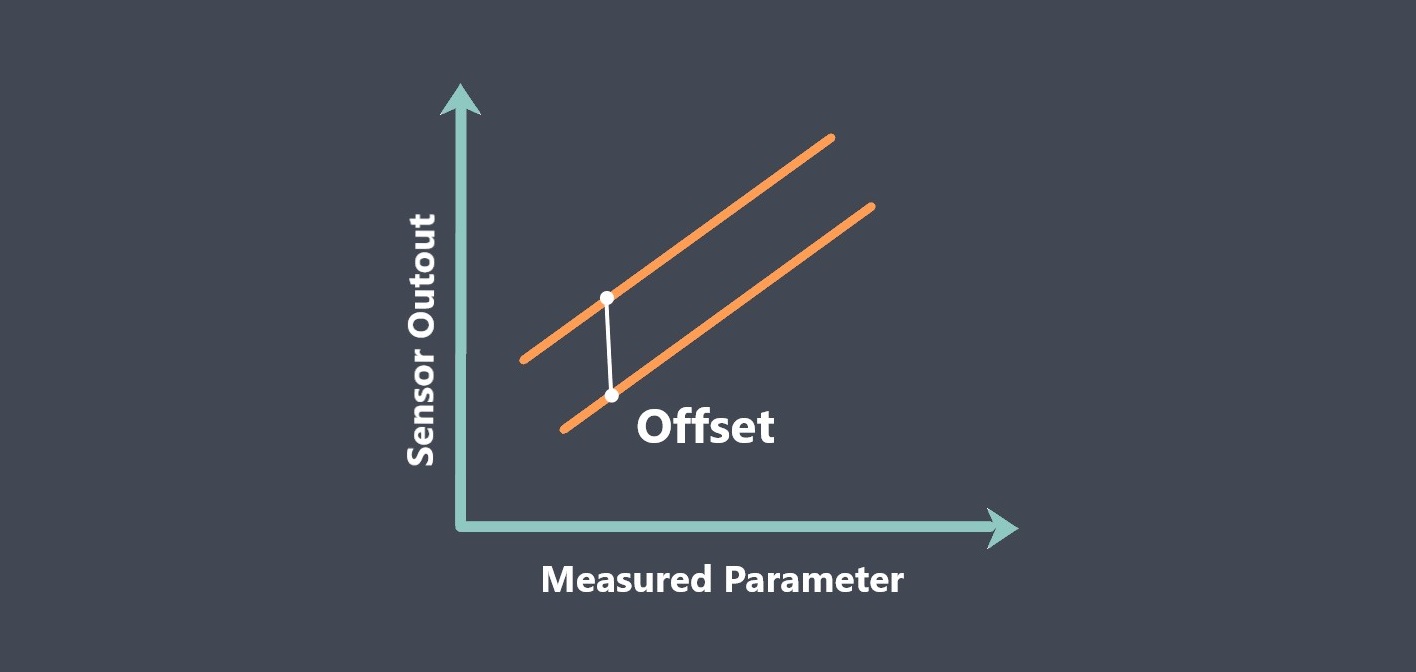
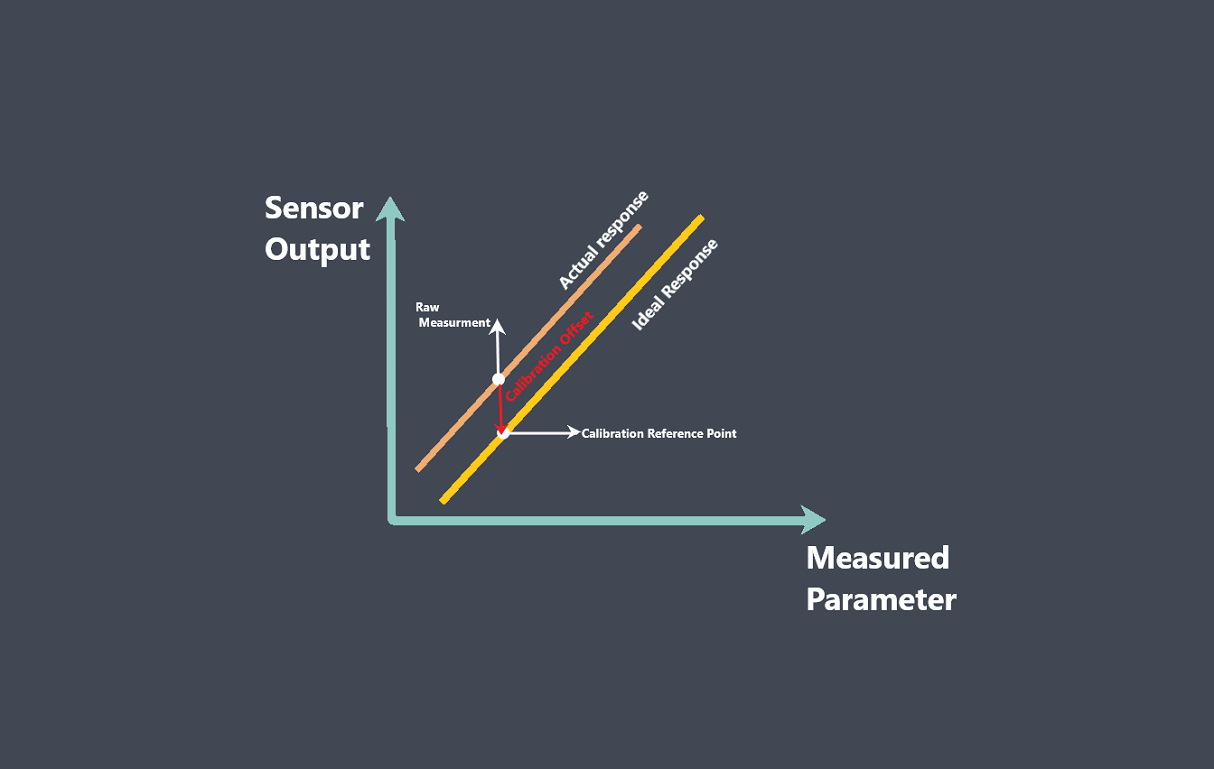
Calibration is a critical factor in maintaining sensor stability. Over time, the performance of a sensor can change due to factors like wear and tear, exposure to harsh environments, and aging. Regular calibration of the sensor can help to ensure that it is providing accurate and reliable measurements.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the sensor can help to prevent damage to the sensor and maintain its performance over time. This may involve cleaning the sensor, checking for wear and tear, and replacing worn or damaged components.
Electrical interference
Electrical interference from other devices or sources can also affect sensor stability. This can cause noise or other errors in the measurement signal, which can degrade the accuracy and stability of the sensor.
Physical damage
Physical damage to the sensor can also affect its stability. This can be caused by factors like impacts, drops, or other forms of mechanical stress. Physical damage can lead to changes in the sensor’s sensitivity or other factors affecting its performance.
Overall, maintaining sensor stability requires careful attention to environmental conditions, physical design and construction, calibration, maintenance, and protection from damage. By monitoring and addressing these factors, it is possible to maintain the accuracy and reliability of the sensor over time.
Some performance characteristics that are important for evaluating sensor stability
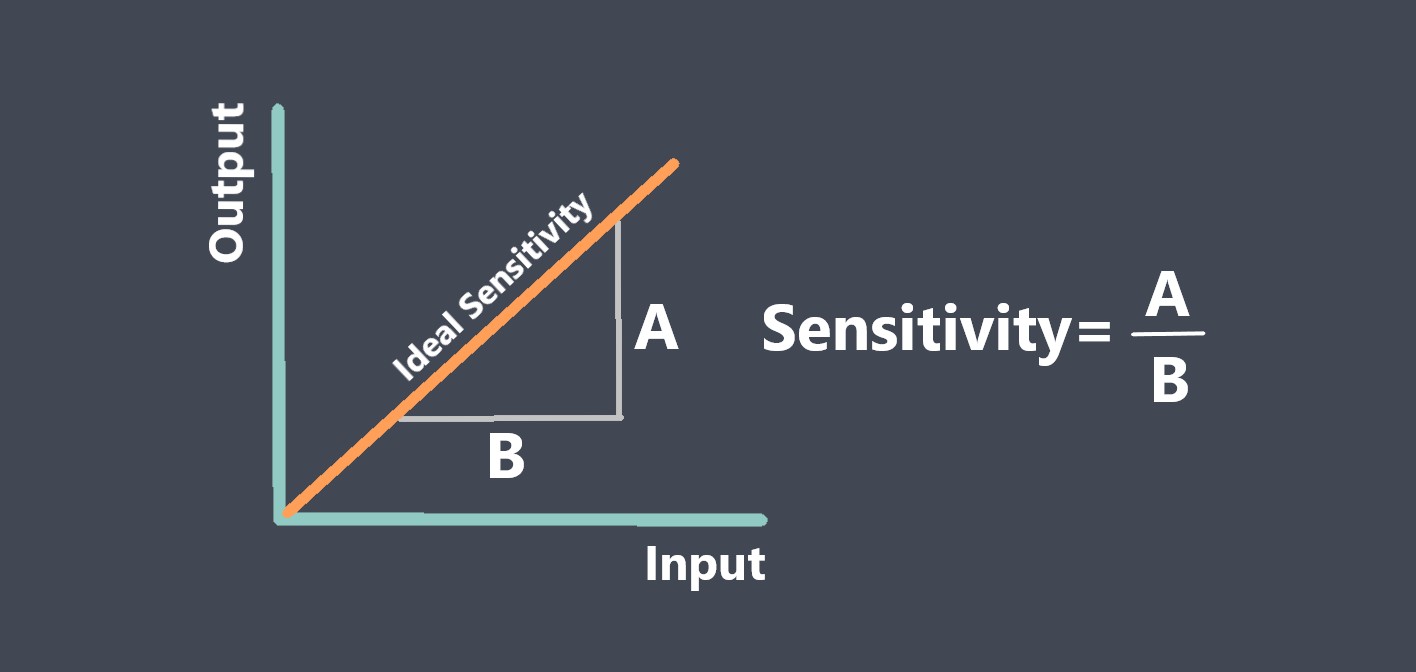
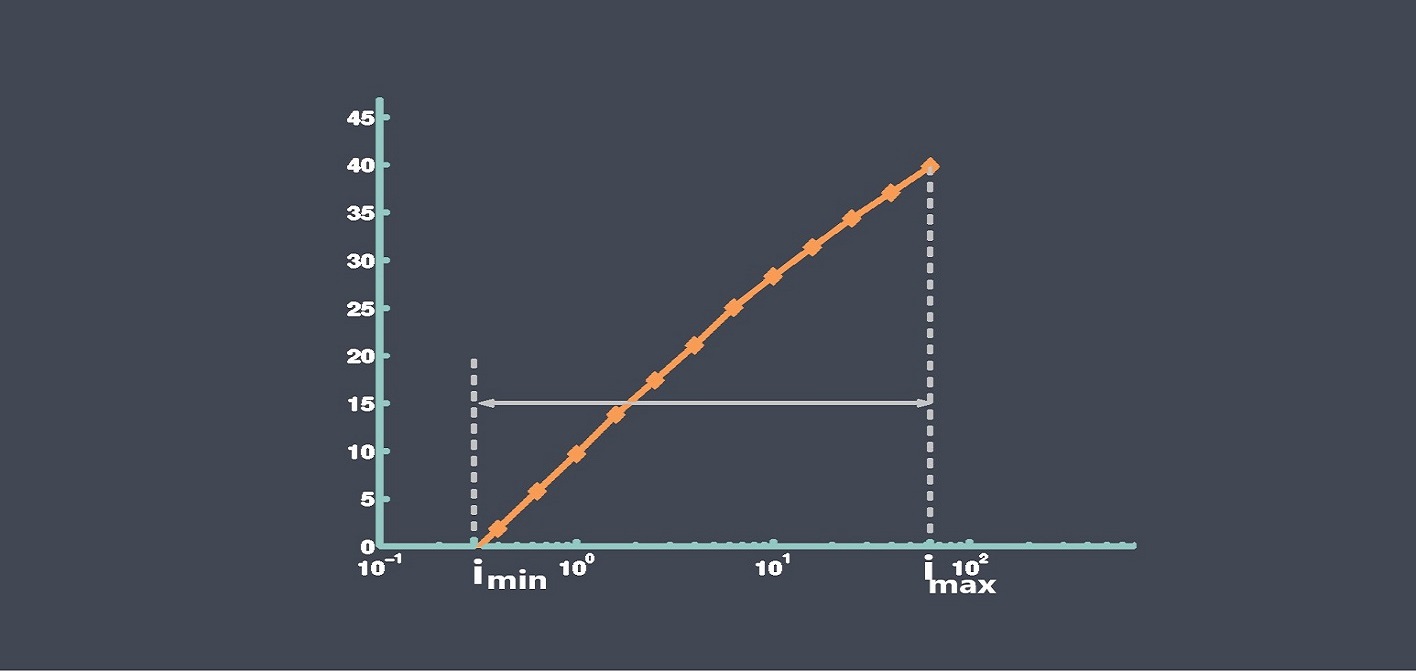
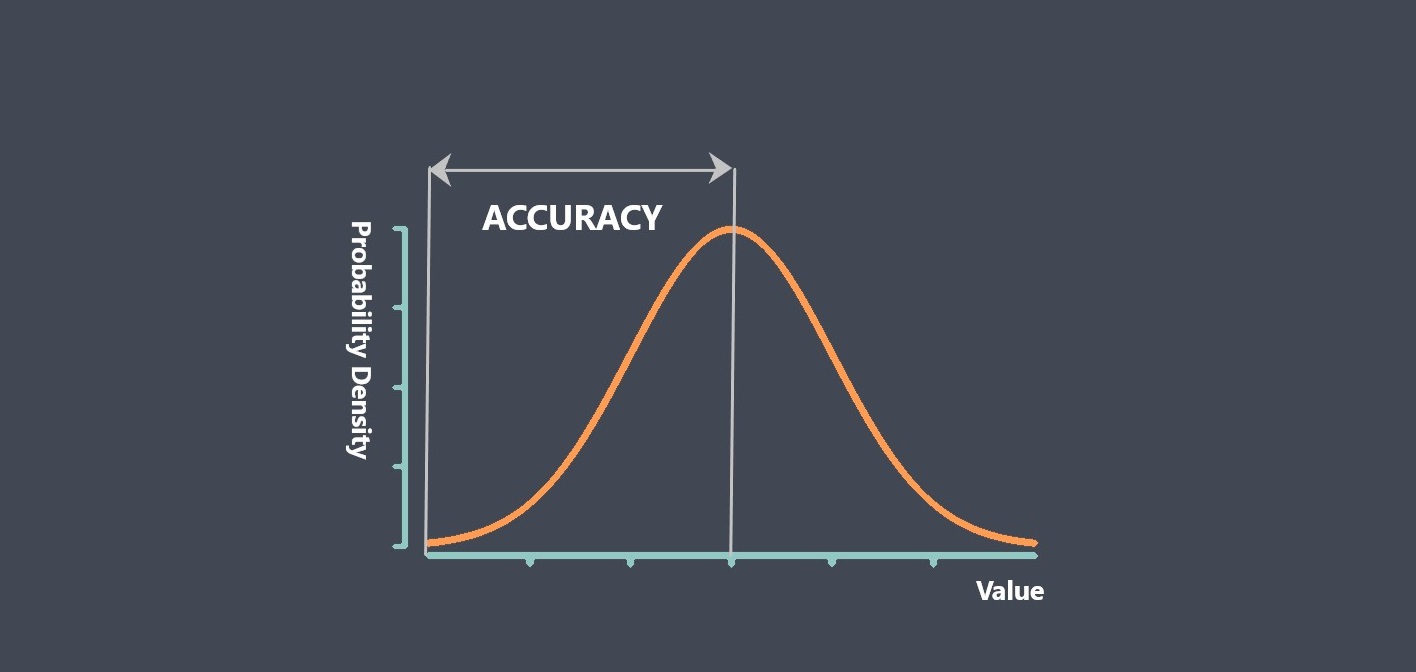
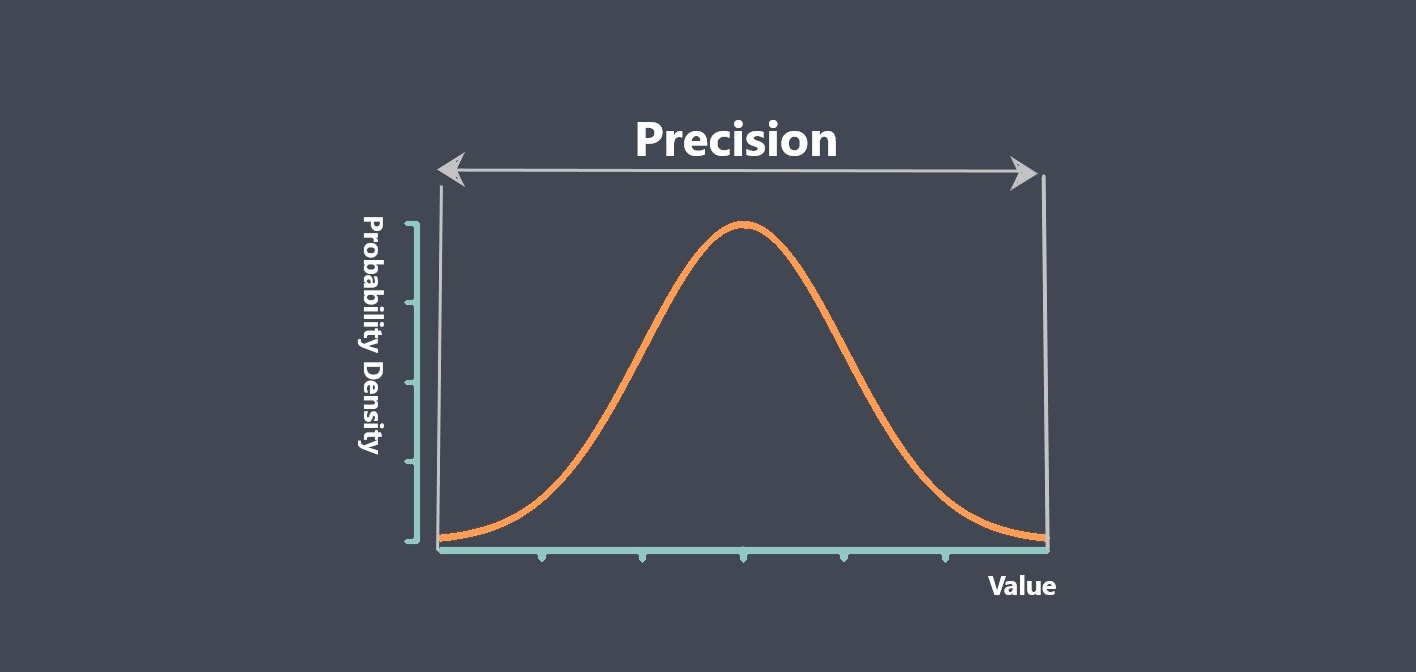
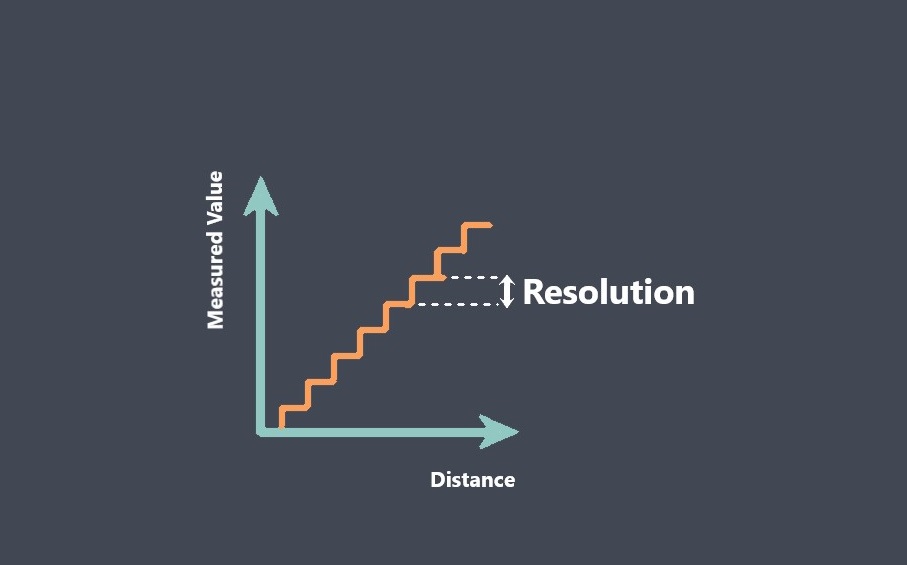
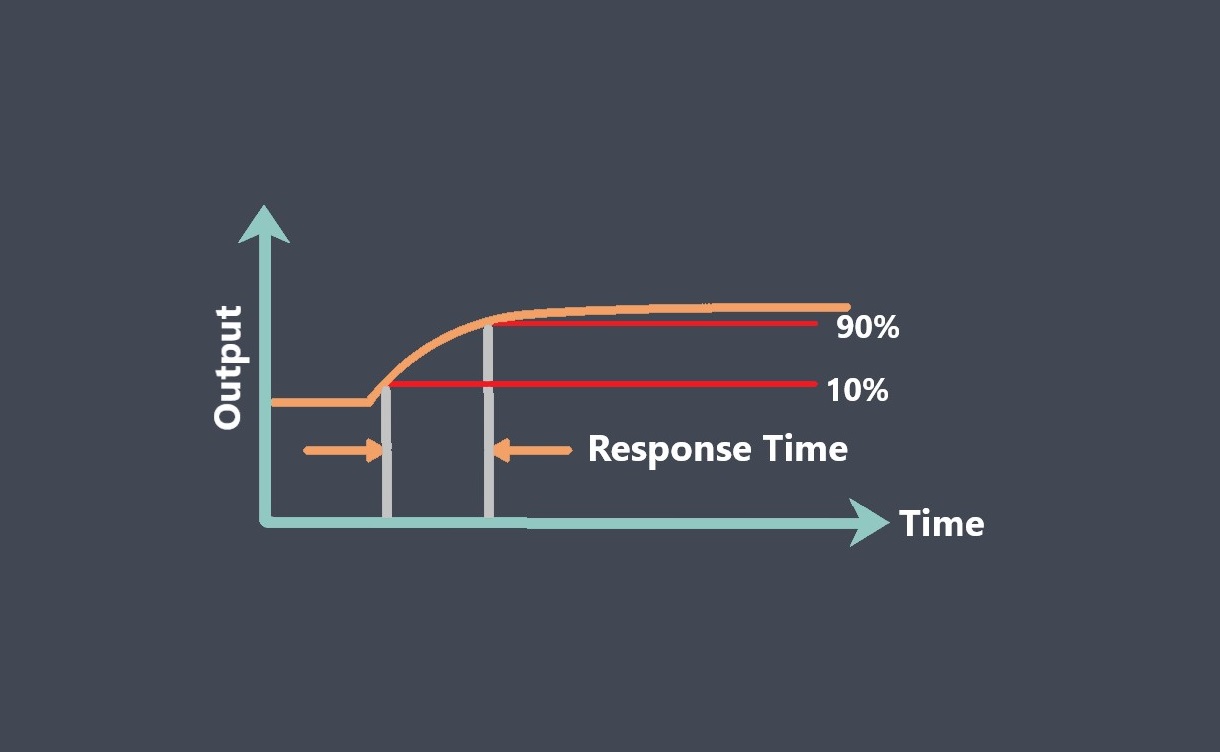
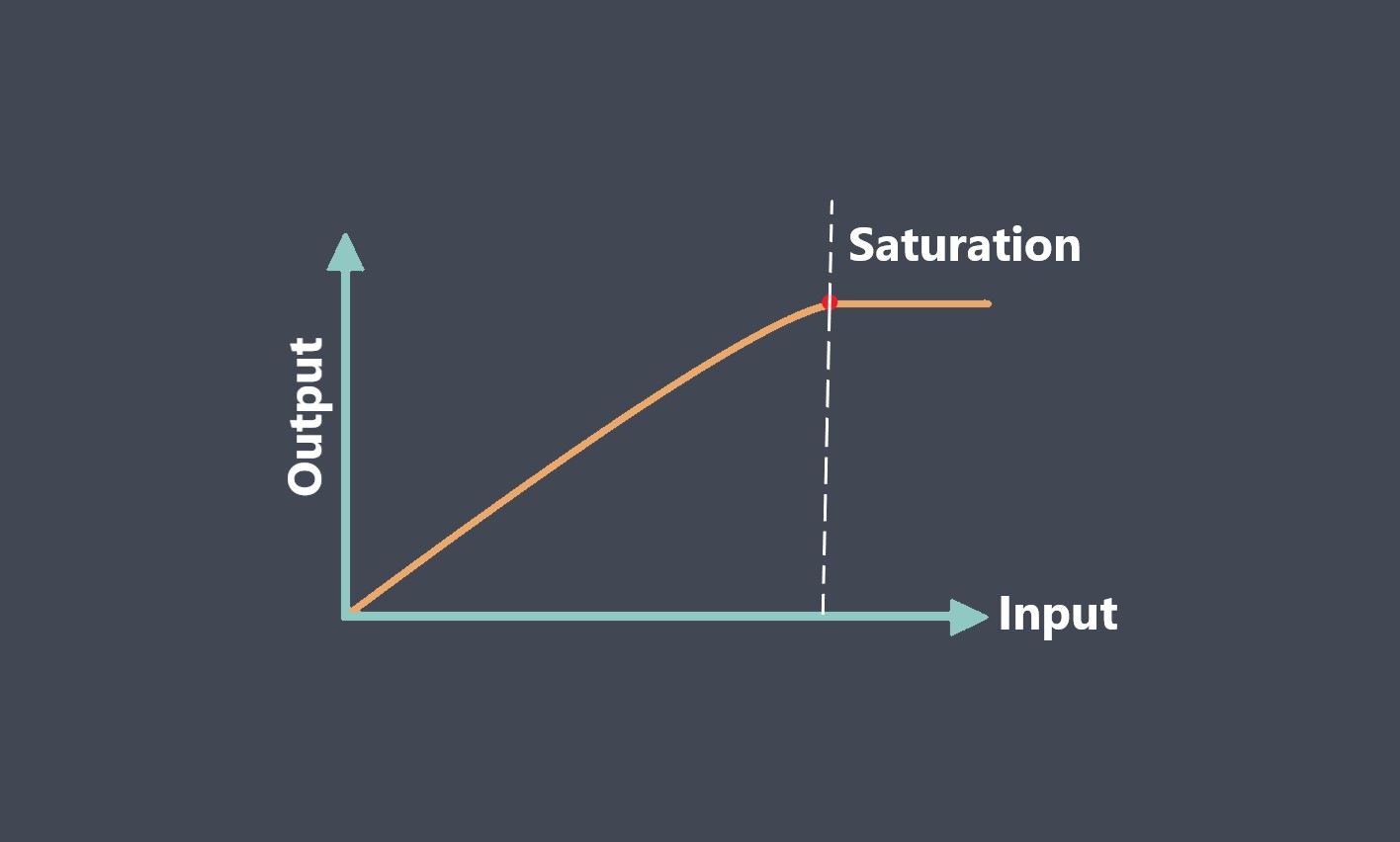
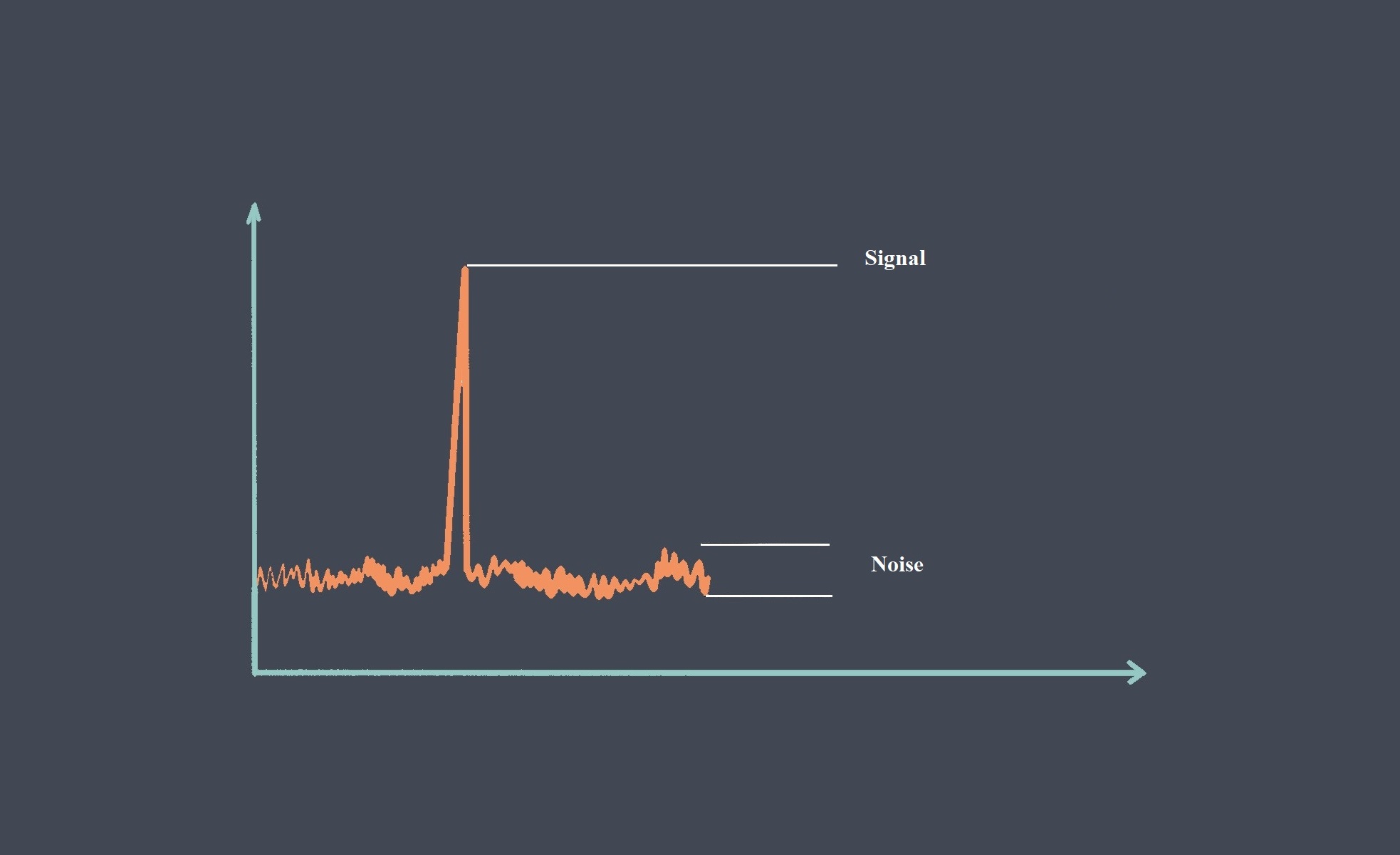
Some of sensor performance characteristics such as Repeatability, Linearity, Sensitivity, Drift, Noise, Response time… are important for evaluating sensor stability, because they can affect the accuracy, reliability, and consistency of the sensor’s output over time. we prepared some articles about all these parameters and you can read more about each of these parameters just by clicking on them.
By evaluating these characteristics, you can determine whether a sensor is stable and suitable for use in your application.
Non-stable sensor
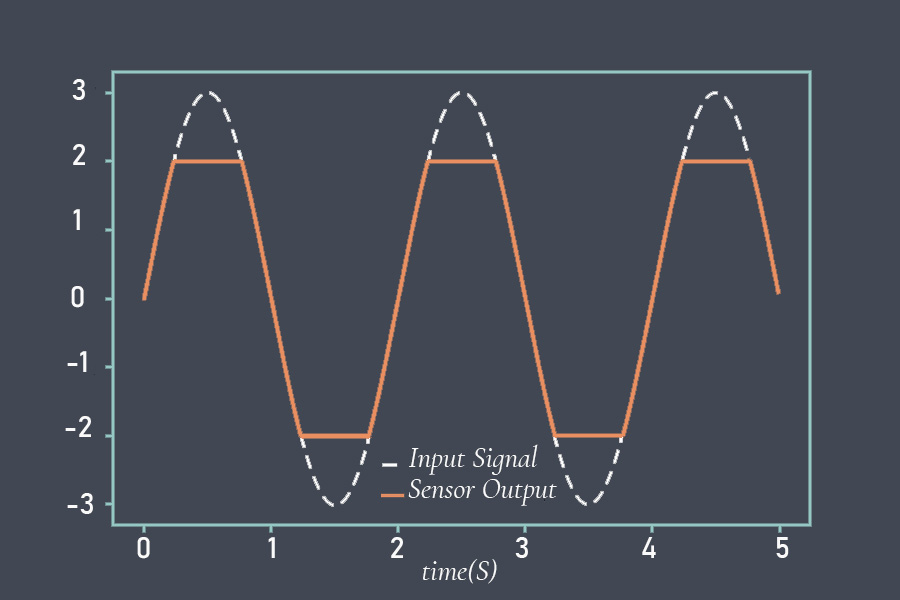
A non-stable sensor is one that does not maintain its accuracy and precision over time, and may produce inconsistent or unreliable readings. Non-stable sensors can be caused by a variety of factors, including environmental conditions, physical damage, calibration issues, electrical interference, and software issues.
Signs of a non-stable sensor may include inconsistent or erratic readings, drift in readings over time, reduced accuracy, increased noise or interference, changes in response time, or poor performance under varying environmental conditions.
Non-stable sensors can be problematic in many applications where accurate and reliable

measurements are critical, such as industrial process control, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnostics.
If you suspect that a sensor is non-stable, it may be necessary to perform more rigorous testing or consult with the manufacturer to diagnose the issue. In some cases, it may be necessary to replace the sensor to ensure accurate and reliable measurements.
How to understand if a sensor is stable or not?
There are several ways to understand if a sensor is stable. Here are some factors to consider:
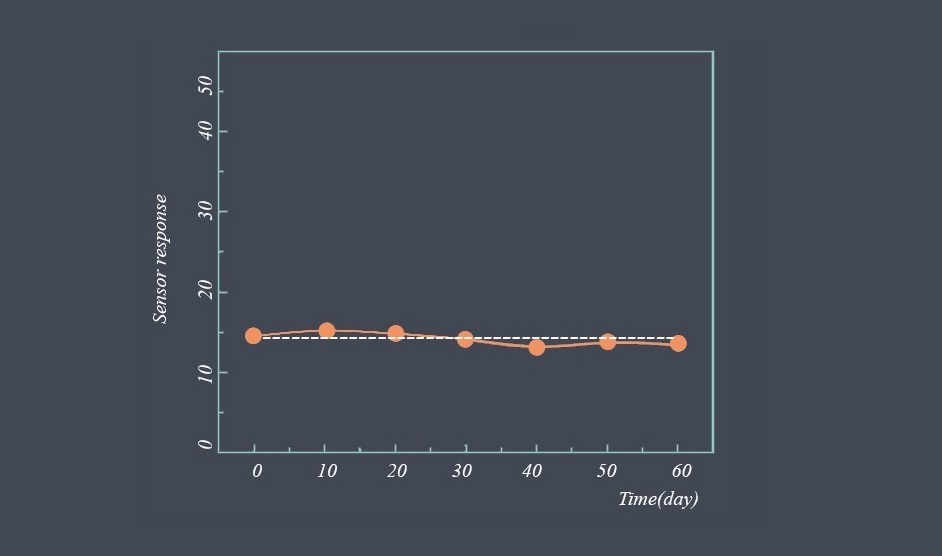
Consistency of readings
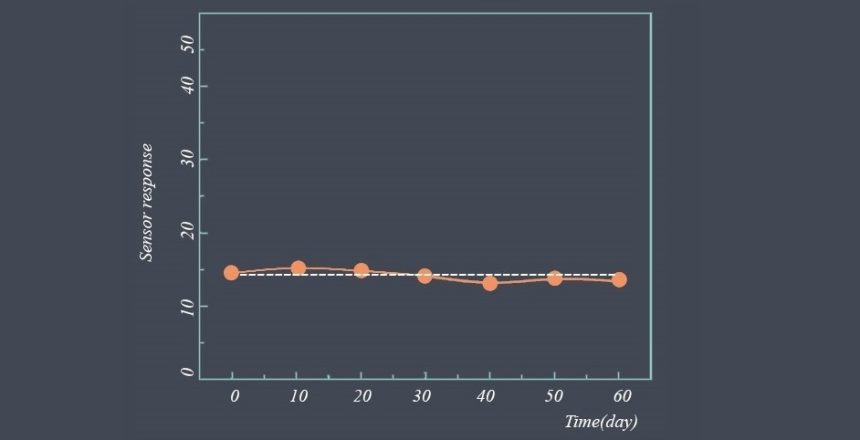
If a sensor is stable, it should provide consistent readings for a given input signal under similar environmental conditions. If the readings vary significantly between measurements, it could be an indication that the sensor’s stability has degraded.
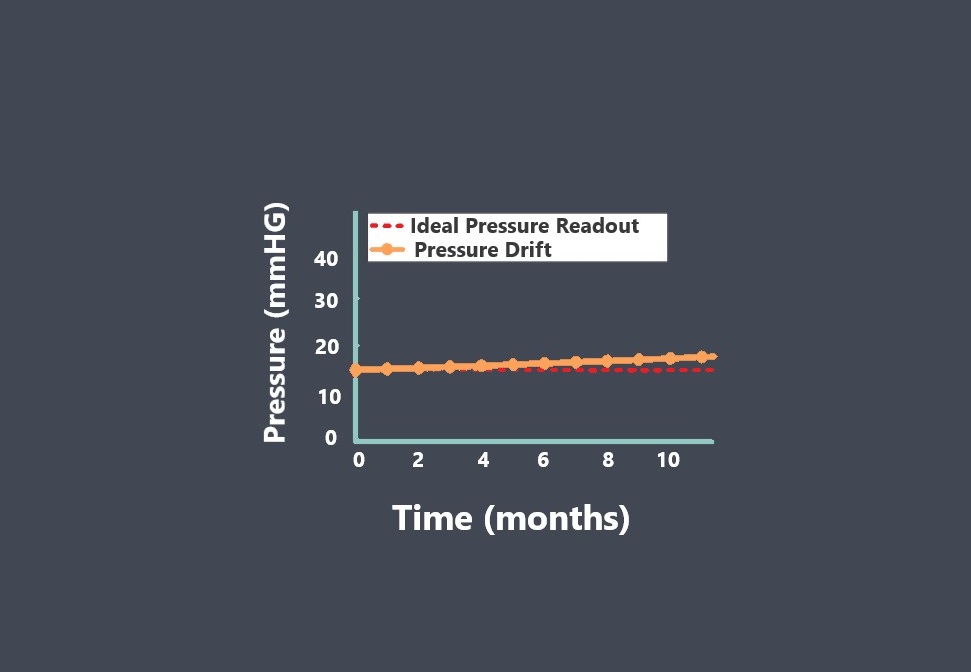
Drift over time
If a sensor is stable, it should maintain its accuracy and precision over time. If the sensor’s readings drift over time, it could be an indication that the sensor’s stability has degraded.
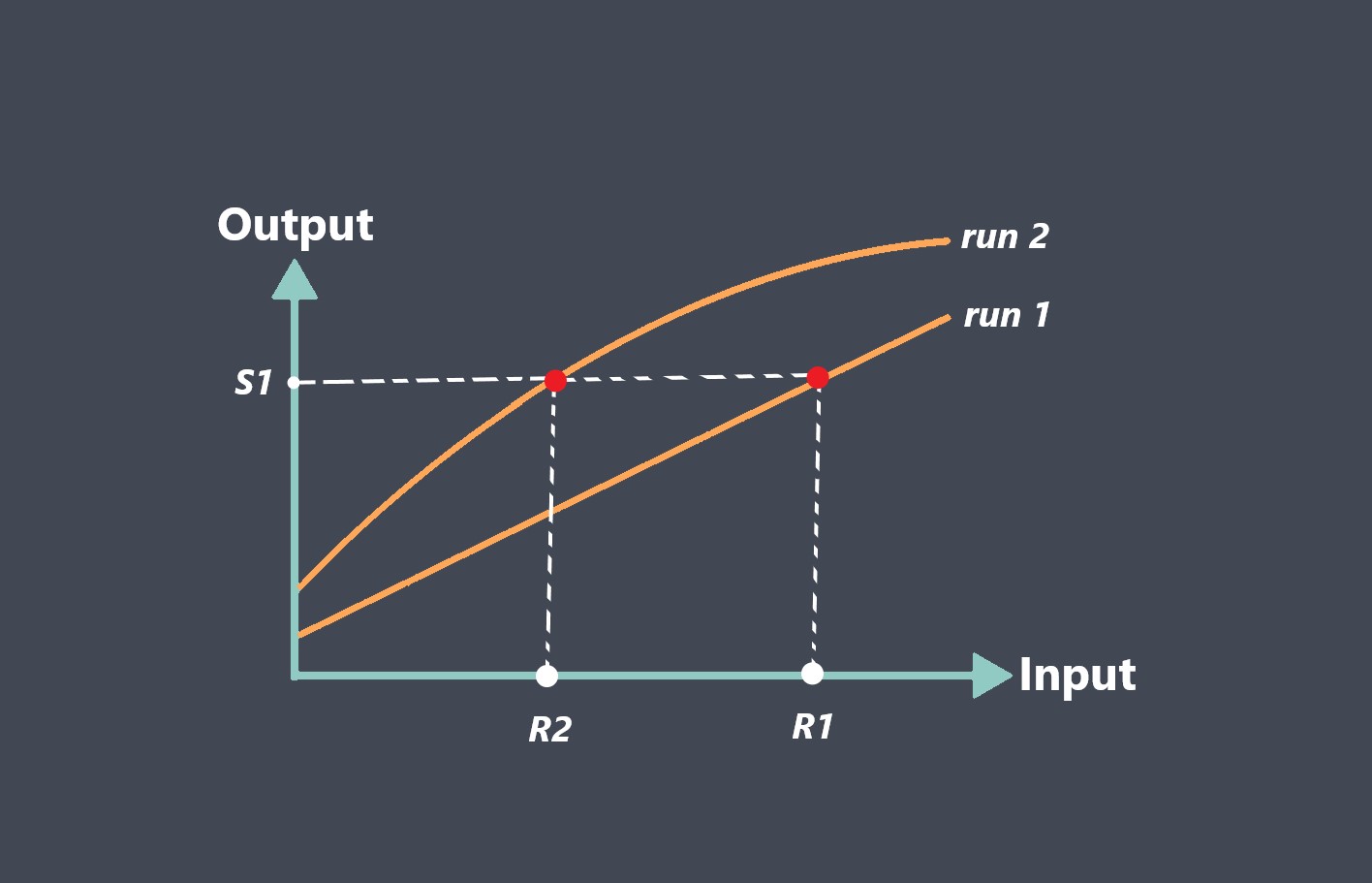
Comparison to a reference standard
One way to evaluate a sensor’s stability is to compare its readings to a reference standard or known value. If the sensor’s readings consistently match the reference standard, it could be an indication that the sensor is stable.
Calibration history
Keeping track of a sensor’s calibration history can help to identify changes in stability over time. If the sensor’s calibration values have remained consistent over multiple calibration cycles, it could be an indication that the sensor is stable.
Environmental testing
Testing a sensor under a range of environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, can help to identify any changes in stability under different conditions. If the sensor’s readings remain consistent under varying environmental conditions, it could be an indication that the sensor is stable.
It’s important to note that these factors are not definitive indicators of sensor stability, and other factors such as physical damage, electrical interference, or software issues can also affect a sensor’s stability.