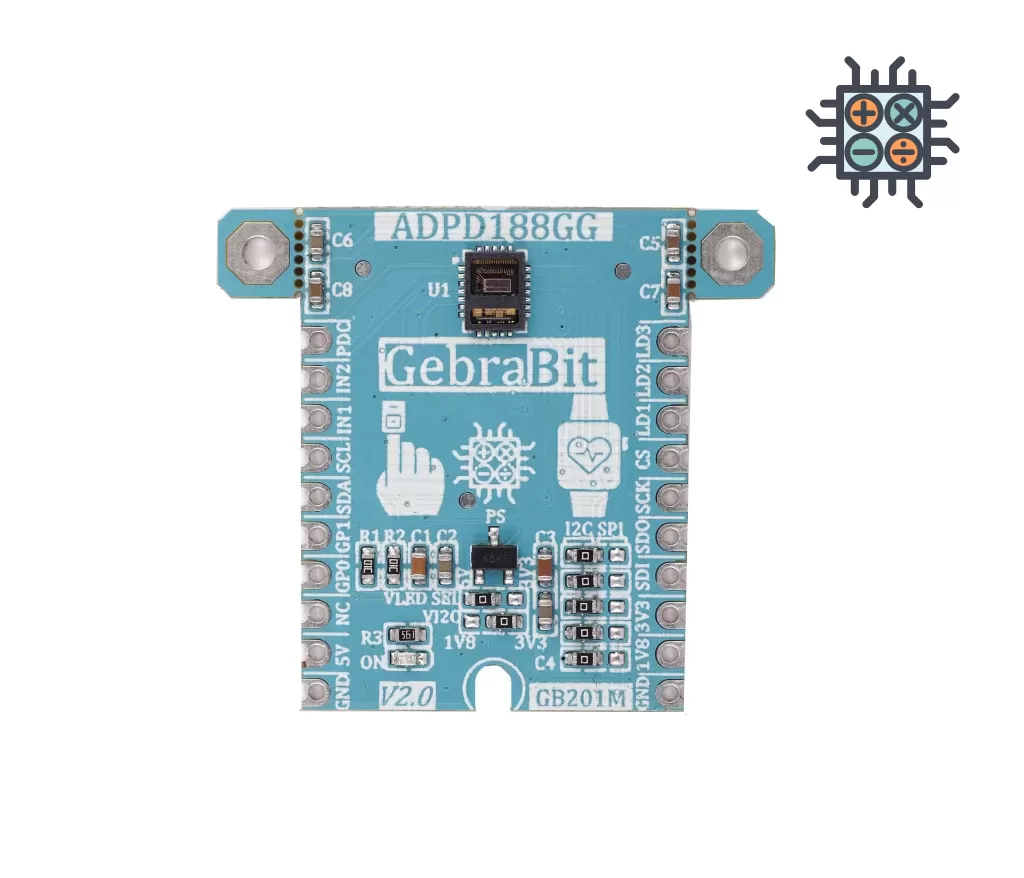
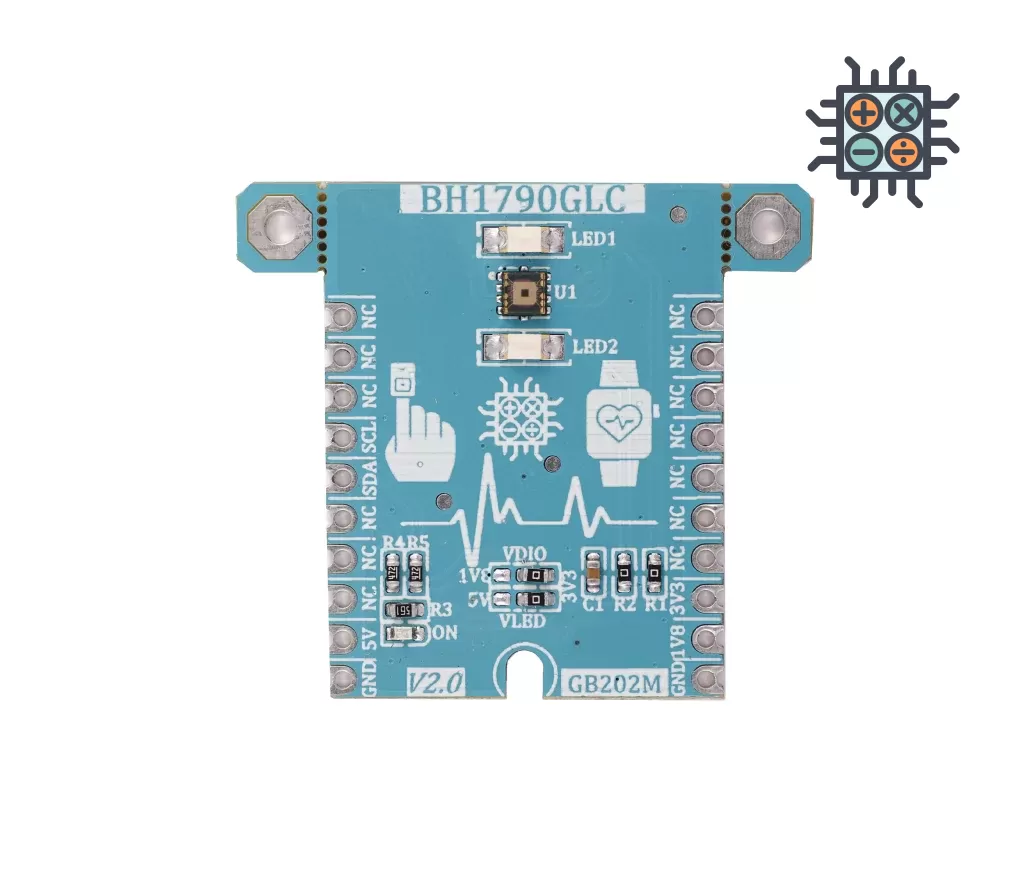
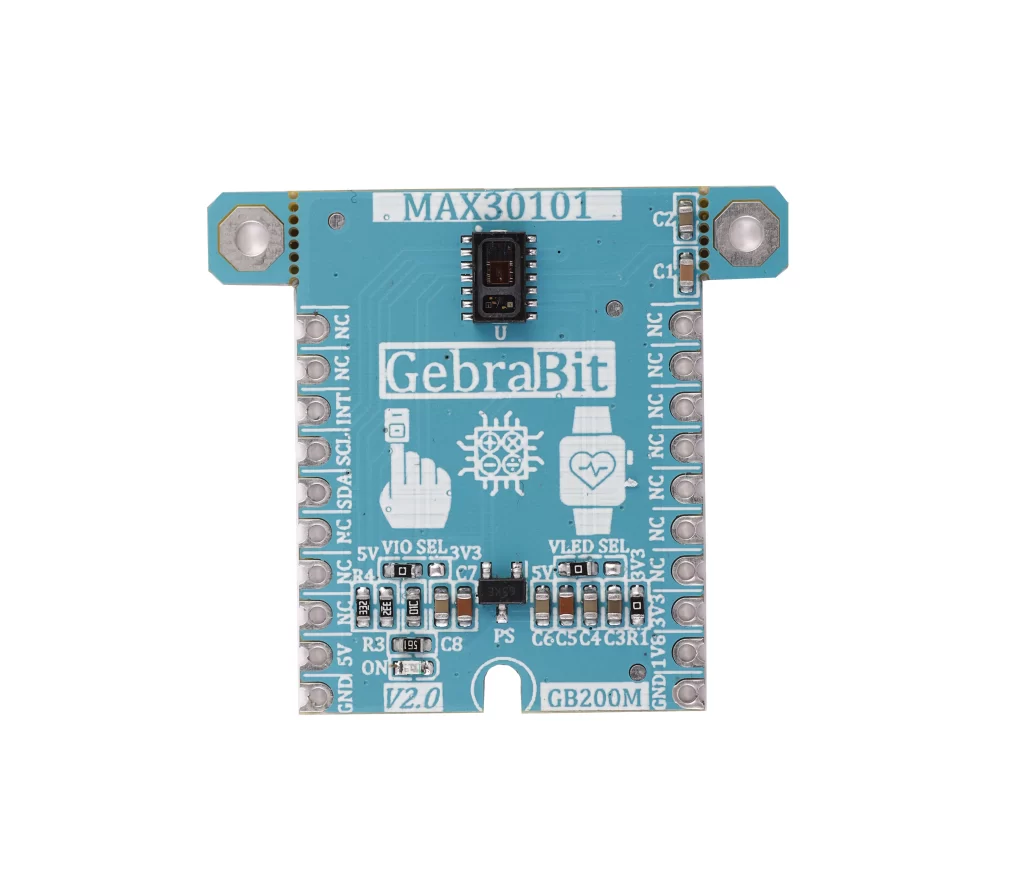
Medical
Heart Rate
Recording of the heart’s activity.


GebrabithEART rATEmodule
Heart rate is a measure of the number of times the heart beats per minute. It is expressed as beats per minute (bpm) and is one of the most important vital signs used to assess a person’s health and fitness. The heart rate can vary greatly depending on factors such as age, physical activity, stress, and medical conditions.
A normal heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute when at rest. During physical activity, the heart rate can increase to provide more oxygen-rich blood to the muscles. After physical activity, the heart rate returns to its resting rate.
Heart rate is an important indicator of overall cardiovascular health and can be used to diagnose heart conditions, such as an irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia) or an enlarged heart (cardiomegaly). Abnormal heart rates can also indicate other medical conditions, such as an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) or an infection.
Overall, heart rate is a crucial vital sign that can provide valuable information about a person’s health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s heart rate sensor?
A heart rate sensor is a device or sensor that measures the heart rate, which is the number of times the heart beats per minute (bpm). It is typically used to monitor and track heart rate during exercise or other physical activities, or as part of medical monitoring in a clinical setting.
There are several types of heart rate sensors, including:
- Chest strap sensors: These sensors typically consist of a strap that is worn around the chest and a sensor that attaches to the strap. The sensor measures the electrical activity of the heart and sends the data to a compatible device, such as a heart rate monitor or a smartphone app.
- Optical sensors: These sensors use light to measure the heart rate. They are typically built into wearable devices, such as fitness trackers or smartwatches. The sensor emits light into the skin and detects the changes in blood flow caused by the heartbeat.
- Finger sensors: These sensors clip onto the finger and use light to measure the heart rate. They are often used in medical settings to monitor heart rate and oxygen levels in the blood.
Heart rate sensors are typically used by athletes and fitness enthusiasts to monitor their heart rate during exercise and track their fitness progress. They can also be used by people with medical conditions, such as heart disease or arrhythmia, to monitor their heart rate and alert them to any potential problems.
What is evident in heartrate?
Heart rate can provide evidence of several things, including:
- Cardiovascular health: A consistently high or low heart rate can be a sign of cardiovascular issues, such as high blood pressure or heart disease.
- Fitness level: A lower resting heart rate generally indicates a higher level of fitness, while a higher resting heart rate may indicate a lower level of fitness.
- Stress and anxiety: Stress and anxiety can cause an increase in heart rate, so monitoring heart rate can help identify periods of increased stress.
- Recovery from exercise: Heart rate can be used to monitor recovery from exercise. A faster recovery heart rate generally indicates better cardiovascular fitness.
- Performance: Heart rate can be used to monitor performance during exercise, helping to ensure that exercise is challenging but not excessive.
Overall, heart rate can be an important metric for tracking health and fitness, and can provide valuable evidence of overall well-being.
What happens if heartrate is abnormal?
If the heart rate is consistently abnormal, it may be a sign of an underlying medical condition that requires evaluation and treatment. Here are some examples of how an abnormal heart rate can affect the body:
- Tachycardia: If the heart rate is consistently too fast (above 100 bpm), it can put a strain on the heart and lead to complications such as heart failure, chest pain, or fainting.
- Bradycardia: If the heart rate is consistently too slow (below 60 bpm), it can reduce blood flow to the body and brain, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and dizziness.
- Arrhythmia: If the heart rate is irregular or has abnormal rhythms, it can increase the risk of blood clots, stroke, and other complications.
- Hypertension: If the heart rate is consistently high, it can lead to high blood pressure, which increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage.
- Diabetes: Consistently high heart rate can also be a symptom of diabetes, which can lead to other complications such as nerve damage, kidney damage, and eye damage.
In summary, an abnormal heart rate can be a sign of an underlying medical condition that requires evaluation and treatment. If you notice consistently abnormal heart rate, it is important to consult a medical professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.